Monolinuron
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
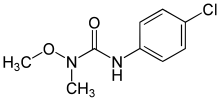
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-(4-Chlorophenyl)-1-methoxy-1-methylurea | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
1-(4-Chlorophenyl)-3-methoxy-3-methylurea | |
| Other names
N′-(4-Chlorophenyl)-N-methoxy-N-methylurea | |
| Identifiers | |
| 1746-81-2 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| 2212523 | |
| ChemSpider | 14868 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.015.572 |
| EC Number | 217-129-5 |
| KEGG | C18794 |
| MeSH | Monolinuron |
| PubChem | 15629 |
| RTECS number | YS6425000 |
| UNII | 6KJJ4XAD6M |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H11ClN2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 214.65 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 80 to 83 °C (176 to 181 °F; 353 to 356 K) |
| 0.735 g/L | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Monolinuron is a pesticide,[1] more specifically a selective systemic herbicide[2] and an algaecide.[3] As an herbicide, it is used to control broad-leaved weeds and annual grasses in vegetable crops such as leeks, potatoes,[2] and dwarf French beans.[4] Monolinuron affects the photosynthesis in weeds. Following uptake of monolinuron through roots and leaves of weeds, monolinuron causes early symptoms of yellowing and die-back of the leaves, eventually resulting in weed death.[4] In fishkeeping it is used to control blanketweed and hair algae.[3]
References
- ↑ Rossoff; Irving S. (2002). Encyclopedia of clinical toxicology. p. 718.
- 1 2 Milne; George W. A. (2005). Gardner's commercially important chemicals. p. 44.
- 1 2 "Pesticides: HSE registered products". Retrieved 2009-07-31.
- 1 2 "Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs, Evaluation of Fully Approved or Provisionally Approved Products, Evaluation on: Monolinuron, May 1995" (PDF). Retrieved 2011-08-19.
External links
- Monolinuron - Identification, toxicity, use, water pollution potential, ecological toxicity and regulatory information
- Monolinuron at the Compendium of Pesticide Common Names
- Monolinuron in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/22/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.