Ottis Toole
| Ottis Toole | |
|---|---|
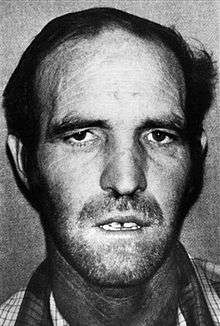 Toole's 1983 mugshot | |
| Born |
Ottis Elwood Toole March 5, 1947 Jacksonville, Florida, U.S. |
| Died |
September 15, 1996 (aged 49) Raiford, Florida, U.S. |
| Cause of death | Cirrhosis |
| Resting place | Florida State Prison Cemetery |
| Nationality | American |
| Criminal charge | Arson, First-degree murder |
| Criminal penalty | Death commuted to life in prison |
| Criminal status | Deceased |
| Killings | |
| Victims | 6 or more |
Span of killings | Unknown–1983 |
| Country | United States |
| State(s) | Florida and Texas |
Date apprehended | April 1983 |
| Imprisoned at | Florida State Prison |
Ottis Elwood Toole (March 5, 1947 – September 15, 1996) was an American drifter who was convicted of six counts of murder. Like his companion Henry Lee Lucas, Toole made confessions he later recanted, but which resulted in murder convictions. The discrediting of the case against Lucas for crimes in which Toole had offered corroborating statements created doubts as to whether either was a genuine serial killer or, as Hugh Aynesworth suggested, both were merely compliant interviewees whom police used to clear unsolved murders from the books. Toole received two death sentences, but on appeal they were commuted to life imprisonment. He died in his cell from cirrhosis, aged 49. Police attributed the murder of Adam Walsh to Toole on the basis of recanted statements. Lucas had backed Toole's confession to the Walsh murder, claiming he had been in possession of the victim's severed head.
Early life
Ottis Elwood Toole (sometimes misspelled "Otis") was born and raised in Jacksonville, Florida. Toole's mother was abusive; Toole claimed she would dress him in girls' clothing and call him Susan.[1] His father was an alcoholic who abandoned him.[1] Ottis claimed that as a young child, he was a victim of sexual assault and incest at the hands of many close relatives and acquaintances, including his older sister and next door neighbor. He claimed that his maternal grandmother was a Satanist, who exposed him to various Satanic practices and rituals in his youth, including self-mutilation and graverobbing and dubbed him "Devil's Child." Toole claimed this abuse began when he came out as gay to his family.[1]
He was often designated as suffering from mild mental retardation, with an I.Q. of 75.[1] He also suffered from epilepsy, which resulted in frequent grand mal seizures. Throughout his childhood, he frequently ran away from home and often slept in abandoned houses. He was a serial arsonist from a young age and was sexually aroused by fire.[1]
In the documentary Death Diploma, Toole claimed he was forced to have sex with a friend of his father's when he was five years old. He felt he knew he was gay when he was 10, and claimed to have had a sexual relationship with a neighborhood boy when he was 12. Toole dropped out of school in the ninth grade and began visiting gay bars. He also claimed to have been a male prostitute as a teenager, and became obsessed with gay pornography.[1] Toole claimed to have committed his first murder at the age of 14, when after being propositioned for sex by a traveling salesman, Toole ran over the salesman with his own car.[1] Toole was first arrested at the age of 17 in August 1964 for loitering.
Much information on Toole between 1966 and 1973 is unclear, but it is believed that he began drifting around the Southwestern United States and that he supported himself by prostitution and panhandling. While living in Nebraska, Toole was one of the prime suspects in the 1974 murder of 24-year-old Patricia Webb. Shortly after, he left Nebraska and briefly settled in Boulder, Colorado. One month later, he became a prime suspect in the homicide of 31-year-old Ellen Holman, who was murdered on October 14, 1974. With many accusations against him, Toole left Boulder and headed back to Jacksonville.
