Biofouling


Biofouling or biological fouling is the accumulation of microorganisms, plants, algae, or animals on wetted surfaces. Such accumulation is referred to as epibiosis when the host surface is another organism and the relationship is not parasitic.
Antifouling is the ability of specifically designed materials and coatings to remove or prevent biofouling by any number of organisms on wetted surfaces.[1] Since biofouling can occur almost anywhere water is present, biofouling poses risks to a wide variety of objects such as medical devices and membranes, as well as to entire industries, such as paper manufacturing, food processing, underwater construction, and desalination plants.[2]
Specifically, the buildup of biofouling on marine vessels poses a significant problem. In some instances, the hull structure and propulsion systems can be damaged.[3] The accumulation of biofoulers on hulls can increase both the hydrodynamic volume of a vessel and the hydrodynamic friction, leading to increased drag of up to 60%.[4] The drag increase has been seen to decrease speeds by up to 10%, which can require up to a 40% increase in fuel to compensate.[5] With fuel typically comprising up to half of marine transport costs, antifouling methods are estimated to save the shipping industry around $60 billion per year.[5] Increased fuel use due to biofouling contributes to adverse environmental effects and is predicted to increase emissions of carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide between 38 and 72% by 2020.[6]
A variety of antifouling methods have historically been implemented to combat biofouling. Recently, scientists have begun researching antifouling methods inspired by living organisms. This type of design imitation is known as biomimicry.
Biology
The variety among biofouling organisms is highly diverse, and extends far beyond attachment of barnacles and seaweeds. According to some estimates, over 1700 species comprising over 4000 organisms are responsible for biofouling.[7] Biofouling is divided into microfouling — biofilm formation and bacterial adhesion — and macrofouling — attachment of larger organisms. Due to the distinct chemistry and biology that determine what prevents them from settling, organisms are also classified as hard- or soft-fouling types. Calcareous (hard) fouling organisms include barnacles, encrusting bryozoans, mollusks, polychaete and other tube worms, and zebra mussels. Examples of non-calcareous (soft) fouling organisms are seaweed, hydroids, algae and biofilm "slime".[8] Together, these organisms form a fouling community.
Ecosystem formation
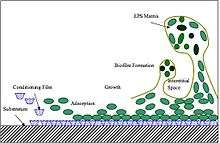
Marine fouling is typically described as following four stages of ecosystem development. The chemistry of biofilm formation describes the initial steps prior to colonization. Within the first minute the van der Waals interaction causes the submerged surface to be covered with a conditioning film of organic polymers. In the next 24 hours, this layer allows the process of bacterial adhesion to occur, with both diatoms and bacteria (e.g. vibrio alginolyticus, pseudomonas putrefaciens) attaching, initiating the formation of a biofilm. By the end of the first week, the rich nutrients and ease of attachment into the biofilm allow secondary colonizers of spores of macroalgae (e.g. enteromorpha intestinalis, ulothrix) and protozoans (e.g. vorticella, Zoothamnium sp.) to attach themselves. Within 2 to 3 weeks, the tertiary colonizers- the macrofoulers- have attached. These include tunicates, mollusks and sessile Cnidarians.[9]
Impact

Governments and industry spend more than US$5.7 billion annually to prevent and control marine biofouling. Biofouling occurs everywhere but is most significant economically to the shipping industries, since fouling on a ship's hull significantly increases drag, reducing the overall hydrodynamic performance of the vessel, and increases the fuel consumption.[10]
Biofouling is also found in almost all circumstances where water-based liquids are in contact with other materials. Industrially important impacts are on the maintenance of mariculture, membrane systems (e.g., membrane bioreactors and reverse osmosis spiral wound membranes) and cooling water cycles of large industrial equipment and power stations. Biofouling can occur in oil pipelines carrying oils with entrained water, especially those carrying used oils, cutting oils, oils rendered water-soluble through emulsification, and hydraulic oils.
Other mechanisms impacted by biofouling include microelectrochemical drug delivery devices, papermaking and pulp industry machines, underwater instruments, fire protection system piping, and sprinkler system nozzles.[2][8] In groundwater wells, biofouling buildup can limit recovery flow rates, as is the case in the exterior and interior of ocean-laying pipes where fouling is often removed with a tube cleaning process. Besides interfering with mechanisms, biofouling also occurs on the surfaces of living marine organisms, when it is known as epibiosis.
