Greek ligatures

The sample shows the -os ligature in the middle of the second line (in the word μέθοδος), the kai ligature below it in the third line, and the -ou- ligature right below that in the fourth line, along many others.

Greek ligatures are graphic combinations of the letters of the Greek alphabet that were used in medieval handwritten Greek and in early printing. Ligatures were used in the cursive writing style and very extensively in later minuscule writing. There were many dozens[1][2] of conventional ligatures. Some of them stood for frequent letter combinations, some for inflectional endings of words, and some were abbreviations of entire words.
In early printed Greek from around 1500, many ligatures fashioned after contemporary manuscript hands continued to be used. Important models for this early typesetting practice were the designs of Aldus Manutius in Venice, and those of Claude Garamond in Paris, who created the influential Grecs du roi typeface in 1541. However, the use of ligatures gradually declined during the 17th and 18th centuries and became mostly obsolete in modern typesetting. Among the ligatures that remained in use the longest are the ligature Ȣ for ου, which resembles an o with an u on top, and the abbreviation ϗ for καὶ ('and'), which resembles a κ with a downward stroke on the right. The ου ligature is still occasionally used in decorative writing, while the καὶ abbreviation has some limited usage in functions similar to the Latin ampersand (&). Another ligature that was relatively frequent in early modern printing is a ligature of Ο with ς (a small sigma inside an omicron) for a terminal ος.
The ligature ϛ for στ, now called stigma, survived in a special role besides its use as a ligature proper. It took on the function of a number sign for "6", having been visually conflated with the cursive form of the ancient letter digamma, which had this numeral function.
Computer encoding
In the modern computer encoding standard Unicode, the abbreviation ϗ has been encoded since version 3.0 of the standard (1999). An uppercase version Ϗ was added in version 5.1 (2008). A lower and upper case "stigma", designed for its numeric use, is also encoded in Unicode. Letters derived from the ου ligature exist for use in Latin, and for Cyrillic, though not for Greek itself. Some attempts have been made at recreating typesetting with ligatures in modern computer fonts, either through Unicode-compliant OpenType glyph replacement,[3] or with simpler but non-standardized methods of glyph-by-glyph encoding.[4]
- Greek digraphs
| Character | Ϗ | ϗ | Ϛ | ϛ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | GREEK CAPITAL KAI SYMBOL | GREEK KAI SYMBOL | GREEK LETTER STIGMA | GREEK SMALL LETTER STIGMA | ||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex |
| Unicode | 975 | U+03CF | 983 | U+03D7 | 986 | U+03DA | 987 | U+03DB |
| UTF-8 | 207 143 | CF 8F | 207 151 | CF 97 | 207 154 | CF 9A | 207 155 | CF 9B |
| Numeric character reference | Ϗ | Ϗ | ϗ | ϗ | Ϛ | Ϛ | ϛ | ϛ |
- Latin and Cyrillic Ou digraphs
| Character | Ȣ | ȣ | Ꙋ | ꙋ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | LATIN CAPITAL LETTER OU | LATIN SMALL LETTER OU | CYRILLIC CAPITAL LETTER MONOGRAPH UK | CYRILLIC SMALL LETTER MONOGRAPH UK | ||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex |
| Unicode | 546 | U+0222 | 547 | U+0223 | 42570 | U+A64A | 42571 | U+A64B |
| UTF-8 | 200 162 | C8 A2 | 200 163 | C8 A3 | 234 153 138 | EA 99 8A | 234 153 139 | EA 99 8B |
| Numeric character reference | Ȣ | Ȣ | ȣ | ȣ | Ꙋ | Ꙋ | ꙋ | ꙋ |
Example images
-
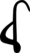
-εῖ-
(-ei-) -
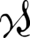
-γερ-
(-ger-) -

καὶ
(kai) -
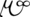
-μω-
(-mō-) -
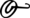
-ος
(-os) -
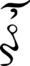
οὖν
(oûn) -
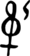
φησὶ
(phēsi) -
-έστ-
(-ést-)
See also
- iota adscript, which is written with a ligatured iota: ᾼ
- iota subscript, also written with a ligatured iota: ᾳ
- Tau-Rho
- Chi-Rho
References
- ↑ The Philokalia Package, for LaTeX
- ↑ Carl Faulmann, Das Buch der Schrift: Schriftzeichen und Alphabete aller Zeiten und Völker, Vienna 1880, p.172-176.
- ↑ e.g. Greek Font Society. "GFS Gazis" (PDF). Retrieved 2012-07-13.; George Douros. "Unicode fonts for ancient scripts". Retrieved 2012-07-13.
- ↑ e.g. Schmidthauser, Andreas. "Renaissance Greek". Retrieved 2012-07-13.