Ikara (missile)
| Ikara | |
|---|---|
|
Ikara missile on launcher | |
| Type | Anti-submarine |
| Place of origin | Australia |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1960s-1990s |
| Used by |
Australia Brazil Chile New Zealand United Kingdom |
| Production history | |
| Designed | Circa 1959-60 |
| Manufacturer | Australian Government Aircraft Factories/Commonwealth Aircraft Corporation (CAC)/Australian Defence Scientific Services (ADSS)[1] |
| Produced | Early 1960s |
| Specifications | |
| Weight | 513 kilograms (1,131 lb) |
| Length | 3.429 metres (135.0 in) |
| Warhead |
Mark 44 (two versions) Mark 46 NDB (Nuclear Depth Bomb). |
Detonation mechanism | none |
|
| |
| Engine | Bristol Aerojet Murawa two-stage solid-fuel rocket engine.[2] |
| Wingspan | 1.524 metres (60.0 in) |
Operational range |
Maximum range: 10 nautical miles (19 km) Minimum (safety) range: 914 metres (1,000 yd) |
| Flight ceiling | 335 metres (1,099 ft) |
| Speed |
Boost max: 713 kilometres per hour (443 mph) Cruise: 658 kilometres per hour (409 mph) Maximum boost acceleration: 10.9G Boost burn time: 1.96 seconds Launcher maximum elevation: 55° Maximum range time interval: 100 sec. |
Guidance system | Command guidance |
Steering system | Elevons |
Launch platform | Ship-borne |
The Ikara missile was an Australian ship-launched anti-submarine missile, named after an Australian Aboriginal word for "throwing stick". It launched an acoustic torpedo to a range of 10 nautical miles (19 km), allowing fast-reaction attacks against submarines at ranges that would otherwise require the launching ship to close for attack, placing itself at risk. Also, by flying to the general area of the target, the engagement time was dramatically reduced, giving the target less time to respond. Submariners referred to IKARA as "Insufficient Knowledge And Random Action".
Design and development
With the development of nuclear power, submarine performance, especially speed, improved dramatically, as did the threat they posed. Simultaneously, sonar detection capability at long range was also improving significantly but the weapons available to surface escort warships were still of the short-range variety. The final British development of the A/S mortar was the Limbo mortar, able to fire in all directions but limited to a maximum range of 914 metres (2,999 ft). Even the latest modern Mark 46 lightweight torpedoes are limited in range to 4 nautical miles (7.4 km), and at their speed of 28 knots (52 km/h) would take 8.5 minutes to travel that distance, and are consequently unable to attack time-urgent targets at extended ranges.
Known initially under the rainbow code name Blue Duck, the Ikara was a "Rocket-Thrown-Weapon" with similarities to the French Malafon. It differed from Malafon, in that the torpedo was semi recessed in the body of missile body rather than mounted in the nose. Ikara's range at 10 nautical miles (19 km) was double that of ASROC.[3] Ikara was generally considered a superior system to ASROC as it was accurately guided during flight to ensure optimal targeting. A submarine would be aware from sonar contacts that it was about to be attacked and could engage in evasive changes of course. In ASROC's flight time to maximum range of 55 seconds,[3] a submarine travelling at 25 knots (46 km/h) would move 700 metres (2,300 ft) from its position at launch, and a prediction would be made of the submarine's likely position at torpedo splashdown. But during the design of Ikara around 1960 the range of the acoustic seeker of the Mk.44 torpedo was limited to 457 metres (1,499 ft) and consequently its kill probability was low. The range of the acoustic seeker was later improved.[4]
The Turana target drone was designed and built in Australia as a development of the Ikara anti-submarine weapon system. It was a target drone with remote control that was launched from the Ikara launcher for use in naval anti-aircraft target practice.

Ikara was powered by a two-stage in-line solid-fuel Murawa rocket engine developed by Bristol Aerojet Ltd in the UK[5] and was guided by radio command link until it reached the vicinity of the submarine, determined by the ship's sonar contact, where it would first jettison the rear ventral fin and torpedo rear covering and then release its 12.7 inch Mark 44 or Mark 46 acoustically-guided anti-submarine torpedo. The torpedo payload would descend by parachute while the missile itself was programmed to splashdown some distance away to avoid interference with the acoustic torpedo's seeker head. The torpedo would then begin a circular search pattern to find and lock-on a submarine contact.
