Grey partridge
| Grey partridge | |
|---|---|
.jpg) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Galliformes |
| Family: | Phasianidae |
| Subfamily: | Perdicinae |
| Genus: | Perdix |
| Species: | P. perdix |
| Binomial name | |
| Perdix perdix (Linnaeus, 1758) | |
| Subspecies | |
|
8, see text | |
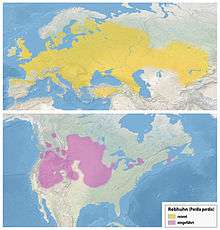 | |
| Range of P. perdix Native range Introduced range | |
The grey partridge (Perdix perdix), also known as the English partridge, Hungarian partridge, or hun, is a gamebird in the pheasant family Phasianidae of the order Galliformes, gallinaceous birds. The scientific name is the Latin for "partridge", and is itself derived from Ancient Greek perdix.[2]
Widespread and common throughout much of its range, the grey partridge is evaluated as "of Least Concern" on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. However, it has suffered a serious decline in the UK, and in 2015 appeared on the "Birds of Conservation Concern" Red List.[3] This partridge breeds on farmland across most of Europe into western Asia, and has been introduced widely into Canada, United States, South Africa, Australia and New Zealand.[4] A popular gamebird in vast areas of North America, it is commonly known as "Hungarian partridge" or just "hun".
The grey partridge is a rotund bird, 28–32 cm (11–13 in) long, brown-backed, with grey flanks and chest. The belly is white, usually marked with a large chestnut-brown horse-shoe mark in males, and also in many females. Hens lay up to twenty eggs in a ground nest. The nest is usually in the margin of a cereal field, most commonly winter wheat. The only major and constant difference between the sexes is the so-called cross of Lorraine on the tertiary coverts of females—these being marked with two transverse bars, as opposed to the one in males. These are present after around 16 weeks of age when the birds have moulted into adult plumage. Young grey partridges are mostly yellow-brown and lack the distinctive face and underpart markings. The song is a harsh kieerr-ik, and when disturbed, like most of the gamebirds, it flies a short distance on rounded wings, often calling rick rick rick as it rises.
They are a seed-eating species, but the young in particular take insects as an essential protein supply. During the first 10 days of life, the young can only digest insects. The parents lead their chicks to the edges of cereal fields, where they can forage for insects. They are also a non-migratory terrestrial species, and form flocks outside the breeding season. Though common and not threatened, it appears to be declining in numbers in some areas of intensive cultivation such as Great Britain, probably due to a loss of breeding habitat and possibly food supplies. Their numbers have fallen in these areas by as much as 85% in the last 25 years. Efforts are being made in Great Britain by organizations such as the Game & Wildlife Conservation Trust to halt this decline by creating conservation headlands. In 1995, it was nominated a Biodiversity Action Plan (BAP) species. In Ireland, it is now virtually confined to the Lough Boora reserve in County Offaly where a recent conservation project has succeeded in boosting its numbers to 900, raising hopes that it may be reintroduced to the rest of Ireland.
Subspecies
There are eight recognized subspecies:
- P. p. perdix (Linnaeus, 1758) – nominate, found in the British Isles and southern Scandinavia to Italy and the Balkans
- P. p. armoricana Hartert, 1917 – found locally in France
- P. p. sphagnetorum (Altum, 1894) – found in the moors of the northern part of the Netherlands and northwest Germany
- P. p. hispaniensis Reichenow, 1892: Iberian partridge, found from central Pyrenees to northeast Portugal
- P. p. italica Hartert, 1917 – Italian grey partridge, extinct
- P. p. lucida (Altum, 1894) – eastern grey partridge, found from Finland east to Ural Mountains and south to Black Sea and northern Caucasus
- P. p. canescens Burturlin, 1906 – southern grey partridge, found from Turkey east to the South Caucasus and northwest Iran
- P. p. robusta Homeyer and Tancré, 1883 – southeastern grey partridge, found from the Ural Mountains to southwestern Siberia and northwestern China
References
- ↑ BirdLife International (2012). "Perdix perdix". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2013.2. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ↑ Jobling, James A (2010). The Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names. London: Christopher Helm. p. 297. ISBN 978-1-4081-2501-4.
- ↑ "BoCC4 Red List" (PDF). Birds of Conservation Concern. Retrieved 2015-12-25.
- ↑ Long, John L. (1981). Introduced Birds of the World. Agricultural Protection Board of Western Australia. pp. 21–493.
- ↑ Sibley, David Allen (2003). The Sibley Field Guide to Birds of Western North America (A Chanticleer Press ed.). Knopf. p. 122. ISBN 0-679-45121-8.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Perdix perdix. |
| Wikispecies has information related to: Perdix perdix |
- BirdLife species factsheet for Perdix perdix
- Game & Wildlife Conservation Trust - Grey Partridge
- "Grey partridge media". Internet Bird Collection.
- Gray Partridge Species Account – Cornell Lab of Ornithology
- Ageing and sexing (PDF; 2.6 MB) by Javier Blasco-Zumeta & Gerd-Michael Heinze
- Feathers of Grey partridge (Perdix perdix)