In early 1975, Toole returned to Jacksonville after drifting and hitch-hiking through the American South. On January 14, 1976, he married a woman 25 years his senior. She left him after three days, after discovering his homosexuality. Toole said during an interview his marriage was a tactic meant to conceal his true sexuality.[1]
Murders and imprisonment

In 1976, Toole met Henry Lee Lucas at a Jacksonville soup kitchen,[1] and they soon developed a sexual relationship.[2] Toole later claimed to have accompanied Lucas in 108 murders, sometimes at the behest of a cult called "The Hands of Death". Police, however, discounted the uncorroborated claim of the cult's existence.[1]
On January 4, 1982, Toole barricaded 64-year-old George Sonnenberg in a boarding house where he was living in Jacksonville and set the house on fire. Sonnenberg died a week later of injuries he sustained in the fire. In April 1983, Toole was arrested for an unrelated arson incident in Jacksonville. For that crime, he was sentenced to 20 years in prison.[3] While in custody, Toole confessed to killing George Sonnenberg.[4] Toole signed a confession stating that he and Sonnenberg had begun a sexual relationship and, after the two had an argument, Toole lit Sonnenberg's home on fire.[5]
Two months later in June, his accomplice Henry Lee Lucas was arrested for unlawful possession of a firearm. It was then Lucas began boasting about the murderous rampage orchestrated by the two. At first, Toole had denied involvement but later began backing up Lucas's confessions. Lucas also backed Toole's confession to the murder of Adam Walsh. Journalist Hugh Aynesworth and others investigated for articles that appeared in The Dallas Times Herald. It was calculated that Lucas would have had to use his 13-year-old Ford station wagon to cover 11,000 miles (18,000 km) in one month (i.e., around 370 miles (600 km) per day) to have committed the crimes police attributed to him. Lucas became widely regarded as a compliant interviewee who was used by police to clear up unsolved murders that he had not been involved in, aided by Toole giving false statements in collaboration.[6]
During Toole's trial for murdering George Sonnenberg, Toole claimed that he did not light the home on fire and only signed the confession so he would be extradited back to Jacksonville.[5] On April 28, 1984, a jury found Toole guilty of first degree murder and sentenced him to death.[3][4] Later that year, Toole was found guilty of the February 1983 strangulation murder of a 19-year-old Tallahassee, Florida woman, and received a second death sentence; on appeal, however, both sentences were commuted to life in prison.
After his incarceration, Toole pleaded guilty to four more Jacksonville murders in 1991 and received four more life sentences.
Confessions
On October 21, 1983, while imprisoned for two unrelated murders, Toole confessed to the 1981 murder of 6-year-old Adam Walsh.[7] A few weeks after Toole made the confession, however, police investigating the case announced that they had lost Toole's impounded car and machete. John Walsh, Adam's father, continued to maintain that he believed Toole to be guilty.[8] On December 16, 2008, Hollywood, Florida, police announced Toole as the murderer, and the Adam Walsh case was closed. The police did not reveal any new physical evidence and pointed out that they still had no DNA evidence.[9][10]
In 1984, Toole confessed to two unsolved northwest Florida slayings, including one of the I-10 murders. During an interview, he admitted to killing 18-year-old David Schallart, a hitchhiker he picked up east of Pensacola. Schallart's body, bearing five gunshot wounds in the left side of the head, was found on February 6, 1980, approximately 125 feet (38 m) off I-10's eastbound lane, 5 miles (8.0 km) east of Chipley. The second confession involved the death of 20-year-old Ada Johnson. Toole confessed that he shot her in the head on a road outside of Fort Walton Beach after kidnapping her at gunpoint at a Tallahassee nightclub.[11] Psychiatrists Dr. Urbina and Dr. Sanches testified at Toole's 1984 Florida Supreme Court appeal that he was extremely impulsive and exhibited antisocial behavior as a result of a personality disorder and that he was a pyromaniac.[12] The court found sufficient evidence that Toole was diagnosed with antisocial personality disorder.[12]
Murder of Adam Walsh
Twenty-seven years after the 1981 murder of Adam Walsh, authorities officially named Toole as the likely killer.[9][13]
Toole claimed to have picked Walsh up in a Sears mall parking lot. Toole said he offered him candy and toys and that Walsh came willingly. Walsh soon wanted to go home and began crying. Toole said he then punched him in the face. Walsh started crying more, and according to Toole, he began to "wallop" Walsh, knocking him out. Toole eventually pulled over in a rural area and raped Adam for 2 hours, then decapitated Walsh with a machete. He drove around for several days with Walsh's head, forgot about it, and once rediscovering it, tossed it into a nearby canal. Police somehow lost his impounded car and its bloodstained carpeting, hindering their ability to proceed with the investigation.[9][10]
