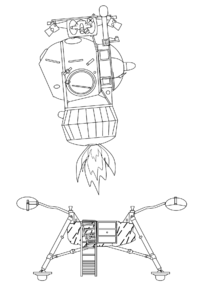
LK-700
| Manufacturer | OKB-52 |
|---|---|
| Country of origin | Soviet Union |
| Operator | Soviet space program |
| Applications | Land cosmonauts on the Moon and bring them back to Earth |
| Production | |
| Status | Canceled |
| Related spacecraft | |
| Derived from | LK-1 |
| Derivatives | TKS spacecraft |
LK-700 was a Soviet direct ascent lunar lander program proposed in 1964.[1] It was developed by Vladimir Chelomey as an alternative to the N1-L3 program. It was also a further development of the LK-1 lunar flyby spacecraft.
It would have been launched using the proposed UR-700[2] rocket (related to the Proton rocket) with a crew of three cosmonauts on a direct flight to the lunar surface and back. The direct landing approach would allow the Soviets to land anywhere on the moon's nearside.[3] The program was canceled in 1974.
Mission profile
Unmanned flights would be followed by manned flights. The proposed schedule was:
- May 1972: First UR-700/LK-700 unmanned launch. Subsequent launches in November 1972 and April 1973.
- April 1973: First manned UR-700/LK-700 launch. Subsequent flights in August and October 1973.
Following initial LK-700 landings, the more ambitious Lunar Expeditionary Complex (LKE) would be delivered to the surface in three UR-700 launches:
- Launch 1: lunar station to enable a six-month stay
- Launch 2: LK-700 with crew
- Launch 3: large rover
Characteristics
- Crew size: 3
- Orbital storage: 45 days
- Spacecraft delta v: 9,061 m/s
- Gross mass: 154,000 kg
- Height: 21.20 m
- Span: 2.70 m
- Thrust: 131.40 kN
- Specific impulse: 326 s
References
- ↑ "LK-700". astronautix.com. Retrieved 5 July 2015.
- ↑ http://www.russianspaceweb.com/ur700.html
- ↑ "What Would a Soviet Moon Landing Have Looked Like?". DNews. Retrieved 5 July 2015.