London dispersion force
London dispersion forces (LDF, also known as dispersion forces, London forces, instantaneous dipole–induced dipole forces, or loosely van der Waals forces) are a type of force acting between atoms and molecules.[1] They are part of the van der Waals forces. The LDF is named after the German-American physicist Fritz London.
The LDF is a weak intermolecular force arising from quantum-induced instantaneous polarization multipoles in molecules. They can therefore act between molecules without permanent multipole moments.
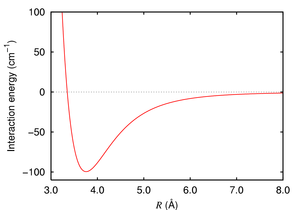
London forces are exhibited by non-polar molecules because of the correlated movements of the electrons in interacting molecules. Because the electrons in adjacent molecules "flee" as they repel each other, electron density in a molecule becomes redistributed in proximity to another molecule (see quantum mechanical theory of dispersion forces). This is frequently described as the formation of instantaneous dipoles that attract each other. London forces are present between all chemical groups, and usually represent the main part of the total interaction force in condensed matter, even though they are generally weaker than ionic bonds and hydrogen bonds.
London forces become stronger as the atom in question becomes larger, and to a smaller degree for large molecules. This is due to the increased polarizability of molecules with larger, more dispersed electron clouds. This trend is exemplified by the halogens (from smallest to largest: F2, Cl2, Br2, I2). Fluorine and chlorine are gases at room temperature, bromine is a liquid, and iodine is a solid. The London forces also become stronger with larger amounts of surface contact. Greater surface area means closer interaction between different molecules.
Quantum mechanical theory of dispersion forces
The first explanation of the attraction between noble gas atoms was given by Fritz London in 1930.[2][3][4] He used a quantum-mechanical theory based on second-order perturbation theory. The perturbation is the Coulomb interaction V between the electrons and nuclei of the two monomers (atoms or molecules) that constitute the dimer. The second-order perturbation expression of the interaction energy contains a sum over states. The states appearing in this sum are simple products of the stimulated electronic states of the monomers. Thus, no intermolecular antisymmetrization of the electronic states is included and the Pauli exclusion principle is only partially satisfied.
London developed the method perturbation V in a Taylor series in , where is the distance between the nuclear centers of mass of the monomers.
This Taylor expansion is known as the multipole expansion of V because the terms in this series can be regarded as energies of two interacting multipoles, one on each monomer. Substitution of the multipole-expanded form of V into the second-order energy yields an expression that resembles somewhat an expression describing the interaction between instantaneous multipoles (see the qualitative description above). Additionally, an approximation, named after Albrecht Unsöld, must be introduced in order to obtain a description of London dispersion in terms of dipole polarizabilities and ionization potentials.
In this manner, the following approximation is obtained for the dispersion interaction between two atoms and . Here and are the dipole polarizabilities of the respective atoms. The quantities and are the first ionization potentials of the atoms, and is the intermolecular distance.
Note that this final London equation does not contain instantaneous dipoles (see molecular dipoles). The "explanation" of the dispersion force as the interaction between two such dipoles was invented after London arrived at the proper quantum mechanical theory. The authoritative work[5] contains a criticism of the instantaneous dipole model[6] and a modern and thorough exposition of the theory of intermolecular forces.
The London theory has much similarity to the quantum mechanical theory of light dispersion, which is why London coined the phrase "dispersion effect." In physics, the term "dispersion" describes the variation of a quantity with frequency, which is the fluctuation of the electrons in the case of the London dispersion.
Relative magnitude
Dispersion forces are usually dominant of the three van der Waals forces (orientation, induction, dispersion) between atoms and molecules, with the exception of molecules that are small and highly polar, such as water. The following contribution of the dispersion to the total intermolecular interaction energy has been given:[7]
| Molecule pair | % of the total energy of interaction |
|---|---|
| Ne-Ne | 100 |
| CH4-CH4 | 100 |
| HCl-HCl | 86 |
| HBr-HBr | 96 |
| HI-HI | 99 |
| CH3Cl-CH3Cl | 68 |
| NH3-NH3 | 57 |
| H2O-H2O | 24 |
| HCl-HI | 96 |
| H2O-CH4 | 87 |
References
- ↑ "Chemguy Chemistry P5T8S9". YouTube. Retrieved 2013-04-01.
- ↑ R. Eisenschitz & F. London (1930), "Über das Verhältnis der van der Waalsschen Kräfte zu den homöopolaren Bindungskräften", Zeitschrift für Physik, 60 (7–8): 491–527, Bibcode:1930ZPhy...60..491E, doi:10.1007/BF01341258
- ↑ London, F. (1930), "Zur Theorie und Systematik der Molekularkräfte", Zeitschrift für Physik, 63 (3–4): 245, Bibcode:1930ZPhy...63..245L, doi:10.1007/BF01421741 and London, F. (1937), Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie, 33: 8–26 Missing or empty
|title=(help). English translations in Parr, Robert G. (2000), H. Hettema, ed., "Quantum Chemistry, Classic Scientific Papers", Physics Today, Singapore: World Scientific, 54 (6): 63, Bibcode:2001PhT....54f..63H, doi:10.1063/1.1387598 - ↑ F. London (1937), "The general theory of molecular forces", Transactions of the Faraday Society, 33: 8–26, doi:10.1039/tf937330008b
- ↑ J. O. Hirschfelder; C. F. Curtiss & R. B. Bird (1954), Molecular Theory of Gases and Liquids, New York: Wiley
- ↑ A. J. Stone (1996), The Theory of Intermolecular Forces, Oxford: Clarendon Press
- ↑ Jacob Israelachvili (1992), Intermolecular and Surface Forces (2nd ed.), Academic Press