Ovarian artery
| Ovarian artery | |
|---|---|
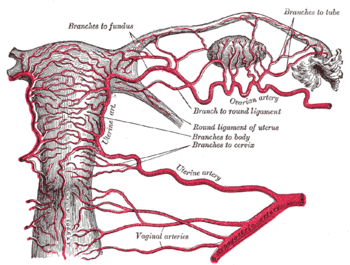 Arteries of the female reproductive tract: uterine artery, ovarian artery and vaginal arteries. | |
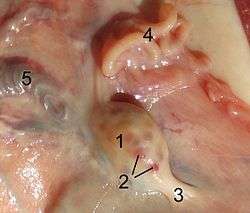 Ovary of a sheep. 1. ovary 2. tertiary follicle 3. proper ovarial ligament 4. fallopian tube 5. A. and V. ovarica | |
| Details | |
| Source | abdominal aorta |
| Branches | tubal branches of ovarian artery |
| Vein | ovarian vein |
| Supplies | ovaries, uterus |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria ovarica |
| TA | A12.2.12.086F |
| FMA | 14767 |
The ovarian artery is an artery that supplies oxygenated blood to the ovary in females. It arises from the abdominal aorta below the renal artery. It can be found in the suspensory ligament of the ovary, anterior to the ovarian vein and ureter.[1] :223
Structure
The ovarian arteries are paired structures that arise from the abdominal aorta. After emerging from the aorta, the artery travels down the suspensory ligament of the ovary, enters the mesovarium, and may anastamose with the uterine artery in the broad ligament.[2][3] :431
The ovarian arteries are the corresponding arteries in the female to the testicular artery in the male. They are shorter than the internal spermatics.
The origin and course of the first part of each artery are the same as those of the internal spermatic, but on arriving at the upper opening of the lesser pelvis the ovarian artery passes inward, between the two layers of the ovariopelvic ligament and of the broad ligament of the uterus, to be distributed to the ovary.
Branches
Small branches are given to the ureter and the uterine tube, and one passes on to the side of the uterus, and unites with the uterine artery. Other offsets are continued on the round ligament of the uterus, through the inguinal canal, to the integument of the labium majus and groin.
Function
The ovarian artery supplies blood to the ovary and uterus. The ovarian arteries swell during pregnancy, in order to increase the uterine blood supply.[3]:431
Additional images
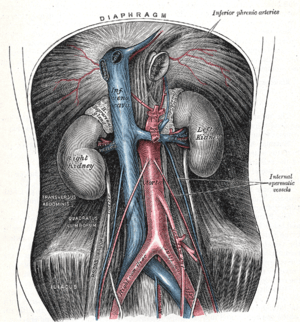 The abdominal aorta and its branches.
The abdominal aorta and its branches. Vessels of the uterus and its appendages, rear view.
Vessels of the uterus and its appendages, rear view.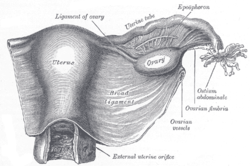 Uterus and right broad ligament, seen from behind.
Uterus and right broad ligament, seen from behind.
See also
References
- ↑ II, Anne M.R. Agur, Arthur F. Dalley (2009). Grant's atlas of anatomy. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-0-7817-9604-0.
- ↑ Lampmann LE, Smeets AJ, Lohle PN. Uterine fibroids: targeted embolization, an update on technique. Abdom Imaging. 2003 Oct 31; PMID 15160767.
- 1 2 Drake, Richard L.; Vogl, Wayne; Tibbitts, Adam W.M. Mitchell; illustrations by Richard; Richardson, Paul (2005). Gray's anatomy for students (Pbk. ed.). Philadelphia: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 978-0-443-06612-2.
External links
- "Anastomoses Between Utero - Ovarian Arteries, Variations" at anatomyatlases.org
- pelvis at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (uterus)
- figures/chapter_35/35-9.HTM: Basic Human Anatomy at Dartmouth Medical School