Lucasuchus
| Lucasuchus Temporal range: Late Triassic | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | †Aetosauria |
| Family: | †Stagonolepididae |
| Subfamily: | †Desmatosuchinae |
| Genus: | †Lucasuchus Long and Murry, 1995 |
| Species | |
| |
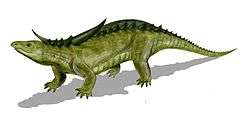
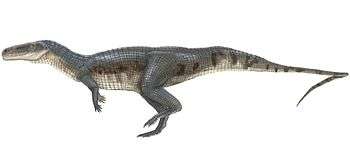
Lucasuchus is an extinct genus of aetosaur. Fossils have been found from the Bull Canyon Formation of the Dockum Group outcropping in the Revuelto Creek locality in Quay County, New Mexico. All specimens date back to the Norian stage of the Late Triassic. The genus was named in 1995 after the American paleontologist Spencer G. Lucas.[1]
Lucasuchus was first proposed to be a junior subjective synonym of Longosuchus in 1999, and several other studies have also considered it to be an invalid genus.[2][3] However, more recent studies concluded that Lucasuchus is not congeneric with any other known aetosaur genus, and is likely to be more closely related to Desmatosuchus and Acaenasuchus than to Longosuchus.[4] The presence of elongate lateral osteoderm horns is shared by all of these genera, which make up the subfamily Desmatosuchinae.[5][6][7][8]
It has been suggested that Lucasuchus is either a sexual dimorph belonging to the same species as Longosuchus meadei or an ontogenetic stage of the species (meaning that it represents one particular age group). However, several characteristics of Lucasuchus may indicate that it is indeed distinct from L. meadei rather than an example of morphological variation. For example, Lucasuchus has a clear radial pattern of pits and grooves on the paramedian osteoderms of the back while Longosuchus has only a random pattern of pits on the paramedians. In Lucasuchus, the paramedians have large conical eminences, or projections, while in Longosuchus these projections are only present in the form of low pyramidal bosses. Lucasuchus also lacks the emarginations (or notches) on the spikes of the lateral osteoderms that are seen in Longosuchus.[9]
References
- ↑ Long, R. A., and Murry, P. A. (1995). Late Triassic (Carnian and Norian) tetrapods from the southwestern United States. New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science Bulletin 4, 254 pp.
- ↑ A new aetosaur (Reptilia: Archosauria) from the Upper Triassic of Texas and the phylogeny of aetosaurs. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 19(1):50-68.
- ↑ Heckert, A. B., Lucas, S. G., Hunt, A. P., and Spielmann, J. A. (2007). Late Triassic aetosaur biochronology revised. In: Lucas, S. G. and Spielmann, J. A., eds., The Global Triassic. New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science Bulletin 41.
- ↑ Harris, S. R., Gower, D. J., and Wilkinson, M. (2003). Intraorganismal homology, character construction, and the phylogeny of aetosaurian archosaurs (Reptilia, Diapsida). Systematic Biology 52(2):239-252.
- ↑ Martz, J. W. and Small, B. J. (2006). Tecovasuchus chatterjeei, a new aetosaur (Archosauria: Stagonolepididae) from the Tecovas Formation (Carnian, Upper Triassic) of Texas. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 26(2):308–320.
- ↑ Huene, F. V. (1942). Lieferungen 3/4. Pseudosuchia, Saurischia, Rhynchosauridae und Schlussabschnitt. Die Fossilen Reptilien des Südamerikanischen Gondwanalandes. Ergebnisse der Sauriergrabungen in Südbrasilien 1928/29. C. H. Beck'sche Verlagsbuchhandlung, München 161-332.
- ↑ Heckert, A. B. and Lucas, S. G. (2000). Taxonomy, phylogeny, biostratigraphy, biochronology, paleobiogeography, and evolution of the Late Triassic Aetosauria (Archosauria: Crurotarsi). Zentralblatt für Geologie und Paläontologie Teil I 1998:1539–1587.
- ↑ Sereno, P. C. (2005). Desmatosuchinae. Stem Archosauria TaxonSearch [version 1.0, 2005 November 7]. Retrieved on 2009-07-18.
- ↑ Parker, W.G.; Martz, J.W. (2010). "Using positional homology in aetosaur (Archosauria: Pseudosuchia) osteoderms to evaluate the taxonomic status of Lucasuchus hunti". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 30 (4): 1100–1108. doi:10.1080/02724634.2010.483536.