Nested polymerase chain reaction
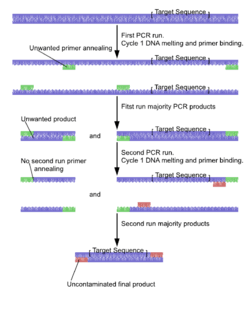
Nested polymerase chain reaction (Nested PCR) is a modification of polymerase chain reaction intended to reduce non-specific binding in products due to the amplification of unexpected primer binding sites.
Polymerase chain reaction itself is the process used to amplify DNA samples, via a temperature-mediated DNA polymerase. The products can be used for sequencing or analysis, and this process is a key part of many genetics research laboratories, along with uses in DNA fingerprinting for forensics and other human genetic cases. Conventional PCR requires primers complementary to the termini of the target DNA. A commonly occurring problem is primers binding to incorrect regions of the DNA, giving unexpected products.
Nested polymerase chain reaction involves two sets of primers, used in two successive runs of polymerase chain reaction, the second set intended to amplify a secondary target within the first run product.
Processes
- The target DNA undergoes the first run of polymerase chain reaction with the first set of primers, shown in green. The selection of alternative and similar primer binding sites gives a selection of products, only one containing the intended sequence.
- The product from the first reaction undergoes a second run with the second set of primers, shown in red. It is very unlikely that any of the unwanted PCR products contain binding sites for both the new primers, ensuring the product from the second PCR has little contamination from unwanted products of primer dimers, hairpins, and alternative primer target sequences.
Resources
Books at your local library about nested polymerase chain reactions
Scholarly articles on nested polymerase chain reactions