Medical devices often include fan-cooled heat sinks, to cool their electronic components. While these systems sometimes include HEPA filters to collect microbes, some pathogens do pass through these filters, collect inside the device and are eventually blown out and infect other patients. Devices used in operating rooms rarely include fans, so as to minimize the chance of transmission. Also, medical equipment, high-end computers, swimming pools, drinking-water systems and other products that utilize liquid lines run the risk of biofouling as biological growth occurs inside them.
Historically, the focus of attention has been the severe impact due to biofouling on the speed of marine vessels. In some instances the hull structure and propulsion systems can become damaged.[3] Over time, the accumulation of biofoulers on hulls increases both the hydrodynamic volume of a vessel and the frictional effects leading to increased drag of up to 60%[5] The additional drag can decrease speeds up to 10%, which can require up to a 40% increase in fuel to compensate.[5] With fuel typically comprising up to half of marine transport costs, biofouling methods are estimated to cost the shipping industry around $1 billion per year.[5] Increased fuel use due to biofouling contributes to adverse environmental effects and is predicted to increase emissions of carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide between 38 and 72 percent by 2020.[6]
Detection
Shipping companies have historically relied on scheduled biofouler removal to keep such accretions to a manageable level. However, the rate of accretion can vary widely between vessels and operating conditions, so predicting acceptable intervals between cleanings is difficult.
LED manufacturers have developed a range of UVC (250-280 nm) equipment that can detect biofouling buildup, and can even prevent it.
Fouling detection relies on the biomass' property of fluorescence. All microorganisms contain natural intracellular fluorphores, which radiate in the UV range when excited. At UV-range wavelengths, such fluorescence arises from three aromatic amino acids - tyrosine, phenylalanine, and tryptophan. The easiest to detect is tryptophan, which radiates at 280 nm when irradiated at 350 nm. (Hari Venugopalan, Photonic Frontiers: LEDs - UVC LEDs reduce marine biofouling, Laser Focus World (July 2016) pp. 28-31 )
Anti-fouling
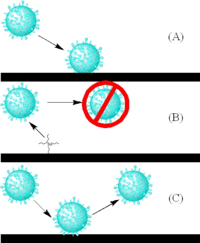
Anti-fouling is the process of removing or preventing these accumulations from forming. In industrial processes, bio-dispersants can be used to control biofouling. In less controlled environments, organisms are killed or repelled with coatings using biocides, thermal treatments, or pulses of energy. Nontoxic mechanical strategies that prevent organisms from attaching include choosing a material or coating with a slippery surface, creation of an ultra-low fouling surface with the use of zwitterions, or creation of nanoscale surface topologies similar to the skin of sharks and dolphins which only offer poor anchor points.[9]
Biocides
Biocides are chemical substances that deter the microorganisms responsible for biofouling. They are incorporated into an anti-fouling surface coating, typically through physical adsorption or through chemical modification of the surface. Biofouling occurs on surfaces after formation of a biofilm. The biofilm creates a surface onto which successively larger microorganisms can attach. In marine environments this usually concludes with barnacle attachment. The biocides often target the microorganisms which create the initial biofilm, typically bacteria. Once dead, they are unable to spread and can detach.[9] Other biocides are toxic to larger organisms in biofouling, such as the fungi and algae. The most commonly used biocide, and anti-fouling agent, is the tributyltin moiety (TBT). It is toxic to both microorganisms and larger aquatic organisms.[11] Biocides are also added to pool water, drinking water, and liquid lines for cooling electronics to control biological growth.
The prevalence of TBT and other tin-based anti-fouling coatings on marine vessels is a current environmental problem. TBT has been shown to harm many marine organisms, specifically oysters and mollusks. Extremely low concentrations of tributyltin moiety (TBT) causes defective shell growth in the oyster Crassostrea gigas (at a concentration of 20 ng/l) and development of male characteristics in female genitalia in the dog whelk Nucella lapillus (where gonocharacteristic change is initiated at 1 ng/l).[11]
Chlorine based anti-fouling solutions offer an alternative to TBT. These types of anti-fouling solutions generally involve a device attached to the end of the probe which bathes the sensors in a chlorine solution, then flushes the device and reintroduces new seawater. One such example would be Green Eyes's ProbeGuard which can be used to protect sensors during long-term submerged deployments.
