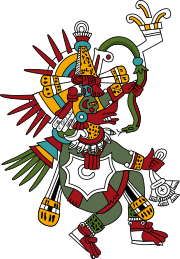
Tonatiuh
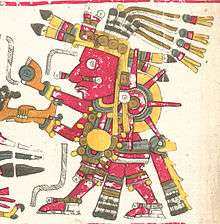
In Aztec mythology, Tonatiuh (Nahuatl: Ōllin Tōnatiuh [oːlːin toːˈnatiʍ] "Movement of the Sun") was the sun god.[1] The Aztec people considered him the leader of Tollan, heaven. He was also known as the fifth sun, because the Aztecs believed that he was the sun that took over when the fourth sun was expelled from the sky.
Description
Aztec theology held that each sun was a god with its own cosmic era, the Aztecs believed they were still in Tonatiuh's era. According to the Aztec creation myth, the god demanded human sacrifice as tribute and without it would refuse to move through the sky. It is said that 20,000 people were sacrificed each year to Tonatiuh and other gods, though this number is thought to be inflated either by the Aztecs, who wanted to inspire fear in their enemies, or the Spaniards, who wanted to vilify the Aztecs. The Aztecs were fascinated by the sun and carefully observed it, and had a solar calendar similar to that of the Maya. Many of today's remaining Aztec monuments have structures aligned with the sun.
In the Aztec calendar, Tonatiuh is the lord of the thirteen days from 1 Death to 13 Flint. The preceding thirteen days are ruled over by Chalchiuhtlicue, and the following thirteen by Tlaloc.
See also
References
- ↑ Bingham, Ann (2004). South and Meso-American mythology A to Z. Infobase Publishing. p. 112. ISBN 0-8160-4889-4.