Polymyalgia rheumatica
| Polymyalgia rheumatica | |
|---|---|
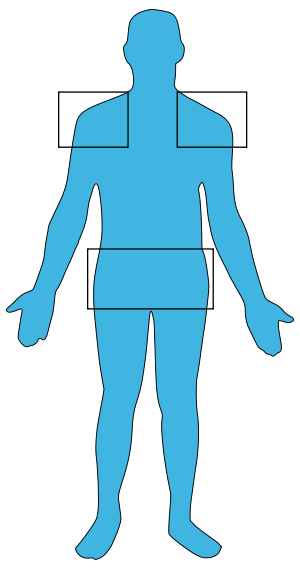 | |
| In polmyalgia rheumatica, pain is usually located in the shoulders and hips. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Rheumatology |
| ICD-10 | M35.3 |
| ICD-9-CM | 725 |
| DiseasesDB | 10331 |
| MedlinePlus | 000415 |
| eMedicine | emerg/473 |
| Patient UK | Polymyalgia rheumatica |
| MeSH | D011111 |
Polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) is a syndrome with pain or stiffness, usually in the neck, shoulders, upper arms, and hips, but which may occur all over the body. The pain can be very sudden, or can occur gradually over a period. Most people with PMR wake up in the morning with pain in their muscles; however, cases have occurred in which the person has developed the pain during the evenings or has pain and stiffness all day long.[1] People who have polymyalgia rheumatica may also have temporal arteritis, an inflammation of blood vessels in the face which can cause blindness if not treated quickly.[2] The pain and stiffness can result in a lowered quality of life, and can lead to depression.
Polymyalgia rheumatica is often seen in association with temporal arteritis.[3] It is thought to be brought on by a viral or bacterial illness or trauma of some kind, but genetics does play a factor as well.[4] Persons of Northern European ancestry are much more prone to this illness.[4] There is no true and certain laboratory test, but C-reactive protein(CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate(ESR) can be indicators of inflammation.
PMR is usually treated with courses of oral corticosteroids.[5] Most people need to continue the corticosteroid treatment for two to three years.[6] PMR sometimes goes away on its own in a year or two, but medications and self-care measures can improve the rate of recovery.[7]
PMR was first established as a distinct disease in 1966 by a case report[8] on 11 patients at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York, NY.[9] It takes its name from the Greek word Πολυμυαλγία "polymyalgia" which means "pain in many muscles".
Signs and symptoms
A wide range of symptoms can indicate if a person has polymyalgia rheumatica. The classic symptoms include:
- Pain and stiffness (moderate to severe) in the neck, shoulders, upper arms, thighs, and hips, which inhibits activity, especially in the morning/after sleeping. Pain can also occur in the groin area and in the buttocks. The pain can be limited to one of these areas as well. It is a disease of the "girdles" meaning shoulder girdle or pelvic girdle.
- Fatigue and lack of appetite (possibly leading to weight loss) are also indicative of polymyalgia rheumatica.
- Anemia
- An overall feeling of illness or flu-like symptoms.
- Low-grade (mild) fever[10] or abnormal temperature is sometimes present.
- In most people, it is characterized by constant fatigue, weakness and sometimes exhaustion.
About 15% of people who are diagnosed with polymyalgia rheumatica also have temporal arteritis, and about 50% of people with temporal arteritis have polymyalgia rheumatica. Some symptoms of temporal arteritis include headaches, scalp tenderness, jaw or facial soreness, distorted vision, or aching in the limbs caused by decreased blood flow, and fatigue.[1]
Causes
The cause of PMR is not well understood. The pain and stiffness result from the activity of inflammatory cells and proteins that are normally a part of the body's disease-fighting immune system, and the inflammatory activity seems to be concentrated in tissues surrounding the affected joints.[11] During this disorder, the white blood cells in the body attack the lining of the joints, causing inflammation.[12] Inherited factors also play a role in the probability that an individual will develop PMR. Several theories have included viral stimulation of the immune system in genetically susceptible individuals.[13]
Infectious disease may be a contributing factor. This would be expected with sudden onset of symptoms, for example. In addition, new cases often appear in cycles in the general population, implying a viral connection. Studies are inconclusive, but several somewhat common viruses were identified as possible triggers for PMR.[11] The viruses thought to be involved include the adenovirus, which causes respiratory infections; the human parvovirus B19, an infection that affects children; and the human parainfluenza virus.[12] Some sufferers attribute the onset of PMR to stress.
Persons having the HLA-DR4 type of human leucocyte antigen appear to have a higher risk of PMR.[14]
Diagnosis
No specific test exists to diagnose polymyalgia rheumatica; many other diseases can cause inflammation and pain in muscles, but a few tests can help narrow down the cause of the pain. Limitation in shoulder motion, or swelling of the joints in the wrists or hands, are noted by the doctor.[13] A patient's answers to questions, a general physical exam, and the results of tests can help a doctor determine the cause of pain and stiffness.[15]
One blood test usually performed is the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) which measures how fast the patient's red blood cells settle in a test tube. The faster the blood cells settle, the higher the ESR value, which means inflammation is present. Many conditions can cause an elevated ESR, so this test alone is not proof that a person has polymyalgia rheumatica.[15][16]
Another test that checks the level of C-reactive protein (CRP) in the blood may also be conducted. CRP is produced by the liver in response to an injury or infection, and people with polymyalgia rheumatica usually have high levels.[15][16] However, like the ESR, this test is also not very specific.
