Object hyperlinking
Object hyperlinking, or simply 'phylinking', is a neologism that usually refers to extending the Internet to objects and locations in the real world. The current Internet does not extend beyond the electronic realm. Object hyperlinking aims to extend the Internet to the physical world by attaching tags with URLs to tangible objects or locations. These object tags can then be read by a wireless mobile device and information about objects and locations retrieved and displayed.
However, object hyperlinking may also be senseable for contexts other than the Internet (e.g. with data objects in data base administering or with text content management).
System components
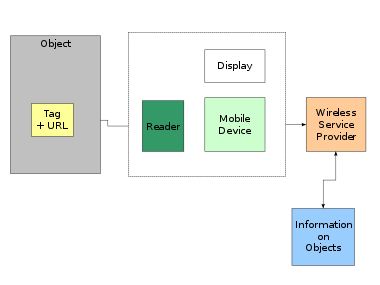
Linking an object or a location to the Internet is a more involved process than linking two web pages. An object hyperlinking system requires seven components:
- A virtual or physical object tag to identify objects and locations. Some tagging systems are described below. To allow the object tags to be located they must be physically embedded in visual markers. For example, the Yellow arrow scheme [see below] prints SMS tags on large adhesive yellow arrows, which can then be stuck on buildings etc.
- A means of reading physical tags, or locating virtual tags.
- A mobile device such as a mobile telephone, a PDA or a portable computer.
- Additional software for the mobile device.
- A commonly open wireless network, such as the existing 2G and 3G networks, for communication between the portable device and the server containing the information linked to the tagged object.
- Information on each linked object. This information could be in existing WWW pages, existing databases of price information etc., or have been specially created.
- A display to view the information on the linked object. At the present time this is most likely to be the screen of a mobile telephone.
Tags and tag readings systems
There are a number of different competing tagging systems.
- RFID tags
- A radio frequency identification device (also known as an 'Arphid') is a small transponder which can be read at short range by a transceiver (reader). Since RFID tags can be very small, they are often embedded in a more visible marker to allow them to be located.
- A RFID reader can be added to an existing mobile telephone as a shell. Nokia produce such a shell for their 3220 mobile phone. More and more mobile phones have RFID/NFC capability, since such RFID/NFC enabled mobiles may be used for cashless payments and other purposes.
- Since 2005 travelers in the city of Hanau, near Frankfurt, Germany have been able to pay for bus tickets by passing their Nokia phones over a smartcard reader installed on the buses. Other applications for RFID enabled mobiles include swapping electronic business cards between phones, and using a mobile to check in at an airport or hotel. Two RFID enabled devices may also be used to enable peer-to-peer transfer of data such as music, images or for synchronizing address books.

- Graphical tags
- A graphical tag consists of an image on a marker, which can be read by a mobile telephone camera. There are a number of competing systems, including open standards like Quick Response QR Codes, Datamatrix, Semacodes[1] (based on Datamatrix), and barcodes; or proprietary systems like ShotCodes. The design of such coding schemes needs to be rich enough to include lots of information and robust enough for the tag to be readable, even when partly obscured or damaged: tags might be on the outside of buildings and exposed to wear and the weather.
- Graphical tags have a number of advantages. They are easy to understand and cheap to produce. They can also be printed on almost anything, including t-shirts. Barcodes are a particularly attractive form of tagging because they are already very widely used, and camera phones can easily read them.
- SMS tags
- An SMS tag comprises a short alphanumerical code, which can be printed on a marker or chalked on a wall. The Short Message Service is then used to send the code and return a message. Yellow arrows[2] are an example of this form of tagging.
- Virtual tags
- In a virtual tagging system there is no physical tag at a location. Instead a URL as a meta-object is associated with a set of geographical coordinates. Using location-based services a mobile phone that enters a particular area can be used to retrieve all URLs associated with that area. The area can be set as a few metres or a much wider area.
- Hardlink
- A hardlink is an alphanumeric combination such as an object's common name or part number that when entered into a cell phone's web browser, targeting a hardlink database, returns information that may have been stored about the target object.
Applications for object hyperlinking
The object hyperlinking systems described above will make it possible to link comprehensive and editable information to any object or location. How this capability can best be used remains to be seen. What has emerged so far is a mixture of social and commercial applications.
- The publishers of the Lonely Planet guidebooks are issuing yellow arrows with one of their guidebooks and encouraging travellers to leave tags to stories and comments wherever they go.
- Siemens see their virtual tagging system being used to tag tourist sites, and also leave messages for friends. They also suggest that virtual tags could be used to link advertisements with locations.[3]
- Nokia have demonstrated that when a 3220 phone with the RFID shell attached is tapped against an RFID-enabled advertisement, a URL can be read and information about the advertised product or service returned to the phone.
- Japanese consumers are able to read barcodes with their mobiles and download comparative prices from Amazon.[4]

- Semapedia have created a system for linking physical objects and Wikipedia articles using the Semacode tagging scheme. Graphical tags can be created that link to the URLs of individual Wikipedia articles. These tags can then be attached to the physical objects mentioned in the Wikipedia articles. Reading a tag with a camera phone will then retrieve an article from Wikipedia and display it on the phone screen, creating a "Mobile Wikipedia".[5][6]
- An alternative to using 2d barcodes is to apply computer vision techniques to identify more complex patterns and images. Companies like kooaba, Daem, or Neven Vision (acquired by Google in 2006)[7] develop image recognition platforms to turn any image into object hyperlinks.
- Microsoft has developed a system for creating hyperlinks using image matching.[8]
- Google is now planning to tag 100,000 businesses in the United States with QR codes.[9]
See also
- Ambient intelligence
- Barcode
- QR Code
- Datamatrix
- Semacode
- Thinglink
- CueCat
- Near Field Communication
- Mobile tagging
- Linked Data
- Hyperdata
- Semantic Web
- SPARQCode
- Internet of Things
- Location-based service
Notes
- ↑ Wired article on semacodes
- ↑ Washington Post article on Yellow Arrow scheme
- ↑ "Digital Graffitti Service". Munich. Feb 2, 2005. Archived from the original on Feb 24, 2006.
- ↑ Longino, Carlo (Nov 23, 2004). "Amazon Heads Off Barcode Comparison Shoppers".
- ↑ http://www.mobile-weblog.com/archives/a_manifesto_for_taking_wikipedia_into_the_physical_world.html
- ↑ http://addiator.blogspot.com/2005/06/mobile-wikipedia.html
- ↑ Google, Neven Vision & Image Recognition
- ↑ Greene, Kate (March 13, 2007). "Mobile Web Searches Using Pictures". MIT Technology Review.
- ↑ Codes on Places: A discussion of links between material place and virtual information
External links
- A video on creating and using 2D barcodes
- Christian Science Monitor article on object linking
- Internet of things: working bibliography
- Tokyo Ubiquitous Technology Project
- New Bar Codes Can Talk With Your Cellphone
- First Visual Search Engine from kooaba
- Video demonstration of object hyperlinking using mobile phone (mobile visual search)