Opus isodomum
.jpg)
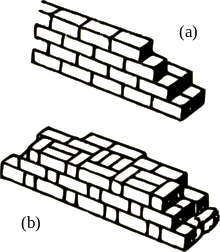
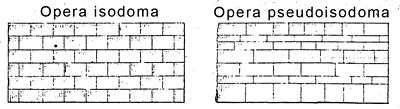
Opus isodomum is an ancient technique of wall construction with ashlars. It uses perfectly cut, completely regular square stone blocks of equal height, and sometimes of the same length.
In classical antiquity this technique was perfected and widely used, especially for public buildings (temples, theaters, amphitheaters etc.). One of the most well-known examples is the Parthenon.[1]
Vitruvius briefly described this technique in his De Architectura, 2nd book, 8th chapter as following: A wall is called “isodomum“ when all the courses are of equal height.
Vitruvius further states that the stone blocks of opus isodomum are bound together by mortar, but more often they are not connected with mortar but with metal ties such as iron cramps, fixed in stone blocks with molten lead.
Completely regular isodomum is relatively rare, especially in the provinces. More frequent is isodomum made of stone blocks of the same height but not of the same length. In order to strengthen this type of wall, builders always take good care that the ends of stone blocks in alternating courses of the wall do not match.[2]
Opus pseudoisodomum is a version of opus isodomum mentioned by Vitruvius, describing that it is a kind of stonemasonery in which "the rows of courses do not match but run unequally", referring to the height and length of the blocks, which are nevertheless still perfectly cut.
Vitruvius considered both types of wall construction as Greek, emphasizing that "both kinds are strong".[3]
Footnotes
Bibliography
- Vitruvius 1990 - Marcus Vitruvius Pollio: Deset knjiga o arhitekturi, translated by Matija Lopac, Sarajevo, 1990, p. 41-46
- Müller / Vogel 1999 - Werner Müller; Gunther Vogel: Atlas arhitekture 1, translated by Milan Pelc, Zagreb, 1999., p. 3, 31, 60, 61
- Suić 1976 - Mate Suić: Antički grad na istočnom Jadranu, Zagreb, 1976, p. 108, 110