ExPRESS Logistics Carrier
An ExPRESS logistics carrier (ELC) is an unpressurized attached payload platform for the International Space Station (ISS) that provides mechanical mounting surfaces, electrical power, and command and data handling services for Orbital Replacement Units (ORUs) as well as science experiments on the ISS. ("ExPRESS" stands for Expedite the Processing of Experiments to the Space Station.) The ELCs were developed primarily at the Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, with support from JSC, KSC, and MSFC. ELC was formerly called "Express Pallet" and is the unpressurized counterpart to the pressurized ExPRESS Rack. An ELC provides scientists with a platform and infrastructure to deploy experiments in the vacuum of space without requiring a separate dedicated Earth-orbiting satellite.
ELCs interface directly with the ISS integrated truss common attach system (CAS).[1] The P3 Truss has two such attach points called Unpressurised Cargo Carrier Attachment System (UCCAS) mechanisms, one facing zenith (space facing) called UCCAS-1, the other facing nadir (earth facing) called UCCAS-2. Whereas the S3 Truss has four similar locations called Payload Attachment System (PAS) mechanisms, two facing Zenith (PAS-1 and PAS-2), and two facing Nadir (PAS-3 and PAS-4).
Description
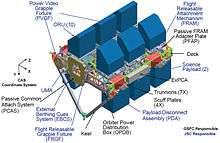

The ELC is an un-pressurized attached payload project for the International Space Station (ISS) that provides mechanical mounting surfaces, electrical power, and command and data handling services for science experiments on the ISS. ("ExPRESS" stands for “expedite the processing of experiments to the Space Station”.) The ELCs have a deck size of about 14 feet by 16 feet and spans the width of the space shuttle’s payload bay. Each one is capable of providing scientists with a platform and infrastructure to deploy experiments in the vacuum of space without requiring a separate dedicated Earth-orbiting satellite. Each carrier is capable of carrying 9,800 lbs. to orbit and will also serve as parking fixtures for spare ISS hardware which can be retrieved when needed.[2]
Electrical subsystem ExPRESS carrier avionics (ExPCA)
Within the electrical subsystem of the ELC, the ExPRESS carrier avionics (ExPCA) provides electrical power distribution to experiments, and data interfaces to the ISS. Within the ExPCA, the ColdFire-based flight computer, software, and related electronics comprise its "flight controller unit" (FCU). The FCU runs the free open-source real-time operating system (RTOS) RTEMS and provides the computing and communication resources as an ELC Command and Data Handling (C&DH) system with the following major goals:
- Provide a low-rate data link (LRDL) interface to ISS to accept commands for the ELC and the resident experiments. The ExPCA is implemented as a remote terminal (RT) on the MIL-STD-1553 "ISS local bus." This interface also returns housekeeping telemetry from the ExPCA and resident experiments to the ISS.
- Provide an LRDL from the ExPCA to the experiments resident on the ELC to forward commands from the ISS to the experiments and to receive telemetry from the experiments for transmission to the ISS. This is another MIL-STD-1553 interface, with the ExPCA acting as the Bus Controller (BC).
- Provide a high-rate data link (HRDL) between the ELC and the ISS. This interface is implemented as a fiber optical data bus with a capacity of up to 95.0 Megabits per second (Mbit/s). The primary function of this interface is the return on high-volume experiment Science data from the resident experiments to the ISS.
- Provide an Ethernet Local Area Network (LAN) between the ELC and the resident experiments up to 6.0 Mbit/s per experiment. The primary function of this interface is the return of science experiment data from to the ISS, relayed through the HRDL.
- Support six analog input channels at each ExPA (ExPRESS payload adapter) location.
- Support six discrete command channels at each ExPA location.
Manifested on ELC-2 was the first ELC-based payload, Materials for ISS Experiment (MISSE-7).[3]
ELC launch schedule
ELC-1 and ELC-2 were transported to the International Space Station by Space Shuttle Atlantis on mission STS-129 in November 2009. ELC-4 launched on mission STS-133 Discovery on 24 February 2011 and was installed on the station on 27 February. ELC-3 launched on mission STS-134 Endeavour on 16 May 2011 and was installed on the station on 18 May.
The Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer occupies the mounting location intended for ELC-5 on the ISS truss.
| Launch date | Mission | Shuttle | ELC |
|---|---|---|---|
| 16 November 2009 | STS-129 (ISS ULF3) | Atlantis | ELC-1 and ELC-2 |
| 24 February 2011 | STS-133 (ISS ULF5) | Discovery | ELC-4 |
| 16 May 2011 | STS-134 (ISS ULF6) | Endeavour | ELC-3 |
Locations and components

ELC-1
|
ELCs 1 & 2 in the Space Shuttle Atlantis cargo bay. | |
| Station statistics | |
|---|---|
| Part of: | International Space Station |
| Launch date: | 11 UTC |
| Launch vehicle: | Space Shuttle/STS-129 |
| Berthed: | 11 at P3 truss |
| Mass: | 13,840 lb (6,280 kg) |

ELC-1 is located on the P3 truss at the UCCAS-2 (nadir, earth facing) site. ELC-1 weighs approx. 13,840 lbs.[4] A FRAM is a Flight Releasable Attachment Mechanism.
- FRAM-1 (top side) Latching End Effector (LEE) launched on ELC-1
- FRAM-2 (top side) Plasma Contactor Unit (PCU) launched on ELC-1
- FRAM-3 (top side) STP-H4 (delivered by the HTV-4 Exposed Pallet, was placed here by the SSRMS/SPDM Aug. 2013)
- FRAM-4 (top side) Battery Charger Discharge Unit (BCDU) launched on ELC-1
- FRAM-5 (top side) Control Moment Gyroscope (CMG SN104) launched on ELC-1
- FRAM-6 (keel side) Nitrogen Tank Assembly (NTA SN0002) launched on ELC-1
- FRAM-7 (keel side) Pump Module (PM SN0007) launched on ELC-1
- FRAM-8 (keel side) OPALS Payload (placed via Dextre/SSRMS May 7, 2014. Delivered by SpaceX Dragon CRS-3)
- FRAM-9 (keel side) Ammonia Tank Assembly (ATA) launched on ELC-1
 ELC-1 and ELC-2 (top side views) prelaunch, with red changes on orbit.
ELC-1 and ELC-2 (top side views) prelaunch, with red changes on orbit. ELC-1 underside view in the SSPF, with labels
ELC-1 underside view in the SSPF, with labels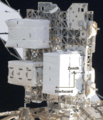 ELC-1 keel side view on orbit
ELC-1 keel side view on orbit JEM Exposed Platform HTV-4
JEM Exposed Platform HTV-4 STP-H4 Experiment package
STP-H4 Experiment package
ELC-2
|
ELCs 1 & 2 in the Space Shuttle Atlantis cargo bay. | |
| Station statistics | |
|---|---|
| Part of: | International Space Station |
| Launch date: | 11 UTC |
| Launch vehicle: | Space Shuttle/STS-129 |
| Berthed: | 11 at S3 truss |
| Mass: | 13,400 lb (6,100 kg) |
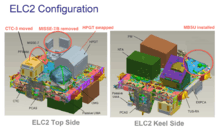
ELC-2 is located on the S3 truss at the PAS-1 (zenith, space facing) site, alongside AMS-2 at PAS-2. ELC-2 weighs approx. 13,400 lbs.[4]
- FRAM-1 (top side) DCSU placed here by SPDM from ESP-2 on Jan. 30, 2013. (CTC-3 moved to FRAM-2 for a test of the SPDM December 22/23, 2011)
- FRAM-2 (top side) Cargo Transport Container-3 (CTC-3) launched on ELC-2 (moved from FRAM-1 – see above)
- FRAM-3 (top side) MISSE base - MISSE-8 was removed by the Exp. 36 crew Jul. 2013 (STS-134 added MISSE-8 replacing MISSE-7 which was launched on ELC-2. STS-135 added MISSE-8 'ORMatE-III exposure plate' to the second MISSE mount).
- FRAM-4 (top side) High Pressure Gas Tank (HPGT) (Oxygen depleted) replaced the one carried up on ELC-2, which was used to replace a depleted tank from Quest in EVA during STS-129[4]
- FRAM-5 (top side) Control Moment Gyroscope (CMG SN102) launched on ELC-2
- FRAM-6 (keel side) Pump Module (PM SN0005) launched on ELC-2
- FRAM-7 (keel side) MBSU (delivered by the HTV-4 Exposed Pallet, and placed here by the SSRMS/SPDM Aug. 2013)
- FRAM-8 (keel side) Mobile Transporter Trailing Umbilical System-Reel Assembly (MT TUS-RA) launched on ELC-2
- FRAM-9 (keel side) Nitrogen Tank Assembly (NTA SN0003) launched on ELC-2
 ELC-1 and ELC-2 (top side views) prelaunch, with red changes on orbit. Note MISSE-7/8 switch.
ELC-1 and ELC-2 (top side views) prelaunch, with red changes on orbit. Note MISSE-7/8 switch. ELC-2 underside during its transfer into the payload canister in the SSPF
ELC-2 underside during its transfer into the payload canister in the SSPF ELC-2 on the SSRMS prior to its placement on the S3 Truss
ELC-2 on the SSRMS prior to its placement on the S3 Truss ELC-2 atop the S3 Truss
ELC-2 atop the S3 Truss ELC-2 showing MISSE-7 and the vacated HPGT FRAM
ELC-2 showing MISSE-7 and the vacated HPGT FRAM
ELC-3
| Station statistics | |
|---|---|
| Part of: | International Space Station |
| Launch date: | 05 UTC |
| Launch vehicle: | Space Shuttle/STS-134 |
| Berthed: | 05 at S3 truss |
| Mass: | 14,023 lb (6,361 kg) |

ELC-3 is located on the P3 truss at the UCCAS-1 (zenith, space facing) site. ELC-3 weighs 14,023 lbs.[5]
- FRAM-1 (top side) Cargo Transport Container-5 (CTC-5) launched on ELC-3
- FRAM-2 (top side) Special Purpose Dextrous Manipulator (SPDM) Arm launched on ELC-3
- FRAM-3 (top side) SCAN Testbed (arrived in July 2012 via HTV-3)[6][7][8]
- FRAM-4 (top side) S band Antenna Sub-System Assembly #3 (SASA) launched on ELC-3
- FRAM-5 (keel side) Space Test Program-Houston 3 (STP-H3) DOD experiment launched on ELC-3 (removed by the SPDM and placed on HTV-4 for disposal).
- FRAM-6 (keel side) Ammonia Tank Assembly (ATA) launched on ELC-3
- FRAM-7 (keel side) High Pressure Gas Tank (HPGT) launched on ELC-3
- FRAM-8 (keel side) S band Antenna Sub-System Assembly #2 (SASA) launched on ELC-3
 ELC-3 top view
ELC-3 top view ELC-3 underside view
ELC-3 underside view ELC-3 in the grasp of Endeavour's robotic arm
ELC-3 in the grasp of Endeavour's robotic arm
ELC-4
|
In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians perform the ELC-4, deck-to-keel mate. | |
| Station statistics | |
|---|---|
| Part of: | International Space Station |
| Launch date: | 02 UTC |
| Launch vehicle: | Space Shuttle/STS-133 |
| Berthed: | 02 at S3 truss |
| Mass: | 8,235 lb (3,735 kg) |

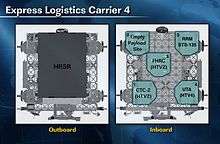
ELC-4 is located on the S3 truss at the PAS-4 (nadir, earth facing) site, alongside ESP-3 at PAS-3. ELC-4 weighs 8,235 lbs.[9]
- Heat Rejection System Radiator (HRSR) launched on the top side of ELC-4[9]
- FRAM-1 (keel side) Cargo Transport Container-2 (CTC-2) delivered to ISS by HTV-2 (EP) via SPDM held by the SPDM[10] since its initial delivery by the HTV-2
- FRAM-2 (keel side) empty
- FRAM-3 (keel side) Robotic Refuelling Mission (RRM) was delivered to the ISS by STS-135, placing it temporarily on the SPDM at Destiny.[11] The RRM held by the SPDM was later moved to this FRAM.
- FRAM-4 (keel side) Utility Transfer Assembly (delivered by HTV-4 EP via SPDM Aug. 2013)
- FRAM-5 (keel side) Flex Hose Rotary Coupler (FHRC SN1005) delivered to the ISS by HTV-2 Exposed Pallet (EP), was then moved to this FRAM via SPDM[10]
 Heat rejection subsystem radiator (HRSR) on ELC-4
Heat rejection subsystem radiator (HRSR) on ELC-4 FHRC and CTC4 on the HTV-2 Exposed Platform
FHRC and CTC4 on the HTV-2 Exposed Platform Mike Fossum rides on the ISS's robotic arm as he transfers the RRM to the SPDM for temporary storage
Mike Fossum rides on the ISS's robotic arm as he transfers the RRM to the SPDM for temporary storage JEM Exposed Platform HTV-4
JEM Exposed Platform HTV-4

See also
- External Stowage Platform
- Integrated Cargo Carrier
- Scientific research on the ISS
- Orbital replacement unit
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to ExPRESS Logistics Carrier. |
- ↑ Johnson Space Center (2006). EXPRESS Logistics Carrier (ELC) Development Specification (Revision B ed.). International Space Station Program. SSP 52055.
- ↑ "Goddard SFC ELCs Description".
- ↑ "MISSE-7".
- 1 2 3 "EVA Checklist: STS-129 Flight Supplement" (PDF).
- ↑ "STS-134 press kit cover print file 3-31-11" (PDF). Retrieved 2013-03-27.
- ↑ "SCaN Testbed". Spaceflightsystems.grc.nasa.gov. 2013-03-13. Retrieved 2013-03-27.
- ↑ Archived April 17, 2011, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ http://spaceflightsystems.grc.nasa.gov/SpaceOps/CoNNeCT/images/Figure_1.png
- 1 2 "EVA Checklist: STS-133 Flight Supplement" (PDF).
- 1 2 "HYV-2 Presskit" (PDF).
- ↑ http://www.nasa.gov/pdf/566071main_STS-135_Press_Kit.pdf
- General
- NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center, ExPRESS Logistics Carrier Project Office, ExPRESS Logistics Carrier Operations Concept Document. ELC-OPS-000131

