Interferon-alpha/beta receptor
| interferon (alpha, beta and omega) receptor 1 | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | IFNAR1 |
| Alt. symbols | IFNAR |
| Entrez | 3454 |
| HUGO | 5432 |
| OMIM | 107450 |
| RefSeq | NM_000629 |
| UniProt | P17181 |
| Other data | |
| Locus | Chr. 21 q22.1 |
| interferon (alpha, beta and omega) receptor 2 | |
|---|---|
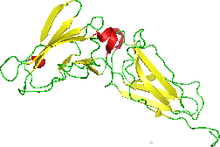 NMR structure of the interferon-binding ectodomain of the human interferon receptor.[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | IFNAR2 |
| Alt. symbols | IFNABR |
| Entrez | 3455 |
| HUGO | 5433 |
| OMIM | 602376 |
| RefSeq | NM_207585 |
| UniProt | P48551 |
| Other data | |
| Locus | Chr. 21 q22.1 |
The interferon-α/β receptor (IFNAR) is a receptor which binds type I interferons including interferon-α and -β. It is a heteromeric cell surface receptor composed of one chain with two subunits referred to as IFNAR1 and IFNAR2.[2] Upon binding of type I IFNs, IFNAR activates the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. Interferon stimulation classically results in an anti-viral immune response.
Structure
The structure was obtained using NMR. Originally 35 conformers were calculated. This was narrowed to 22 with low energy being the criteria. It was the first helical cytokine receptor's structure to be determined in solution. The molecule has one polymer The structure reveals the nature of binding. A model of the IFNAR2 reveals a predominantly hydrophobic patch on the receptor that interacts with a matching hydrophobic surface on IFN-alpha. An adjacent motif of charged side chains then guides the proteins into a tight complex. The binding interface may account for crossreactivity and ligand specificity of the receptor. The source for experiments was human but was expressed in Escherichia coli.
SCOP Classification
IFNAR is clustered into the group beta proteins based on its secondary structural content. IFNAR's folds show a clear evolutionary relationship to the Immunoglobulin beta-sandwich. It is grouped into the superfamily and family Fibronectin type III based on structural and functional similarities that show probable common evolution. The domain, or evolutionary unit observed in nature, is the Interferon-alpha/beta receptor beta chain. Species was human.
References
- ↑ PDB: 1n6u; Chill JH, Quadt SR, Levy R, Schreiber G, Anglister J (July 2003). "The human type I interferon receptor: NMR structure reveals the molecular basis of ligand binding". Structure. 11 (7): 791–802. doi:10.1016/S0969-2126(03)00120-5. PMID 12842042.
- ↑ Uzé G, Schreiber G, Piehler J, Pellegrini S (2007). "The receptor of the type I interferon family". Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 316: 71–95. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-71329-6_5. PMID 17969444.
External links
- Receptor, Interferon alpha-beta at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)