The international maritime community has recognized this problem and is phasing out the use of tin-based coatings, including a ban on their use in new vessels.[12] This phase-out of toxic biocides in marine coatings is a severe problem for the shipping industry; it presents a major challenge for the producers of coatings to develop alternative technologies. Safer methods of biofouling control are actively researched.[9] Copper compounds have successfully been used in paints, heat sinks inside of medical electronics, and continue to be used as metal sheeting (for example Muntz metal which was specifically made for this purpose), though there is still debate as to the safety of copper.[13]
Non-toxic coatings
Non-toxic anti-sticking coatings prevent attachment of microorganisms thus negating the use of biocides. These coatings are usually based on organic polymers, which allow researchers to add additional functions, such as antimicrobial activity.[14]
There are two classes of non-toxic anti-fouling coatings. The most common class relies on low friction and low surface energies. This results in hydrophobic surfaces. These coatings create a smooth surface which can prevent attachment of larger microorganisms. For example, fluoropolymers and silicone coatings are commonly used.[15] These coatings are ecologically inert but have problems with mechanical strength and long-term stability. Specifically, after days biofilms (slime) can coat the surfaces which buries the chemical activity and allows microorganisms to attach.[9] The current standard for these coatings is polydimethylsiloxane, or PDMS, which consists of a non-polar backbone made of repeating units of silicon and oxygen atoms.[16] The non-polarity of PDMS allows for biomolecules to readily adsorb to its surface in order to lower interfacial energy. However, PDMS also has a low modulus of elasticity that allows for the release of fouling organisms at speeds of greater than 20 knots. The dependence of effectiveness on vessel speed prevents use of PDMS on slow-moving ships or those that spend significant amounts of time in port.[2]
The second class of non-toxic anti-fouling coatings are hydrophilic coatings. They rely on high amounts of hydration in order to increase the energetic penalty of removing water for proteins and microorganisms to attach. The most common examples of these coatings are based on highly hydrated zwitterions, such as glycine betaine and sulfobetaine. These coatings are also low-friction, but are considered by some to be superior to hydrophobic surfaces because they prevent bacteria attachment, preventing biofilm formation.[17] These coatings are not yet commercially available and are being designed as part of a larger effort by the Office of Naval Research to develop environmentally safe biomimetic ship coatings.[4]
Mussel adhesive proteins
One of the more common methods of antifouling comes from growing polymer chains from a surface, often by poly(ethylene glycol) or PEG.[18] However, challenges exist in creating a functionalized surface to which PEG chains may be grown, especially in aqueous environments. Researchers have been able to study the methods by which the common blue mussel Mytilus edulis' is able to adhere to solid surfaces in marine environments using mussel adhesive proteins, or MAPs. MAPs typically comprise several proteins, of which the most common repeating sequence is Ala-Lys-Pro-Ser-Tyr-trans-2,3-cis-3,4-dihydroxyproline (DHP) -Hyp-Thr-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA) -Lys.[19] The inclusion of the hydroxylated DHP and DOPA amino acids is thought to contribute to the adhesive nature of the MAPs. Recent studies have looked into using a short chain of DOPA residues as an adhesive end-group for antifouling PEG polymers which show promise in adsorbing onto certain metal surfaces. Increasing the number of DOPA residues to three greatly improves the total amount of adsorbed DOPA-PEG polymers and exhibits antifouling properties exceeding most other 'grafting-to' polymeric functionalization methods.[18]
