Hurricane Nora (1997)
| Category 4 major hurricane (SSHWS/NWS) | |
 Hurricane Nora shortly after peak intensity on September 22, 1997 | |
| Formed | September 16, 1997 |
|---|---|
| Dissipated | September 26, 1997 |
| Highest winds |
1-minute sustained: 130 mph (215 km/h) |
| Lowest pressure | 950 mbar (hPa); 28.05 inHg |
| Fatalities | 2 direct, 4 indirect |
| Damage | $100 million (1997 USD) |
| Areas affected | Baja California, Southwestern United States |
| Part of the 1997 Pacific hurricane season | |
Hurricane Nora was only the third tropical cyclone on record to reach Arizona as a tropical storm. Nora was the fourteenth named tropical cyclone and seventh hurricane of the 1997 Pacific hurricane season. The September storm formed off the Pacific coast of Mexico, and aided by waters warmed by the 1997–98 El Niño event, eventually peaked at Category 4 intensity on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane scale.
Nora took an unusual path, making landfall twice as a hurricane in Baja California. Weakening quickly after landfall, its remnants lashed the Southwestern United States with tropical-storm-force winds, torrential rain and flooding. The storm was blamed for two direct casualties in Mexico, as well as substantial beach erosion on the Mexican coast, flash flooding in Baja California, and record precipitation in Arizona. It persisted far inland and eventually dissipated near the Arizona–Nevada border.
Meteorological history
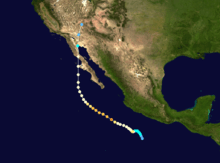
Nora formed early on September 16, 1997, while located 290 miles (460 km) southwest of the Mexican port of Acapulco, Guerrero, from the same tropical wave that had earlier created Hurricane Erika. Due to favorable conditions associated with El Niño,[1] the tropical disturbance quickly achieved deep convection and became well-organized. By 6 a.m. UTC, the U.S. National Hurricane Center had designated the disturbance as Tropical Depression Sixteen-E. Half a day later, it had gained enough strength to be named Tropical Storm Nora.[2]
A high pressure area over northern Mexico forced the storm to move west-northwest for the first few days. During that time, Nora kept intensifying, becoming a Category 1 hurricane on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane scale by noon UTC on September 18. Nora slowed and became stationary for two days from September 18. The eye vanished, and convection began to decrease. This was presumed to have happened because of a drop in sea-surface temperatures. The cool waters temporarily weakened Nora's winds to 75 mph (120 km/h) down from a maximum of 105 mph (165 km/h).[2] After leaving the area of cool waters, the storm began moving nearly parallel to Mexico's western coast. There was a period of rapid intensification and the eye reappeared. Cloud tops cooled and at midday UTC on September 21, Nora reached its peak intensity of 950 mbar (28 inHg) and 135 mph (210 km/h) winds, a Category 4 hurricane.[2] The peak was brief as the cyclone encountered cool waters in the wake of Hurricane Linda, weakening the storm's winds to 80 mph (130 km/h) by September 23 and broke its eyewall.[2]
Nora crossed an area of abnormally warm water near the west coast of the Baja California Peninsula. It restrengthened slightly before making its first landfall near Bahía Tortugas, Baja California Sur, on September 25.[3] When Nora was inland, the area of the storm located in the Gulf of California began to reintensify.[1] Hurricane Nora then made a second landfall about 60 miles (95 km) south-southeast of San Fernando, Baja California.[2] Nora was one of the few hurricanes to make landfall in Northern Baja.
