List of motorways in Turkey
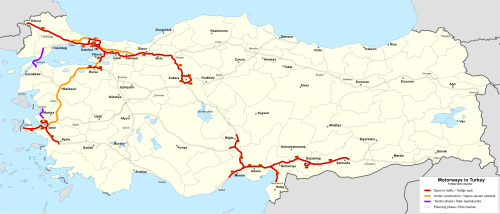



Motorways in Turkey (Turkish: otoyol[1]) are a network in development. The length of the current network is 2155 km.[2][3] The minimum speed limit on the Turkish motorways is 40 km/h and the maximum is 120 km/h.[4] Most of the network is 6 lanes wide (3 in each direction). The motorway sign in Turkey is green and uses Highway Gothic typeface.
History
The motorway network in Turkey is relatively new. In 1980, the network was only 27 km long and was focused on Istanbul. Currently, great efforts are being made to expand the network. In September 2009, plans were unveiled for 12 new highway routes that are to be built by 2023, a total length of about 4773 km.[5]
Toll
All the motorways are toll roads. The toll is based on the distance traveled. On most sections, the toll can be paid only with RFID-based HGS and OGS. Cash and KGS card payment methods have mostly been abolished in recent years. Only the newly opened Otoyol 5 and Otoyol 6 have sections were it is possible to pay by cash or with credit card. Apart from motorways, the other state roads in Turkey are free of charge.
The revenue from tolls in 2001 were still about $203 million, rising by 2012 to approximately $542 million. In 2012, the Bosphorus bridges saw 150 million vehicles pass and the other toll roads saw over 210 million vehicles.[6] In 2015, both bridges were used by 141 million vehicles while the other toll motorways were used by 271 million vehicles, generating a total revenue of $391 million (both bridges and motorways combined).[7]
Standards
Mainly because the country already has a wide network of double carriageways, the standards for motorways in comparison are very high. Each direction has at least 3 lanes, aside from the İzmit Bypass and a small stretch of the Otoyol 3 between Silivri and Esenyurt which only have 2. The lanes are each 3.75 meters wide. Most exits have a connection road, which helps avoiding wrong-way driving and illegal access to the road (bikes, tractors and horses are not allowed on otoyols).
The minimum speed is 40 km/h (25 miles per hour) and the maximum allowed speed is 120 km/h (75 miles per hour), although speeding is not punished under 132 km/h (82 miles per hour).
Alongside otoyols, there are resting areas, which are standardized as A, B, C and D type service areas. The D type is mainly a parking area. The C type has a fuel station added. The B type has a fuel station and a vehicle service station added. The A type additionally has a motel.
Dangerous stretches such as tunnels or bridges where there is often fog, exits, interchanges and service areas are illuminated.
Since gradients are expected to be very low and turning radii are expected to be very high, otoyols have many bridges and tunnels which makes them very expensive.
Projects
Under construction:
- Orhangazi-Bursa-Izmir Motorway (Otoyol 5) (Iznik South-Ovaakça (26 km)) & (Başköy-Kemalpaşa (280 km))
- Northern Marmara Motorway (Otoyol 7) (Kınalı-Odayeri (88 km)) & (Paşaköy-Akyazı (169 km))
- Remaining parts of the Izmir Beltway (Menemen bypass) (Otoyol 30) (8 km)
- Edirne - Pazarkule link (including Maritsa Bridge) (Otoyol 3) (8 km)
Tender Phase
- Ankara-Niğde (Gölcük) Motorway (including link to Kırşehir) (Otoyol 21) (330 km)
- Ankara-Kırıkkale-Delice Motorway (119 km)
- Çeşmeli-Erdemli-Silifke-Taşucu Motorway (Otoyol 51) (98 km)
- Menemen-Aliağa-Çandarlı Motorway (Otoyol 30) (76 km)
- Kınalı-Tekirdağ-Çanakkale-Balıkesir Motorway (including Çanakkale 1915 Bridge over Dardanelles Strait) (352 km)
- Aydın-Kuyucak-Denizli-Burdur Motorway (Otoyol 57) (315 km)
Being planned:[8]
2023 Targets
- Afyonkarahisar-Burdur-Antalya Motorway (350 km)
- Antalya-Alanya Motorway (187 km)
- Ankara-Sivrihisar Motorway (164 km)
- Sivrihisar-Bursa Motorway (Otoyol 22) (231 km)
- Sivrihisar-İzmir Motorway (408 km)
- Şanlıurfa-Mardin-Habur Motorway (including link to Diyarbakır) (Otoyol 52) (454 km)
- Delice-Samsun Motorway (including Samsun bypass to Bafra and Ünye) (447 km)
- Gerede-Merzifon Motorway (336 km)
- Merzifon-Gürbulak Motorway (919 km)
- Yalova-İzmit Motorway (91 km)
2035 Targets
- Afyonkarahisar-Konya-Ereğli-Niğde (Ulukışla) Motorway (440 km)
- Afyonkarahisar-Bozüyük Motorway (105 km)
- Alanya-Silifke Motorway (200 km)
- Düzce-Zonguldak Motorway (105 km)
- Delice-Sivas-Refahiye Motorway (500 km)
- Nevşehir-Kayseri-Malatya-Diyarbakır Motorway (600 km)
- Sivas-Malatya Motorway (220 km)
- Şanlıurfa-Akçakale Motorway (50 km)
- Diyarbakır-Gürbulak Motorway (475 km)
- Trabzon-Refahiye-Malatya-Kahramanmaraş Motorway (540 km)
- Pasinler-Türközü Motorway (250 km)
- Rize-Erzurum-Diyarbakır Motorway (460 km)
- İskenderun-Cilvegözü Motorway (Otoyol 53) (78 km)
- Malkara-İpsala Motorway (Greek border) (50 km)
- Malkara-Havsa Motorway (110 km)
- Bandırma-Susurluk Motorway (56 km)
- Bandırma-Lapseki Motorway (130 km)
- Çandarlı-Bergama-Savaştepe Motorway (Otoyol 30) (80 km)
- Aydın-Muğla Motorway (90 km)
List of motorways
See also
- International E-road network
- Asian Highway Network
- General Directorate of Highways (Turkey)
- List of motorway tunnels in Turkey
External links
References
- ↑ Also quite widely called otoban, which is the Turkish spelling of the German word Autobahn
- ↑ http://www.kgm.gov.tr/Sayfalar/KGM/SiteTr/Kurumsal/YolAgi.aspx
- ↑ "YILLAR İTİBARIYLA İŞLETMEYE AÇIK OTOYOLLAR" (PDF) (in Turkish). KGM. Retrieved 18 June 2013.
- ↑ "Hız Sınırları" (in Turkish). KGM. Retrieved 14 April 2014.
- ↑ Infrastrukturprojekte sollen die türkische Bauwirtschaft ankurbeln, Germany Trade and Invest, 24. November 2009
- ↑ "Otoyol ve Köprü Gelirleri (2001-2012)" (PDF) (in Turkish). KGM. Retrieved 18 June 2013.
- ↑ http://www.kgm.gov.tr/SiteCollectionDocuments/KGMdocuments/Istatistikler/OtoyolMaliBilgileri/OtoyolVeKopruGelirleri%282001-2015%29.pdf Otoyol statistics
- ↑ "Otoyol Projeleri" (in Turkish). KGM. Retrieved 10 January 2016.