Monomethyl auristatin E
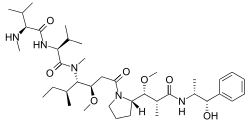 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(S)-N-((3R,4S,5S)-1-((S)-2-((1R,2R)-3-(((1S,2R)-1-hydroxy-1-phenylpropan-2-yl)amino)-1-methoxy-2-methyl-3-oxopropyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl)-3-methoxy-5-methyl-1-oxoheptan-4-yl)-N,3-dimethyl-2-((S)-3-methyl-2-(methylamino)butanamido)butanamide | |
| Other names
Monomethylauristatin E | |
| Identifiers | |
| 474645-27-7 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| Abbreviations | MMAE |
| ChemSpider | 9716967 |
| PubChem | 11542188 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C39H67N5O7 | |
| Molar mass | 717.99 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) is a synthetic antineoplastic agent. Because of its toxicity, it cannot be used as a drug itself; instead, it is linked to a monoclonal antibody (MAB) which directs it to the cancer cells. In International Nonproprietary Names for MMAE-MAB-conjugates, the name vedotin refers to MMAE plus its linking structure to the antibody.[1] It is a potent antimitotic drug derived from peptides occurring in marine shell-less mollusc Dolabella auricularia called dolastatins which show potent activity in preclinical studies, both in vitro and in vivo, against a range of lymphomas, leukemia and solid tumors. These drugs show potency of up to 200 times that of vinblastine, another antimitotic drug used for Hodgkin lymphoma as well as other types of cancer.[2]
MMAE is actually desmethyl-auristatin E; that is, the N-terminal amino group has only one methyl substituent instead of two as in auristatin E itself.[2]
Mechanism of action
Monomethyl auristatin E is an antimitotic agent which inhibits cell division by blocking the polymerisation of tubulin. The linker to the monoclonal antibody is stable in extracellular fluid, but is cleaved by cathepsin once the conjugate has entered a tumour cell, thus activating the antimitotic mechanism.[3][4]
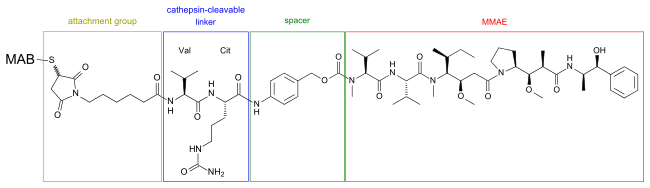 Structure of a MMAE-MAB-conjugate. The linker, consisting of the amino acids valine (Val) and citrulline (Cit), is cleaved by cathepsin inside tumour cells.[5]
Structure of a MMAE-MAB-conjugate. The linker, consisting of the amino acids valine (Val) and citrulline (Cit), is cleaved by cathepsin inside tumour cells.[5]
The spacer (paraaminobenzoic acid) is marked green, the cathepsin-cleavable linker is blue, and the attachment group (consisting of maleimide and caproic acid) is brown. The whole radical inside the four boxes is called vedotin.
Monoclonal antibodies/ADCs
MMAE has been tested with various monoclonal antibodies (usually forming an antibody-drug conjugate).
- targeting the protein CD30 which is found on malignant cells in anaplastic large cell lymphoma and Hodgkin's lymphoma:
- Brentuximab (cAC10), 3–5 units of MMAE per molecule[3][4]
- targeting the glycoprotein GPNMB which is found in aggressive melanoma, glioma, breast cancer and other tumours:
- Glembatumumab (CR011, CDX-011), investigated for the treatment of breast cancer and melanoma[6][7]
- targeting CD37:
- AGS67E, to treat lymphoid malignancy[8][9]
Examples:
- Sofituzumab vedotin
- Polatuzumab vedotin (RG7596)
- Enfortumab vedotin
- Pinatuzumab vedotin
- Lifastuzumab vedotin
- Brentuximab vedotin
- Glembatumumab vedotin
- Indusatumab vedotin (MLN-0264) in phase II trials[10]
See also
References
- ↑ Statement on a nonproprietary name adopted by the USAN Council: Vedotin
- 1 2 Dosio, F.; Brusa, P.; Cattel, L. (2011). "Immunotoxins and Anticancer Drug Conjugate Assemblies: The Role of the Linkage between Components". Toxins. 3 (12): 848. doi:10.3390/toxins3070848.
- 1 2 Seattle Genetics: Brentuximab vedotin (SGN-35)
- 1 2 Francisco, Joseph A; et al. (2003). "cAC10-vcMMAE, an anti-CD30–monomethyl auristatin E conjugate with potent and selective antitumor activity" (PDF). Blood. 102 (4): 1458–1465. doi:10.1182/blood-2003-01-0039. PMID 12714494.
- ↑ A. Klement (13 May 2013). "Sprunginnovation beim Hodgkin-Lymphom: Adcetris". Österreichische Apothekerzeitung (in German) (10/2013): 67f.
- ↑ Medical News Today: CuraGen Announces Expansion Of CR011-vcMMAE Phase II Trial In Advanced Breast Cancer
- ↑ NCI Drug Dictionary: Glembatumumab vedotin
- ↑ AGS67E, an Anti-CD37 Monomethyl Auristatin E Antibody-Drug Conjugate as a Potential Therapeutic for B/T-Cell Malignancies and AML: A New Role for CD37 in AML.
- ↑ A study of Escalating Doses of AGS67E Given as Monotherapy in Subjects With Refractory or Relapsed Lymphoid Malignancies
- ↑ Indusatumab vedotin (MLN-0264) Clinical Trials. March 2015