The antifouling characteristics of PEG are well documented, but the service life of PEG antifouling coatings is debated due to the hydrolysis of PEG chains in air, as well as by the low concentrations of transition metal ions present in seawater.[2] Using DOPA residues as attachment points, new polymers similar in structure to the polypeptide backbone of proteins are being investigated, such as peptidomimetic polymer (PMP1). PMP1 uses a repeat unit of N-substituted glycine instead of ethylene glycol to impart antifouling properties. The N-substituted glycine is structurally similar to ethylene glycol and is hydrophilic, so easily dissolves in water. In controlled studies, PMP1-coated titanium surfaces were seen to be resistant to biofouling over a period of 180 days, even with continued addition and exposure to microfouling organisms.[18][20]
Energy methods
Pulsed laser irradiation is commonly used against diatoms. Plasma pulse technology is effective against zebra mussels and works by stunning or killing the organisms with microsecond duration energizing of the water with high voltage electricity.[8]
There are several companies that offer alternatives to paint-based antifouling, using ultrasonic transducers mounted in or around the hull of small to medium-sized boats. Research has shown these systems can help reduce fouling, by initiating bursts of ultrasonic waves through the hull medium to the surrounding water, killing or denaturing the algae and other micro-organisms that form the beginning of the fouling sequence. The systems cannot work on wooden-hulled boats, or boats with a soft-cored composite material, such as wood or foam. The systems have been loosely based on technology proven to control algae blooms.[21]
Similarly, another method shown to be effective against algae buildups bounced brief high-energy acoustic pulses down pipes.[22]
The medical industry utilizes a variety of energy methods to address bioburden issues associated with biofouling. Autoclaving typically involves heating a medical device to 121 °C (249 °F) for 15–20 minutes. Ultrasonic cleaning, UV light, and chemical wipe-down or emersion can also be used for different types of devices.
Other methods
Regimens to periodically use heat to treat exchanger equipment and pipes have been successfully used to remove mussels from power plant cooling systems using water at 105 °F (40 °C) for 30 minutes.[23]
Medical devices used in operating rooms, ICUs, isolation rooms, biological analysis labs, and other high contamination risk areas have negative pressure (constant exhaust) in the rooms, maintain strict cleaning protocols, require equipment with no fans, and often drape equipment in protective plastic.
As of 2016, researchers have shown that deep-ultraviolet UVC irradiation, a noncontact, nonchemical solution that can be used across a range of instruments. Radiation in the UVC range prevents biofilm formation by deactivating the DNA in bacteria, viruses, and other microbes. Preventing biofilm formation prevents larger organisms from attaching themselves to the instrument and eventually rendering it inoperable. (Hari Venugopalan, Photonic Frontiers: LEDs - UVC LEDs reduce marine biofouling, Laser Focus World (July 2016) pp. 28-31 )
History
Biofouling, especially of ships, has been a problem for as long as humanity has been sailing the oceans.[24] The earliest written mention of fouling was by Plutarch who recorded this explanation of its impact on ship speed: "when weeds, ooze, and filth stick upon its sides, the stroke of the ship is more obtuse and weak; and the water, coming upon this clammy matter, doth not so easily part from it; and this is the reason why they usually calk their ships."[25]
Techniques of using pitch and copper plating as anti-fouling techniques were attributed to ancient seafaring nations such as the Phoenicians and Carthaginians (1500- 300BC). Wax, tar and asphaltum have been used since early times.[24] An Aramaic record dating from 412 B.C. tells of a ship's bottom being coated with a mixture of arsenic, oil and sulphur.[26] In Deipnosophistae, Athenaeus described the anti-fouling efforts taken in the construction of the great ship of Hieron of Syracuse (died 467 BC).[27]
Before the 18th century, various anti-fouling techniques were used, with three main substances employed: "White stuff", a mixture of train oil, rosin and sulfur; "Black stuff", a mixture of tar and pitch; and "Brown stuff", which was simply sulfur added to Black stuff.[28] In many of these cases, the purpose of these treatments is ambiguous. There is dispute whether many of these treatments were actual anti-fouling techniques, or whether, when they were used in conjunction with lead and wood sheathing, they were simply intended to combat wood-boring shipworms.