At landfall, a trough was accelerating Nora northwards, causing it to reach a forward speed of 30 mph (50 km/h). Late on September 25 (UTC), still a tropical storm, it entered the continental United States at the California-Arizona state line. Nora began to weaken rapidly, and was downgraded to a tropical depression three hours later,[2] while located between Blythe and Needles, California.[4] Nora reached Arizona while still tropical, becoming the third known system to do so.[5] Nora degenerated over land, and the low-level center moved towards the north-northeast. A remnant circulation aloft persisted, however, and was likely responsible for a period of near hurricane-force winds observed at the NWS Cedar City, Utah Doppler weather radar. The remnants gradually became more diffuse over the following two days while moving generally northeastward, through portions of Utah, Colorado, Idaho and Wyoming.[2]
Preparations
While Nora stayed off the Pacific coast of Mexico, the Servicio Meteorológico Nacional (National Meteorological Service) issued a hurricane watch for the coast between Lázaro Cárdenas, Michoacán, and Puerto Vallarta, Jalisco,[2] and several major ports in the shoreline closed to navigation.[6] As the storm moved away from the mainland coast and towards the Baja California Peninsula, about 500 people were evacuated from their homes near Cabo San Lucas, Baja California Sur, and placed in shelters to prepare for the storm's impact. At the same time, in Sonora, another 50 were evacuated from a fishing camp in Guaymas.[7] Meanwhile, the SMN issued tropical storm warnings along the Baja California coast, as well as hurricane watches and warnings around the entire Gulf of California between Santa Rosalía, Baja California Sur, and Bahía Kino, Sonora. [2][8]
On September 24, Arizona Governor Jane Dee Hull activated an emergency response center to prepare the state's response to the flash flooding the storm would cause on the dry desert floor,[8] and Yuma residents began to fill approximately 55,000 sandbags to contain the possible flooding.[9] Hull also activated the state's National Guard, and sent drinking water and electric generators to Yuma.[10] Further inland, the National Weather Service issued flash flood watches for western Arizona, southeastern California, southwestern Colorado, southern Nevada and southern Utah on September 26.[11]
Impact
Hurricane Nora caused two direct deaths in Mexico and three or four indirect fatalities in the United States. Although the total cost of damage is not known, Nora caused up to several hundred millions of dollars of damage. The system also dropped heavy rain in the United States and Mexico, which caused flooding and power outages.[2]
Mexico

Nora killed two in Mexico: an electrocution by a downed power line in Mexicali, Baja California, and a diver caught in strong underwater currents created by Nora off the coast of the San Quintin Valley.[2]
Although Nora's center of circulation remained well offshore from southwestern mainland Mexico, the Associated Press reported that waves up to 20 feet (6.1 m) hit that coastline, destroying dozens of homes.[12] Nora's winds also produced rough seas and high waves, which caused substantial beach erosion, particularly around Acapulco, where the Pie de la Cuesta beaches were washed away.[2] In the states of Guerrero and Jalisco, Nora brought down trees and washed away the foundations of homes, although no injuries were reported there.[12]
Heavy rains also fell along the storm's northeast periphery, with the highest amounts of 20.94 inches (532 mm) falling at La Cruz/Elota and 16.79 inches (426 mm) being measured at Ligui/Loreto.[13] About 350–400 people were left homeless by floodwaters in the town of Arroyo de Santa Catarina in northern Baja California. Heavy damage and flooding was reported in San Felipe, on the northwestern shore of the Gulf of California, as well as extensive beach erosion.[4] Local roads and highways were destroyed and the town's dock was severely damaged.[14] On the northeastern shore, at Puerto Peñasco, Nora blew down trees, billboards, electric wires, taco stands, and ripped sheet-metal from homes. Waves of 10 feet (3.0 m) were reported there.[2]
United States

In the United States, there were no direct deaths blamed on the hurricane. However, the California Highway Patrol attributed three or four traffic fatalities in southern California to the weather.[15]
Damage totals in the United States are not fully known, although media summaries of Nora included a loss to agriculture preliminarily estimated at several hundred million dollars, and at least one study places the figure at $150–200 million (1997 USD).[16] It is estimated that $30–40 million (1997 USD) in damage to lemon trees occurred.[17] Although Nora was significantly weakened, near hurricane-force winds were observed at the Dixie National Forest in southwestern Utah, where strong gusts sheared off the tops of large trees.[18]
The Yuma radar indicated a small area of 10 inches (250 mm) rainfall totals along the northern Gulf of California coast of Baja California. In the United States, the largest total rainfall was recorded at the Harquahala Mountains in Arizona, where 11.97 inches (304 mm) of rainfall were recorded as a result of Nora, causing flash floods in western Arizona.[5]
Near Phoenix, rainfall from the storm caused the Narrows Dam, a small earthen dam, to fail.[5] In other locations in Arizona, California, Nevada, and Utah, more than 3 inches (76 mm) fell in a few localized areas,[1] precipitation in some places was comparable to the entire local yearly average rainfall. Flooding was also reported in Somerton, San Diego, El Centro, Palm Springs and Indio, while 12,000 people lost power in Yuma,[19] as well as Los Angeles and southwestern Utah.
