Oscillatoria
| Oscillatoria | |
|---|---|
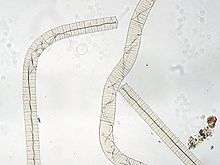 | |
| Oscillatoria princeps | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Bacteria |
| Phylum: | Cyanobacteria |
| Class: | Cyanophyceae |
| Order: | Nostocales |
| Family: | Oscillatoriaceae |
| Genus: | Oscillatoria Vaucher ex Gomont, 1822 |
| Type species | |
| Oscillatoria princeps Vaucher ex Gomont | |
Oscillatoria is a genus of filamentous cyanobacterium which is named after the oscillation in its movement. Filaments in the colonies can slide back and forth against each other until the whole mass is reoriented to its light source. It is commonly found in watering-troughs waters, and is mainly blue-green or brown-green. Oscillatoria is an organism that reproduces by fragmentation. Oscillatoria forms long filaments of cells which can break into fragments called hormogonia. The hormogonia can grow into a new, longer filament. Breaks in the filament usually occur where dead cells (necridia) are present. Oscillatoria uses photosynthesis to survive and reproduce. Each filament of oscillatoria consists of trichome which is made up of rows of cells. The tip of the trichome oscillates like a pendulum.
Oscillatoria sp. is the subject of research into the natural production of butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT),[1] an antioxidant, food additive and industrial chemical.
Oscillatoria contains the following species:[2]
- Oscillatoria amoena (Kützing) Gomont
- Oscillatoria anguiformis (P. González Guerrero) Anagnostidis
- Oscillatoria anguina Bory ex Gomont
- Oscillatoria annae van Goor
- Oscillatoria bonnemaisonii (P. L. Crouan & H. M. Crouan) P. L. Crouan & H. M. Crouan ex Gomont
- Ocillatoria chalybea
- Oscillatoria chilkensis Biswas
- Oscillatoria crassa (Rao) Anagnostidis
- Oscillatoria croasdaleae Kamat
- Oscillatoria curviceps C. Agardh ex Gomont
- Oscillatoria depauperata (Copeland) Anagnostidis
- Oscillatoria engelmanniana Gaidukov
- Oscillatoria euboeica Anagnostidis
- Oscillatoria fischeri Corda ex Forti
- Oscillatoria fracta Carlson
- Oscillatoria froelichii Kützing ex Gomont
- Oscillatoria funiformis (Vouk) Komárek
- Oscillatoria indica P. C. Silva
- Oscillatoria jenensis G. Schmid
- Oscillatoria levis (Gardner) Anagnostidis
- Oscillatoria limosa C. Agardh ex Gomont
- Oscillatoria mahabaleshwarensis Kamat
- Oscillatoria major Vaucher ex Hansgirg
- Oscillatoria margaritifera Kützing ex Gomont
- Oscillatoria miniata (Zanardini) Hauck ex Gomont
- Oscillatoria minutissima P. González
- Oscillatoria muralis (Dillwyn) C. Agardh
- Oscillatoria nitida Schkorbatov
- Oscillatoria nylstromica Claassen
- Oscillatoria obscura Brühl & Biswas
- Oscillatoria olivaceobrunnea L. Hoffmann & V. Demoulin
- Oscillatoria princeps Vaucher ex Gomont
- Oscillatoria proboscidea Gomont
- Oscillatoria pulchra Lindstedt
- Oscillatoria rhamphoidea Anagnostidis
- Oscillatoria ribeyi F. E. Drouet
- Oscillatoria sancta Kützing ex Gomont
- Oscillatoria subbrevis Schmidle
- Oscillatoria subcapitata Ponomarev
- Oscillatoria tapetiformis Zenker ex Gomont
- Oscillatoria tenioides (Bory de Saint-Vincent) Bory de Saint-Vincent ex Gomont
- Oscillatoria trichoides Szafer
- Oscillatoria versicolor G. Martens ex Prain
- Oscillatoria willei
References
- ↑ Babu B, Wu JT (December 2008). "Production of Natural Butylated Hydroxytoluene as an Antioxidant by Freshwater Phytoplankton" (PDF). Journal of Phycology. 44 (6): 1447–1454. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8817.2008.00596.x.
- ↑ M. D. Guiry. "Oscillatoria Vaucher ex Gomont, 1892: 198". AlgaeBase. Retrieved March 8, 2011.