In 1708, Charles Perry suggested copper sheathing explicitly as an anti-fouling device but the first experiments were not made until 1761 with the sheathing of HMS Alarm, after which the bottoms and sides of several ships' keels and false keels were sheathed with copper plates.[24]
The copper performed well in protecting the hull from invasion by worm, and in preventing the growth of weed, for when in contact with water, the copper produced a poisonous film, composed mainly of oxychloride, that deterred these marine creatures. Furthermore, as this film was slightly soluble it gradually washed away, leaving no way for marine life to attach themselves to the ship. From about 1770, the Royal Navy set about coppering the bottoms of the entire fleet and continued to the end of the use of wooden ships. The process was so successful that the term copper-bottomed came to mean something that was highly dependable or risk free.
With the rise of iron hulls in the 19th century, copper sheathing could no longer be used due to its galvanic corrosive interaction with iron. Anti-fouling paints were tried, and in 1860, the first practical paint to gain widespread use was introduced in Liverpool and was referred to as "McIness" hot plastic paint.[24] These treatments had a short service life, were expensive, and relatively ineffective by modern standards.[9]
By the mid-twentieth century, copper oxide-based paints could keep a ship out of drydock for as much as 18 months, or as little as 12 in tropical waters.[24] The shorter service life was due to rapid leeching of the toxicant, and chemical conversion into less toxic salts which accumulated as a crust which would inhibit further leaching of active cuprous oxide from the layer under the crust.[29]
The 1960s brought a breakthrough, with self-polishing paints which used seawater's ability to hydrolize the paint's copolymer bond and release the stored toxin at a slow, controlled rate. These paints employed organotin chemistry ("tin-based") biotoxins such as tributyltin oxide (TBT) and were effective for up to 4 years. The discovery that these biotoxins have severe impact on mariculture, with biological effects to marine life at a concentration of 1 nanogram per liter, led to their worldwide ban by the International Maritime Organization in October 2001.[30][31] TBT in particular has been described as the most toxic pollutant ever deliberately released in the ocean.[11]
As an alternative to organotin toxins, there has been renewed interest in copper as the active agent in ablative or self polishing paints, with reported service lives up to 5 years. Modern adhesives permit application of copper alloys to steel hulls without creating galvanic corrosion. However, copper alone is not impervious to diatom and algae fouling. Some studies indicate that copper may also present an unacceptable environmental impact.[32]
Research
Modern empirical study of biofouling began in the early 19th century with Davy's experiments linking the effectiveness of copper to its solute rate.[24] Insights into the stages of formation grew in the 1930s when the microbiologist Claude ZoBell defined the sequence of events initiating the fouling of submerged surfaces. He showed that the attachment of organisms must be preceded by the adsorption of organic compounds now referred to as extracellular polymeric substances.[33][34]
One trend of research is the study of the relationship between wettability and anti-fouling effectiveness. Another trend is the study of living organisms as the inspiration for new functional materials. An example of biomimetic antifouling research was conducted at the University of Florida into how marine animals such as dolphins and sharks are able to effectively deter biofouling on their skin. Researchers examined the nanoscale structure of sharks and designed an anti-fouling surface known commercially as Sharklet. Studies show that the nanoscale topologies function not only due to the reduction of sites for macrofoulers to attach, but also due to the same thermodynamic barrier that any surface with low wettability presents.[35]
Materials research into superior antifouling surfaces for fluidized bed reactors suggest that low wettability plastics such as Polyvinyl chloride ("PVC"), high-density polyethylene and polymethylmethacrylate ("plexiglas") demonstrate a high correlation between their resistance to bacterial adhesion and their hydrophobicity.[36]
Study of the biotoxins used by organisms has revealed several effective compounds, some of which are more powerful than synthetic compounds. Bufalin, a bufotoxin, was found to be over 100 times more potent than TBT, and over 6000 times more effective in anti-settlement activity against barnacles.[37]
See also
- Fouling
- Biomimetic Antifouling Coatings
- Tributyltin
- Bottom paint
- Keelhauling - Form of punishment at sea that involved 'hauling' an offender underneath the hull of a vessel, scraping them against the growths.
References
- ↑ Yebra, D.M.; Kiil, S.; Johansen, K.D. (2004). "Antifouling technology-past,present and future steps toward efficient and environmentally friendly antifouling coatings". Progress in Organic Coatings. 50 (2): 75–104. doi:10.1016/j.porgcoat.2003.06.001.