See also
- List of Arizona hurricanes
- List of California hurricanes
- List of Pacific hurricanes
- List of wettest tropical cyclones in Arizona
- List of Category 4 Pacific hurricanes
- Timeline of the 1997 Pacific hurricane season
- Hurricane Odile (2014)—regenerated in the Gulf of California, proceeding to affect southeastern California and Arizona in a similar manner days after slamming Cabo San Lucas
References
- 1 2 3 Farfán, Luis M.; Zehnder, Joseph A. (August 2001). "An Analysis of the Landfall of Hurricane Nora (1997)". Monthly Weather Review. 129 (8): 2073–2088. Bibcode:2001MWRv..129.2073F. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(2001)129<2073:AAOTLO>2.0.CO;2.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Rappaport, Edward N (October 30, 1997). Preliminary Report: Hurricane Nora September 16 - 26, 1997 (PDF) (Report). United States National Hurricane Center.
- ↑ Servicio Meteorológico Nacional (Mexico) (1997). "Huracán Nora" (in Spanish). Comisón Nacional del Agua. Archived from the original on May 5, 2006. Retrieved 2006-02-21.
- 1 2 Lawrence, Miles B. (October 1999). "Eastern North Pacific Hurricane Season of 1997". Monthly Weather Review. 127 (10): 2440–2454. Bibcode:1999MWRv..127.2440L. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1999)127<2440:ENPHSO>2.0.CO;2.
- 1 2 3 Flood Control District of Maricopa County (1997). "TS Nora Storm Report". Retrieved 2006-02-26.
- ↑ "North-moving Nora lashes Baja's southern tip". Associated Press. September 23, 1997. Archived from the original on 2006-05-06. Retrieved 2006-04-10.
- ↑ "Hurricane Nora lashes Baja California". Associated Press. September 24, 1997. Archived from the original on 2005-03-07. Retrieved 2006-05-11.
- 1 2 "Hurricane Nora to hit Baja Thursday morning". Associated Press. September 25, 1997. Archived from the original on February 12, 2005. Retrieved 2006-05-11.
- ↑ "Hurricane Nora nears Mexico". Associated Press. September 24, 1997. Archived from the original on May 18, 2006. Retrieved 2006-05-11.
- ↑ "Nora weakens, but heavy rains threaten U.S.". Associated Press. September 25, 1997. Archived from the original on February 12, 2005. Retrieved 2006-05-11.
- ↑ Hydrometeorological Prediction Center. "Storm Summary for Tropical Depression Nora, 4 a.m. EDT September 26, 1997". NOAA. Retrieved 2006-03-06.
- 1 2 "Hurricane Nora lashes Mexico's Pacific coast". Associated Press. September 22, 1997. Archived from the original on May 6, 2006. Retrieved 2006-05-11.
- ↑ Hydrometeorological Prediction Center. Hurricane Nora - September 14 – 28, 1997. Retrieved on 2007-01-04.
- ↑ "Hurricane Nora, San Felipe, Baja California". San Felipe, Baja California Official Website. September 1997. Retrieved 2006-03-29.
- ↑ "Nora gives Arizona a soaking". Associated Press. September 25, 1997. Archived from the original on 2004-11-25. Retrieved 2006-05-11.
- ↑ National Drought Mitigation Center. "Reported Effects of the 1997–98 El Niño" (PDF). University of Nebraska-Lincoln. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-03-04. Retrieved 2006-02-26.
- ↑ National Climatic Data Center (September 25, 1997). "NCDC Event Details". NOAA. Retrieved 2006-07-08.
- ↑ Cooperative Program for Operational Meteorology, Education and Training. "Nora: After Landfall (VIS)". University Corporation for Atmospheric Research. Retrieved 2006-04-10.
- ↑ Rebecca Carter (2002). "Tropical Storm Impacts on Arizona and New Mexico" (PDF). Climate Assessment for the Southwest Project, Institute for the Study of Planet Earth, University of Arizona. Retrieved 2006-03-03.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Hurricane Nora (1997). |