British variant differences

A variant fitted to the British Royal Navy's Leander class frigate differed in several respects from the original Australian version designed to operate in the Pacific. The Royal Navy required changes to the frequencies used, to enable Ikara to be used in the NATO area, where different electronic warfare conditions and international frequency agreements had to be taken into account. Neither the Australian-built analogue computer system, or the American Bunker Ramo Corporation 133 digital computer system, used in most RAN systems, were compatible with the ADA digital battle-control computers being fitted into Royal Navy ships, and this was also changed. The UK-manufactured version of the Mark 44 torpedo also differed from the US-built version purchased by the Australians for their Ikara missiles. The British also required the missile payload to be changeable aboard ship to permit different payload combinations to be used, including a Nuclear Depth Bomb (NDB) option, and this, together with the different internal ship layouts required further changes to the missile, storage and handling arrangements. The Australian practice was to combine the missile and payload at a shore-based ordnance facility, before issuing the complete unit to a ship. Repair or maintenance was only possible ashore, whereas in the British ships, the changes made enabled a faulty torpedo to be removed and replaced on a functioning missile, and thereby increasing the flexibility of use of very limited stocks aboard; especially on lengthy deployments around the globe, as was more common with British ships than their Australian counterparts. The facility to change a torpedo payload aboard ship also permitted a change from a conventional torpedo to a WE.177A NDB, a facility for a nuclear option that was not needed on ships fitted with the Australian variant of Ikara.[4]
Ikara fitted ships
Ikara was fitted to all of the Royal Australian Navy's River class frigates/destroyer escorts and Perth class guided missile destroyers. There were three main variants of the system fitted to RAN ships; F1, F2, and F3. The F1 system, using an analogue computer, a single launcher and without a data link, was fitted to HMA Ships Stuart and Derwent only. The F3 system, with a digital computer, digital display, single launcher and a digital data link, was fitted to the other four River class ships. HMAS Stuart and Derwent were fitted with F3/0 systems during Half-life refits during the 1980s. The F2 system, using a digital computer, digital display, two launchers and with a digital data link, was fitted to the three Perth class destroyers. The computer used by the RAN was the AN/UYK-1 NTDS (Naval Tactical Data System) (Bunker Ramo 133).
Ikara was also operated by the Brazilian Navy, Chilean Navy, Royal Navy, and Royal New Zealand Navy. It was phased out in the early 1990s. The British purchased Ikara to fit to the two new CVA-01 aircraft carriers planned (and later cancelled) in the 1960s, and their escorts, the Type 82 destroyers, of which only one, HMS Bristol was built. With the cancellation of the remaining escorts, the British were left with purchased Ikara missiles in storage, and opted to fit them into eight existing Batch 1 Leander class frigates in need of modernisation:[8] HM Ships Ajax, Arethusa, Aurora, Dido, Euryalus, Galatea, Leander and Naiad.
Operators
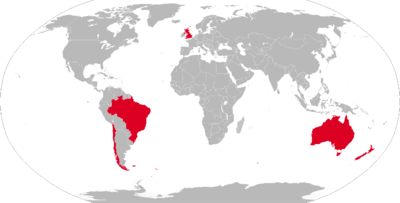
Former operators
References
- ↑ "Chapter 13 - Defence Science and Technology". Technology in Australia 1788-1988. Austehc.unimelb.edu.au. Australian Academy of Technological Sciences and Engineering. p. 921. ISBN 0-908029-49-7. Retrieved 2011-01-26.
- ↑ "Part of RecordSearch unavailable". Naa12.naa.gov.au. Retrieved 2011-01-26.
- 1 2 "Record Summary". The National Archives. Retrieved 2008-10-10.
- 1 2 "Record Summary". The National Archives. Retrieved 2008-10-10.
- ↑ http://naa12.naa.gov.au/scripts.ItemDetail.asp?M=0&B=930305. Retrieved November 12, 2006. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ artist: Brian Burnell
- ↑ "Bristol Aero Collection". Bristolaero.com. Retrieved 2011-01-26.
- ↑ Mike Potter. "LEANDER class". Hazegray.org. Retrieved 2011-01-26.
External links
- http://www.middle-watch.co.uk/Ikara.htm
- http://www.adastra.adastron.com/projects/ikara.htm
- http://www.skomer.u-net.com/projects/ikara.htm
- http://naa12.naa.gov.au/scripts/PhotoSearchItemDetail.asp?M=0&B=11437004
- http://web.ukonline.co.uk/aj.cashmore/.weapons/australia/.asw.html
- http://www.probertencyclopaedia.com/cgi-bin/xphrase.pl?keyword=malafon
- https://fas.org/man/dod-1-1/sys/missile/vla.htm
- http://www.destroyers.org/Ord-Articles/ASROC.htm
- http://www.gyrodynehelicopters.com/asroc.htm
- http://www.nuclear-weapons.info/vw.htm#WE.177%20further_development_proposals