- 1 2 3 4 Vladkova, T. (2009), "Surface Modification Approach to Control Biofouling", Marine and Industrial Biofouling, Springer Series on Biofilms, 4 (1): 135–163, doi:10.1007/978-3-540-69796-1_7, ISBN 978-3-540-69794-7, retrieved 2 June 2011
- 1 2 L.D. Chambers; et al. (2006). "Modern approaches to marine antifouling coatings". Surface and Coatings Technology. 6 (4): 3642–3652. doi:10.1016/j.surfcoat.2006.08.129. Retrieved 25 May 2011.
- 1 2 Vietti, Peter (4 June 2009), New hull coatings for Navy ships cut fuel use, protect environment, Office of Naval Research, retrieved 21 May 2012
- 1 2 3 4 5 Vietti, P. (Fall 2009). "New Hull Coatings Cut Fuel Use, Protect Environment" (PDF). Currents: 36–38. Retrieved 6 June 2011.
- 1 2 Salta, M.; et al. (2008). "Designing biomimetic antifouling surfaces". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society. 368 (1929): 4729–4754. doi:10.1098/rsta.2010.0195. Retrieved 25 May 2011.
- ↑ Almeida, E; Diamantino, Teresa C.; De Sousa, Orlando (2007), "Marine paints: The particular case of antifouling paints", Progress in Organic Coatings, 59 (1): 2–20, doi:10.1016/j.porgcoat.2007.01.017, retrieved 6 June 2011
- 1 2 3 Stanczak, Marianne (March 2004), Biofouling: It's Not Just Barnacles Anymore, ProQuest, retrieved 21 May 2012
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Yebra, Diego Meseguer; Kiil, Soren; Dam-Johansen, Kim (July 2004), "Antifouling technology--past, present and future steps towards efficient and environmentally friendly antifouling coatings", Progress in Organic Coatings, 50 (2): 75–104, doi:10.1016/j.porgcoat.2003.06.001, ISSN 0300-9440
- ↑ Woods Hole Oceanographic Institute (1952), "The Effects of Fouling", Marine Fouling and its Prevention (PDF), United States department of the Navy, Bureau of Ships
- 1 2 3 Evans, S.M.; Leksono, T.; McKinnell, P.D. (January 1995), "Tributyltin pollution: A diminishing problem following legislation limiting the use of TBT-based anti-fouling paints", Marine Pollution Bulletin, 30 (1): 14–21, doi:10.1016/0025-326X(94)00181-8, ISSN 0025-326X
- ↑ M.A. Champ, Published in the Proceedings of the 24th UJNR (US/Japan) Marine Facilities Panel Meeting in Hawaii, 7-8 November 2001.
- ↑ Greenwood, Bob (19 November 2006), "Antifouling - Copper not so bad after all?", Sailing World, retrieved 21 May 2012
- ↑ Gang Cheng; et al. (2 June 2010), "Integrated Antimicrobial and Nonfouling Hydrogelsto Inhibit the Growth of Planktonic Bacterial Cells and Keep the Surface Clean", Langmuir, 26 (13): 10425–10428, doi:10.1021/la101542m
- ↑ Brady, R.F. (1 January 2000), "Clean Hulls Without Poisons: Devising and Testing Nontoxic Marine Coatings", Journal of Coatings Technology, 72 (900): 44–56, retrieved 22 May 2012
- ↑ Krishnan, S; Weinman, Craig J.; Ober, Christopher K. (2008), "Advances in polymers for anti-biofouling surfaces", Journal of Materials Chemistry, 12 (29): 3405–3413, doi:10.1039/B801491D, retrieved 6 June 2011
- ↑ Jiang, S.; Cao, Z. (2010), "Ultralow-Fouling, Functionalizable, and Hydrolyzable Zwitterionic Materials and Their Derivatives for Biological Applications", Advanced Materials, 22 (9): 920–932, doi:10.1002/adma.200901407, PMID 20217815
- 1 2 3 Dalsin, J.; Messersmith, P. (2005). "Bioinspired antifouling polymers". Materials Today. 8 (9): 38–46. doi:10.1016/S1369-7021(05)71079-8. Retrieved 25 May 2011.