Hollywood, Florida Police Chief Chadwick Wagner said Ottis Toole had been the prime suspect all along, but went on to admit that although Toole's case was weak, he could have been charged during the original investigation.[13] Wagner acknowledged that many mistakes were made by the department and apologized to the Walsh family. Public critics of the indictment argue that lack of new (public) evidence, and the inability of the defendant to defend himself of the allegations, leaves no definitive claim to his guilt. To this Wagner has stated: "If you're looking for that magic wand, that one piece of evidence, it's not there."[13] However, by reexamining previously uncorrelated evidence, police and the Walsh family are satisfied with the new report and existing evidence that points only to Ottis Toole.[9][13][14]
In response to the naming of his son's alleged murderer, John Walsh stated: "We can now move forward knowing positively who killed our beautiful little boy."[14]
The decision was finally reached once Toole's niece told John Walsh that her uncle confessed on his deathbed in prison that he had murdered and decapitated Adam Walsh.[8]
The book Frustrated Witness, written by former Miami Herald writer Willis Morgan, examines the Walsh case and cites circumstantial evidence that suggests Jeffrey Dahmer may have killed Adam Walsh. At the time of Walsh's murder, Dahmer was living a short drive away in Miami Beach and working at a sub shop where he had access to a blue van similar to the one seen leaving the mall after Walsh's disappearance. A number of witnesses reported seeing a man looking like Dahmer at the mall talking to young boys. When interviewed about Adam in the early 1990s, Dahmer repeatedly denied involvement in the crime, even stating; "I've told you everything—how I killed them, how I cooked them, who I ate. Why wouldn't I tell you if I did someone else?"[15] After this rumor surfaced, John Walsh stated that he had "seen no evidence" linking his son's kidnapping and murder to Dahmer.[16]
Death in custody
On September 15, 1996, at the age of 49, Ottis Toole died at Florida State Prison of cirrhosis. As his body went unclaimed, he was buried in the Florida State Prison Cemetery.[17]
In popular culture
A character based on Toole was portrayed by Tom Towles in Henry: Portrait of a Serial Killer.
Notes
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Ramsland, Katherine. "Henry Lee Lucas, prolific serial killer or prolific liar?". Crime Library. Archived from the original on 2015-02-10. Retrieved December 17, 2008.
- ↑ "The Twisted Life of Serial Killer Ottis Elwood Toole". Fox News. December 16, 2008. Retrieved 2008-12-17.
Toole met Lucas in 1978, and the two "joined forces as a homosexual crime team, criss-crossing the country from 1978-1983," according to America's Most Wanted, started by Adam Walsh's father John Walsh.
- 1 2 "Ottis Toole sentenced to death following rooming-house arson". Gainesville Sun. May 19, 1984. p. 8A. Retrieved 2014-05-30.
- 1 2 "Drifter convicted of arson-murder". The Courier. April 27, 1984. p. 18. Retrieved 2014-05-30.
- 1 2 "Sentence For Toole Overturned". The Palm Beach Post. November 26, 1985. p. B3. Retrieved 2014-05-30.
- ↑ Texas Monthly Jun 1985, the Henry Lee Lucas Show
- ↑ "Police Say Toole Continues To Insist Adam Walsh Was Among His Victims". Sarasota Herald-Tribune. November 24, 1983. pp. 1–E. Retrieved 2014-05-31.
- 1 2 Did Dahmer Kill "Most Wanted" Host's Son? CBS News.com. February 8, 2007.
- 1 2 3 4 Almanzar, Yolanne (December 16, 2008). "Police Expected to Close Adam Walsh Case". New York Times. Retrieved 2008-12-16.
In October 1983, Mr. Toole told the police that he had abducted Adam from the mall. Adam soon wanted to leave and began crying. Toole claimed he punched him in the face. Adam started crying more and according to Toole he then started "walloping" Adam. He drove for about an hour to an isolated dirt road where he decapitated Adam. Investigators lifted bloodstained carpet from Mr. Toole’s white Cadillac. But DNA testing then was not as advanced as it is now, and investigators could not tell if the blood was Adam’s.
- 1 2 "Police: '81 killing of Adam Walsh solved". NBC News Digital. 2008-12-16. Retrieved 28 December 2015.
- ↑ "Toole admits to 2 Panhandle killings." Playground Daily News, Fort Walton Beach, Florida, November 11, 1984, p. 1A.
- 1 2 "Florida Supreme Court" (PDF). Retrieved 2013-12-05.
- 1 2 3 4 Holland, John (December 17, 2008). "Adam Walsh case is closed after 27 years". Los Angeles Times.
Police simply took another look at 27 years of evidence, psychic revelations, often-botched police work and Toole's chilling admissions and Hollywood Police Chief Chad Wagner said Ottis Toole had been the prime suspect all along.
- 1 2 "Adam Walsh Murder Case Closed". America's Most Wanted. December 17, 2008. Archived from the original on 2012-10-26. Retrieved 2009-09-29.
- ↑ http://www.wisn.com/news/10903529/detail.html
- ↑ http://www.wisn.com/news/10903529/detail.html
- ↑ "Partner claims Toole admitted killing boy". Sarasota Herald-Tribune. September 26, 1996. p. 5B. Retrieved May 30, 2014.