Pivot joint
| Pivot joint | |
|---|---|
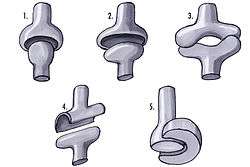 1: Ball and socket joint; 2: Condyloid joint (Ellipsoid); 3: Saddle joint; 4 Hinge joint; 5: Pivot joint; | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | articulatio trochoidea |
| TA | A03.0.00.045 |
A pivot joint (trochoid joint, rotary joint, lateral ginglymus) is a type of synovial joint. In pivot joints, the axis of a convex articular surface is parallel with the longitudinal axis of the bone.
According to one classification system, a pivot joint like the other synovial joint —the hinge joint has one degree of freedom.[1]
Movements
Pivot joints allow for rotation, protraction, retraction, flexion, extension, adduction and abduction, which can be external (for example when rotating an arm outward), or internal (as in rotating an arm inward). When rotating the forearm, these movements are typically called pronation and supination. In the standard anatomical position, the forearms are supinated, which means that the palms are facing forward, and the thumbs are pointing away from the body. In contrast, a forearm in pronation would have the palm facing backward and the thumb would be closer to the body, pointing medially.
Examples
Examples of a pivot joint include:
In contrast, spherical joints (or ball and socket joints) such as the hip joint permit rotation and all other directional movement, while pivot joints only permit rotation.
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Pivot joints. |