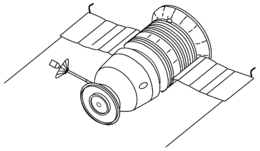
Zond 8
|
Zond 8 | |
| Names | Soyuz 7K-L1 s/n 14 |
|---|---|
| Mission type | Spacecraft test |
| Operator | Soviet Union |
| COSPAR ID | 1970-088A |
| SATCAT № | 4591 |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Bus | Soyuz 7K-L1 |
| Manufacturer | OKB-1 |
| Launch mass | 5,375 kilograms (11,850 lb) |
| End of mission | |
| Recovered by | Soviet recovery vessel Taman |
| Landing date | October 27, 1970 |
| Landing site | 730 kilometres (450 mi) SE of the Chagos Archipelago |
| Flyby of Moon | |
| Closest approach | October 24, 1970 |
| Distance | 1,110.4 km (690.0 mi) |
Zond 8, a formal member of the Soviet Zond program and unmanned version of Soyuz 7K-L1 manned Moon-flyby spacecraft, was launched from an Earth orbiting platform, Tyazheliy Sputnik (1970-088B), towards the Moon.
The announced objectives of Zond 8 were investigations of the Moon and circumlunar space and testing of onboard systems and units. The spacecraft obtained photographs of Earth on 21 October from a distance of 64,480 km. The spacecraft transmitted flight images of Earth for three days. Zond 8 flew past the Moon on October 24, 1970, at a distance of 1110.4 km and obtained both black-and-white and color photographs of the lunar surface. Scientific measurements were also obtained during the flight.
Zond 8 reentered the Earth's atmosphere and splashed down 730 km SE of the Chagos Archipelago, in the Indian Ocean on 27 October 1970, 24 km from the USSR recovery ship Taman.[1][2]
See also
References
- ↑ "Zond 8, Recovery Ship, Miss Distance", Soviet and Russian lunar exploration By Brian Harvey - page 218, Recovery Ship and Miss Distance.
- ↑ "Zond 8, Landing Point" Archived September 27, 2011, at the Wayback Machine., NASA Solar System Exploration - Zond 8, Splashdown area.
External links
- Soviet Lunar Images
- Astronautix.com - detailed on Soyuz 7K-L1 (Zond) program
- NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day: The Moon from Zond 8 (16 July 2013)
This article was originally based on material from NASA (NSSDC) information on Zond 8