Mary Richardson
| Mary Richardson | |
|---|---|
 Mary Richardson, circa 1913 | |
| Born | 1882/3 |
| Died | 7 November 1961 |
| Nationality | British |
| Occupation | Journalist |
| Known for | Slashing the Rokeby Venus |
Mary Raleigh Richardson (1882/3 – 7 November 1961) was a Canadian suffragette active in the women's suffrage movement in the United Kingdom, an arsonist and later the head of the women's section of the British Union of Fascists (BUF) led by Sir Oswald Mosley.
Life
She grew up in Belleville, Ontario, Canada. In 1898, she travelled to Paris and Italy. She lived in Bloomsbury, and witnessed Black Friday.[1]
Militant actions
At the beginning of the 20th century, the suffragette movement, frustrated by a failure to achieve equal voting rights for women, began adopting increasingly militant tactics. In particular, the Women's Social and Political Union (WSPU), led by the charismatic Emmeline Pankhurst, frequently endorsed the use of property destruction to bring attention to the issue of women's suffrage. Richardson was a devoted supporter of Pankhurst and a member of the WSPU.
Richardson claimed to be at the Epsom races on Derby Day, 4 June 1913, when Emily Davison jumped in front of the King's horse. Emily Davison died in Epsom Cottage Hospital; Mary Richardson was reportedly chased and beaten by an angry mob but was given refuge in Epsom Downs station by a railway porter.[2]
She committed a number of acts of arson, smashed windows at the Home Office and bombed a railway station. She was arrested nine times, receiving prison terms totalling more than three years.[3][4] She was one of the first two women force-fed under the 1913 Cat and Mouse Act in HM Prison Holloway.[5]
Slashing the Rokeby Venus
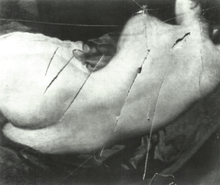
Richardson's most famous act of defiance occurred on 10 March 1914 when she entered the National Gallery in London and slashed the Rokeby Venus with a chopper she smuggled into the gallery.[7]
She wrote a brief statement explaining her actions to the WSPU which was immediately printed by the press:[8]
"I have tried to destroy the picture of the most beautiful woman in mythological history as a protest against the Government for destroying Mrs Pankhurst, who is the most beautiful character in modern history. Justice is an element of beauty as much as colour and outline on canvas. Mrs Pankhurst seeks to procure justice for womanhood, and for this she is being slowly murdered by a Government of Iscariot politicians. If there is an outcry against my deed, let every one remember that such an outcry is an hypocrisy so long as they allow the destruction of Mrs Pankhurst and other beautiful living women, and that until the public cease to countenance human destruction the stones cast against me for the destruction of this picture are each an evidence against them of artistic as well as moral and political humbug and hypocrisy."[9]
As a Fascist
In 1932, after forming the belief that fascism was the "only path to a 'Greater Britain'", Richardson joined the British Union of Fascists (BUF), led by Oswald Mosley. Despite the apparent contradiction inherent in a suffragette supporting a totalitarian form of government, she claimed that, "I was first attracted to the Blackshirts because I saw in them the courage, the action, the loyalty, the gift of service and the ability to serve which I had known in the suffragette movement".[10] Richardson rose quickly through the BUF ranks and by 1934 was Chief Organiser for the Women's Section of the party. She left within two years after becoming disillusioned with the sincerity of its policy on women.[11]
Two other prominent suffragette leaders to gain high office in the BUF were Norah Elam[12] and Commandant Mary Sophia Allen.[13]
Later life
Richardson published her autobiography, Laugh a Defiance, in 1953. She died at her flat in Hastings on 7 November 1961.[1]
See also
Notes
- 1 2 Kean 2004.
- ↑ Hastings PressGoogle Books
- ↑ English Women's History
- ↑ Feminine fascism: women in Britain's fascist movement – Julie V. Gottlieb – Google Books
- ↑ Mary Richardson suffragette, socialist, fascist, Hilda Kean
- ↑ Potterton, Homan. The National Gallery. London: Thames and Hudson, 1977. 15
- ↑ BBC Radio 4 – Woman's Hour – Women's History Timeline: 1910 – 1919
- ↑ Gamboni, The Destruction of Art, p. 94.
- ↑ "Miss Richardson's Statement". The Times. 11 March 1914.
- ↑ Gottlieb, op cit at 164
- ↑ McCouat, P, "From Rokeby Venus to Fascism", Journal of Art in Society,
- ↑ McPherson, Angela; McPherson, Susan (2011). Mosley's Old Suffragette – A Biography of Norah Elam. ISBN 978-1-4466-9967-6.
- ↑ Boyd, N, From Suffragette to Fascist, The History Press, 2013
References
- Kean, Hilda. "Richardson, Mary Raleigh (1882/3–1961)". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography (online ed.). Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/56251. (Subscription or UK public library membership required.)
Bibliography
- Gamboni, Dario. The Destruction of Art: Iconoclasm and Vandalism since the French Revolution. Reaktion Books – Picturing History, 2007. ISBN 1-86189-316-7
- Nead, Lynda. The Female Nude: Art, Obscenity, and Sexuality. Routledge, 1992. ISBN 0-415-02677-6
- Prater, Andreas. Venus at Her Mirror: Velázquez and the Art of Nude Painting. Prestel, 2002. ISBN 3-7913-2783-6