Ileocecal valve
| Ileocecal valve | |
|---|---|
 Interior of the cecum and lower end of ascending colon with the ileocecal valve labeled as "colic valve" | |
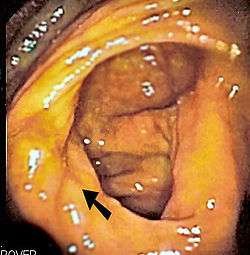 Endoscopic image of cecum with arrow pointing to ileocecal valve in foreground | |
| Details | |
| Artery | Ileocolic artery |
| Vein | Ileocolic vein |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Valva ileocaecalis or papilla ilealis |
| MeSH | A03.556.124.684.249.400 |
| FMA | 15973 |
The ileocecal valve (ileal papilla, ileocaecal valve, Tulp's valve, Tulpius valve, Bauhin's valve, ileocecal eminence, valve of Varolius or colic valve) is a sphincter muscle valve that separates the small intestine and the large intestine.[1] Its critical function is to limit the reflux of colonic contents into the ileum.[2] Roughly two litres of fluid enters the colon daily through the ileocecal valve.
The ileocecal valve is distinctive because it is the only site in the gastrointestinal tract that is used for Vitamin B12 and bile acid absorption.[3][4]
Etymology
It was described by the Dutch physician Nicolaes Tulp (1593–1674), and thus it is sometimes known as Tulp's valve.
The valve was also described in 1588 by Gaspard Bauhin—hence the name Bauhin's Valve or Valve of Bauhin—in the preface of his first writing, De corporis humani partibus externis tractatus, hactenus non editus.
Histology
The histology of the ileocecal valve shows an abrupt change from a villous mucosa pattern of the ileum to a more colonic mucosa. A thickening of the muscularis mucosa, which is the smooth muscle tissue found beneath the mucosal layer of the digestive tract. A thickening of the muscularis externa is also noted.[1]
There is also a variable amount of lymphatic tissue found at the valve.[5]
The ileocecal valve has a papillose structure.
Clinical significance
During colonoscopy, the ileocecal valve is used, along with the appendiceal orifice, in the identification of the cecum. This is important as it indicates that a complete colonoscopy has been performed. The ileocecal valve is typically located on the last fold before entry into the cecum, and can be located from the direction of curvature of the appendiceal orifice, in what is known as the bow and arrow sign.[6]
Intubation of the ileocecal valve is typically performed in colonoscopy to evaluate the distal, or lowest part of the ileum. Small bowel endoscopy can also be performed by double-balloon enteroscopy through intubation of the ileocecal valve.[7]
Tumors of the ileocecal valve are rare, but have been reported in the literature.[8][9]
Additional images
- Ileum, cecum and ascending colon
- Cecum and ileum
- Ileo-cecal valve
- Ileo-cecal valve
References
- 1 2 Pollard, MF; Thompson-Fawcett, MW; Stringer, MD (2012). "The human ileocaecal junction: anatomical evidence of a sphincter". Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy. 34 (1): 21–9. doi:10.1007/s00276-011-0865-z. PMID 21863224.
- ↑ Barret KE. "Lange Gastrointestinal Physiology". The McGraw-Hill Companies, 2006.
- ↑ Fornaro, R.; Belcastro, E.; Lo Presti, G.; Carissimi, T.; Ferraris, R. (1991). "The ileocecal valve as a prognostic factor in extensive resection of the small intestine". Chirurgia italiana. 43 (1–2): 49–54. PMID 1769094.
- ↑ Steiner, M. S.; Morton, R. A. (1991). "Nutritional and gastrointestinal complications of the use of bowel segments in the lower urinary tract". The Urologic clinics of North America. 18 (4): 743–754. PMID 1949406.
- ↑ Burkitt HG, Young B, Heath JW. Wheater's Functional Histology: a text and colour atlas. Churchill Livingstone, London, 1993.
- ↑ Cotton PB, Williams CB. Practical Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Blackwell Publishers, London, 1996
- ↑ Ross, AS; Waxman, I; Semrad, C; Dye, C (2005). "Balloon-assisted intubation of the ileocecal valve to facilitate retrograde double-balloon enteroscopy". Gastrointestinal endoscopy. 62 (6): 987–8. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2005.09.002. PMID 16301054.
- ↑ Yörük, G; Aksöz, K; Buyraç, Z; Unsal, B; Nazli, O; Ekinci, N (2004). "Adenocarcinoma of the ileocecal valve: report of a case". The Turkish Journal of Gastroenterology. 15 (4): 268–9. PMID 16249985.
- ↑ Song, HJ; Ko, BM; Cheon, YK; Ryu, CB; Lee, JS; Lee, MS; Shim, CS (2005). "Isolated ileocecal lymphoma". Gastrointestinal endoscopy. 61 (2): 293–4. doi:10.1016/S0016-5107(04)02548-9. PMID 15729248.
External links
- Diagram at amatsu.co.uk
- largeintestine at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (cecuminside)