- ↑ Taylor, S.; et al. (1994). "trans-2,3-cis-3,4-Dihydroxyproline, a New Naturally Occurring Amino Acid, Is the Sixth Residue in the Tandemly Repeated Consensus Decapeptides of an Adhesive Protein from Mytilus edulis". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 116 (23): 10803–10804. doi:10.1021/ja00102a063.
- ↑ Statz, A.; et al. (2005). "New Peptidomimetic Polymers for Antifouling Surfaces". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127 (22): 7972–7973. doi:10.1021/ja0522534. PMID 15926795.
- ↑ "Ultrasonic irradiation for blue-green algae bloom control". PubMed.gov.
- ↑ Walch, M.; Mazzola, M.; Grothaus, M. (2000), Feasibility Demonstration of a Pulsed Acoustic Device for Inhibition of Biofouling in Seawater Piping (pdf), Bethesda, MD: Naval Surface Warfare Center Carderock Div., NSWCCD-TR-2000/04, retrieved 21 May 2012
- ↑ Sommerville, David C. (September 1986), "Development of a Site Specific Biofouling Control Program for the Diablo Canyon Power Plant", Oceans 86 Proceedings, IEEE Conference Publications, pp. 227–231, doi:10.1109/OCEANS.1986.1160543
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Woods Hole Oceanographic Institute (1952), "The History and Prevention of Foulng", Marine Fouling and its Prevention (PDF), United States department of the Navy, Bureau of Ships
- ↑ Plutarch, "Essays and Miscellanies", The Complete Works of Plutarch, Volume 3
- ↑ Culver, Henry E.; Grant, Gordon, The Book of Old Ships, Dover Publications, ISBN 978-0486273327
- ↑ Athenaeus of Naucratis, The deipnosophists, or, Banquet of the learned of Athenæus, Volume I, Book V, Chapter 40 ff.
- ↑ Lavery, Brian (2000), The Arming and Fitting of English Ships of War 1600-1815, Conway Maritime Press, ISBN 0-85177-451-2
- ↑ Dowd, Theodore (1983), An Assessment of Ablative Organotin Antifouling (AF) Coatings, US Navy, ADA134019], retrieved 22 May 2012
- ↑ Focus on IMO - Anti-fouling systems (PDF), International Maritime Organisation, 2002, retrieved 22 May 2012
- ↑ Gajda, M.; Jancso, A. (2010), "Organotins, formation, use, speciation and toxicology", Metal ions in life sciences, Cambridge: RSC publishing, 7, Organometallics in environment and toxicology, ISBN 9781847551771
- ↑ Swain, Geoffrey (September 1999), Redefining Antifouling Coatings (PDF), 16 (9), Steel Structures Painting Council, pp. 26–35, ISSN 8755-1985, retrieved 23 May 2012
- ↑ Shor, Elizabeth Noble (1978), Scripps Institution of Oceanography: Probing the Oceans 1936 to 1976, San Diego, Calif: Tofua Press, p. 225, retrieved 21 May 2012
- ↑ Lappin-Scott, Hilary M., "Claude E. Zobell – his life and contributions to biofilm microbiology", Microbial Biosystems: New Frontiers, Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Microbial Ecology (PDF), Halifax, Canada: Society for Microbial Ecology, ISBN 9780968676332, retrieved 23 May 2012
- ↑ M.L. Carman; et al. (2006), "Engineered antifouling microtopographies – correlating wettability with cell attachment" (PDF), Biofouling, 22 (1–2): 11–21, doi:10.1080/08927010500484854, PMID 16551557, retrieved 21 May 2012
- ↑ R. Oliveira; et al., "Hydrophobicity in Bacterial Adhesion", Biofilm community interactions: chance or necessity? (PDF), BioLine, ISBN 978-0952043294
- ↑ Omae, Iwao (2003), "General Aspects of Tin-Free Antifouling Paints" (PDF), Chemical Reviews, American Chemical Society, 103 (9): 3431–3448, doi:10.1021/cr030669z, retrieved 23 May 2012
Further reading
- Bio-Inspired Antifouling Strategies, doi:10.1146/annurev-matsci-070511-155012