Indian gray mongoose
| Indian grey mongoose | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Adult in the wild (Hyderabad, India) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | Herpestidae |
| Subfamily: | Herpestinae |
| Genus: | Herpestes |
| Species: | H. edwardsii |
| Binomial name | |
| Herpestes edwardsii É. Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, 1818 | |
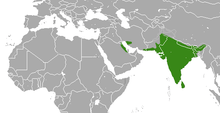 | |
| Indian grey mongoose range | |
The Indian grey mongoose or common grey mongoose (Herpestes edwardsii) is a species of mongoose mainly found in the Indian Subcontinent, in India, Nepal, Sri Lanka, Pakistan, Bhutan, Bangladesh and some other parts of Asia. In North Indian languages (Hindi, Urdu, Punjabi, etc.) it is called Nevalaa. The grey mongoose is commonly found in open forests, scrublands and cultivated fields, often close to human habitation. It lives in burrows, hedgerows and thickets, among groves of trees,taking shelter under rocks or bushes and even in drains. It is very bold and inquisitive but wary, seldom venturing far from cover. It climbs very well. Usually found singly or in pairs. It preys on rodents, snakes, birds’ eggs and hatchlings, lizards and variety of invertebrates. Along the Chambal River it occasionally feeds on gharial eggs. It breeds throughout the year.
Description
The Indian grey mongoose or common grey mongoose, is medium-sized tawny or yellowish grey with a lighter underside, darker feet (this separates it from the syntopic small Asian mongoose), and dark red tail tip. They have a reddish tint to their heads. Their tail length equals their body length. Body length: 36–45 cm (14-17 inches) Tail length: 45 cm (17 inches), weight: 0.9-1.7 kg (2-4 lb). Males are significantly larger than the females. Mongooses can see colours, unlike most mammals, which have only partial colour vision.
A mongoose cracks eggs open by standing with its back to a wall and throwing the eggs under its body and between its back legs so that the eggs break against the wall. Indian grey mongooses are often kept as pets to keep houses free from rats and other pests. The mongoose closes its outer ear when hunting in soil to keep out dirt and water.[2]
Feeding
Being carnivorous it feeds on many species ranging from rats to snakes. The mongoose is a skilful hunter which actively searches for prey by using its strong senses of smell and sight. It eats anything it can catch. The Indian grey mongoose commonly eats small mammals such as rats, as well as eggs and a variety of arthropods, including the scorpion. The mongoose sniffs the ground and turns over rocks and stones in its search for prey. If the animal tries to flee, the mongoose chases it. It kills its prey while they are both running by delivering a bite to the neck or head. Although the mongoose eats snakes, including the venomous cobra, the main part of its diet consists of small animals that live on or under the ground. The mongoose is a fast and agile hunter with a thick coat and specialised acetylcholine receptors which render them resistant or immune to snake venom.[3] It is always watchful for prey.[4]
-
-_is_it-_at_Hyderabad%2C_AP_W_106.jpg)
in Hyderabad, India.
-

-
-_is_it-_at_Hyderabad%2C_AP_W_101.jpg)
in Hyderabad, India.
-

Baby mongooses, in Chennai, India
References
- ↑ Choudhury, A.; Wozencraft, C.; Muddapa, D.; Yonzon, P.; Jennings, A. & Geraldine, V. (2011). "Herpestes edwardsii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2011.2. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 18 January 2012. Database entry includes a brief justification of why this species is of least concern
- ↑ Did you know about Indian Gray Mongoose http://ladywildlife.com/animals/indiangraymongoose.html
- ↑ "How the Mongoose Defeats the Snake". Retrieved 2010-10-25.
- ↑ Ladywidlife's Indian Grey Mongoose http://ladywildlife.com/animals/indiangraymongoose.html