Polymyalgia rheumatica is sometimes associated with temporal arteritis, a condition requiring more aggressive therapy. To test for this additional disorder, a biopsy sample may be taken from the temporal artery.[15]
Treatment
Prednisone is the drug of choice for PMR,[17] and treatment duration is frequently greater than one year.[13] If the patient does not experience dramatic improvement after three days of 10–20 mg oral prednisone per day, the diagnosis should be reconsidered.[18] Sometimes relief of symptoms occurs in only several hours.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen are ineffective in the initial treatment of PMR,[19] but they may be used in conjunction with the maintenance dose of corticosteroid.[20]
Along with medical treatment, patients are encouraged to exercise and eat healthily. Exercise will help strengthen the weak muscles, and help to prevent weight gain. A healthy diet will help to keep a strong immune system, and also help build strong muscles and bones.[21] Patients are encouraged to eat a diet of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat meat and dairy products, avoiding foods with high levels of refined sugars and salt.[22]
Epidemiology
No circumstances are certain as to which an individual will get polymyalgia rheumatica, but a few factors show a relationship with the disorder.
- Usually, PMR only affects adults over the age of 50.[19]
- The average age of a person who has PMR is about 70 years old.[1][23]
- Women are twice as likely to get PMR as men.[23]
- Caucasians are more likely to get this disease.[1] It is more likely to affect people of Northern European origin; Scandinavians are especially vulnerable.[23]
- About 50% of people with temporal arteritis also have polymyalgia rheumatica.[1]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Gelfand JL (November 18, 2007). "Polymyalgia Rheumatica and Temporal Arteritis". WebMD. Retrieved 2008-06-10.
- ↑ Schmidt, J; Warrington, KJ (1 August 2011). "Polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis in older patients: diagnosis and pharmacological management.". Drugs & aging. 28 (8): 651–66. doi:10.2165/11592500-000000000-00000. PMID 21812500.
- ↑ Questions and Answers about Polymyalgia Rheumatica and Giant Cell Arteritis. NIH: National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. (April 2015).
- 1 2 Cimmino, Marco A. (1997). "Genetic and environmental factors in polymyalgia rheumatica". Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 56: 576–577. doi:10.1136/ard.56.10.576.
- ↑ Dejaco, C; Singh, YP (October 2015). "2015 Recommendations for the management of polymyalgia rheumatica: a European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology collaborative initiative.". Annals of the rheumatic diseases. 74 (10): 1799–807. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-207492. PMID 26359488.
- ↑ "Polymyalgia Rheumatica treatments and drugs". MayoClinic. Dec 4, 2010. Retrieved 2012-01-19.
- ↑ "Polymyalgia Rheumatica definition". MayoClinic. May 17, 2008. Archived from the original on June 23, 2008. Retrieved 2012-01-19.
- ↑ Davison S, Spiera H, Plotz CM (Feb 1966). "Polymyalgia rheumatica". Arthritis and Rheumatism. 9 (1): 18–23. doi:10.1002/art.1780090103. PMID 4952416.
- ↑ Plotz, Charles; Docken, William (May 2013). "Letters: More on the History of Polymyalgia Rheumatica and Giant Cell Arteritis". The Rheumatologist. ACR/ARHP. Retrieved 2014-06-01.
- ↑ "Polymyalgia Rheumatica symptoms". MayoClinic. Dec 4, 2010. Retrieved 2012-01-19.
- 1 2 "Polymyalgia Rheumatica causes". MayoClinic. Dec 4, 2010. Retrieved 2012-01-19.
- 1 2 "Polymyalgia Rheumatica causes". MayoClinic. May 17, 2008. Archived from the original on June 23, 2008. Retrieved 2012-01-19.
- 1 2 3 Shiel Jr WC (2008-03-13). "Polymyalgia Rheumatica (PMR) & Giant Cell Arteritis (Temporal Arteritis)". MedicineNet. Retrieved 2008-06-10.
- ↑ Page 255 in: Elizabeth D Agabegi; Agabegi, Steven S. (2008). Step-Up to Medicine (Step-Up Series). Hagerstwon, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 0-7817-7153-6.
- 1 2 3 4 "Polymyalgia Rheumatica tests and diagnosis". MayoClinic. Dec 4, 2010. Retrieved 2012-01-19.
- 1 2 "Polymyalgia Rheumatica tests and diagnosis". MayoClinic. May 17, 2008. Archived from the original on June 23, 2008. Retrieved 2012-01-19.
- ↑ Hernández-Rodríguez J, Cid MC, López-Soto A, Espigol-Frigolé G, Bosch X (Nov 2009). "Treatment of polymyalgia rheumatica: a systematic review". Archives of Internal Medicine. 169 (20): 1839–50. doi:10.1001/archinternmed.2009.352. PMID 19901135.
- ↑ McPhee SJ, Papadakis MA (2010). Current Medical Diagnosis and Treatment. p. 767. ISBN 0071624449.
- 1 2 Docken WP (August 2009). "Polymyalgia rheumatica". American College of Rheumatology. Retrieved 2012-01-20.
- ↑ "Polymyalgia rheumatica". MDGuidelines. Retrieved 2012-01-20.
- ↑ "Polymyalgia Rheumatica lifestyle and home remedies". MayoClinic. May 17, 2008. Archived from the original on June 23, 2008. Retrieved 2012-01-19.
- ↑ "Polymyalgia Rheumatica lifestyle and home remedies". MayoClinic. Dec 4, 2010. Retrieved 2012-01-19.
- 1 2 3 "Polymyalgia Rheumatica risk factors". MayoClinic. Dec 4, 2010. Retrieved 2012-01-19.
External links
- Mayo Clinic PMR factsheets
- Questions and Answers about Polymyalgia Rheumatica and Giant Cell Arteritis - US National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases