Gamma globulin
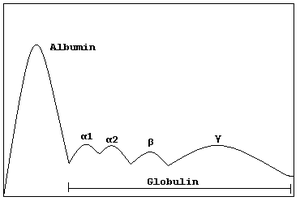
Gamma globulins are a class of globulins, identified by their position after serum protein electrophoresis. The most significant gamma globulins are immunoglobulins (antibodies), although some immunoglobulins are not gamma globulins, and some gamma globulins are not immunoglobulins.
Use as medical treatment
Gamma globulin injections are usually given in an attempt to temporarily boost a patient's immunity against disease. Being a product derived from blood, gamma globulin injections, along with blood transfusions and intravenous drug use, can pass along hepatitis C to their recipients. Once hepatitis C was identified in 1989, blood banks began screening all blood donors for the presence of the virus in their bloodstream. However, since hepatitis C is known to have been present since at least the 1940s, a gamma globulin shot received prior to the early 1990s put the recipient at risk of being infected.
Injections are most commonly used on patients having been exposed to hepatitis A or measles, or to make a kidney donor and a recipient compatible regardless of blood type of tissue match. Injections are also used to boost immunity in patients unable to produce gamma globulins naturally because of an immune deficiency, such as X-linked agammaglobulinemia and hyper IgM syndrome. Such injections are less common in modern medical practice than they were previously, and injections of gamma globulin previously recommended for travelers have largely been replaced by the use of hepatitis A vaccine.
Gamma globulin infusions are also used to treat some immunological diseases, such as idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura (ITP), a disease in which the platelets are being attacked by antibodies, leading to seriously low platelet counts. It appears that gamma globulin causes the spleen to ignore the antibody-tagged platelets, thus allowing them to survive and function.
A recent clinical trial of gamma globulin in chronic fatigue syndrome patients had no recognizable benefit, while an older trial showed improvement. The success of this treatment remains uncertain.
Another theory on how gamma globulin administration works in autoimmune disease is by overloading the mechanisms that degrade gamma globulins. Overloading the degradation mechanism causes the harmful gamma globulins to have a much shorter halflife in sera.
Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) may be used in Kawasaki disease.
Intravenous gamma globulin was FDA-approved in 2004 to reduce antibodies in a patient with kidney failure to allow that person to accept a kidney from a donor with a different blood type (ABO-incompatible), or who is an unacceptable tissue match. Stanley Jordan at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles pioneered this treatment.[1]
Pathology
An excess is known as hypergammaglobulinemia. A deficiency is known as hypogammaglobulinemia.
A disease of gamma globulins is called a "gammopathy" (for example, in monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance).
References
External links
- gamma-Globulins at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)