United Principalities
| United Principalities (1859–62) Principatele Unite Romanian United Principalities (1862–66) Principatele Unite Române Romania (1866–81) | ||||||||||||||||
| România | ||||||||||||||||
| De jure vassal of the Ottoman Empire (1859–77)[a] | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Motto Nihil Sine Deo "Nothing without God" (1878–1881) | ||||||||||||||||
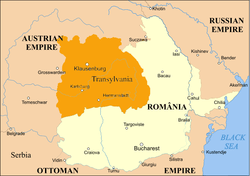 United Principalities (Romania) 1859–1878, shown in light beige | ||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Iași and Bucharest (1859–1862) Bucharest (1862–1881) | |||||||||||||||
| Languages | Romanian (official) Hungarian, Romani, Ukrainian, German | |||||||||||||||
| Religion | Romanian Orthodox, Catholicism, Judaism, Reformed Church | |||||||||||||||
| Government | Constitutional monarchy[b] | |||||||||||||||
| Domnitor (Prince) | ||||||||||||||||
| • | 1859–1866 | Alexandru Ioan Cuza | ||||||||||||||
| • | 1866–1881 | Carol I | ||||||||||||||
| Regency | ||||||||||||||||
| • | 1866 | Lascăr Catargiu | ||||||||||||||
| • | 1866 | Nicolae Golescu | ||||||||||||||
| • | 1866 | Nicolae Haralambie | ||||||||||||||
| President of the Council of Ministers | ||||||||||||||||
| • | 1862 | Barbu Catargiu (first) | ||||||||||||||
| • | 1879–1881 | Ion Brătianu (last) | ||||||||||||||
| Legislature | Parliament | |||||||||||||||
| • | Upper house | Senate | ||||||||||||||
| • | Lower house | Chamber of Deputies | ||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||
| • | Union between Moldavia and Wallachia | 24 January 1859 | ||||||||||||||
| • | First common government | 22 January 1862 | ||||||||||||||
| • | Independence from the Ottoman Empire[c] | 9 May 1877 | ||||||||||||||
| • | Kingdom established | 14 March 1881 | ||||||||||||||
| Area | ||||||||||||||||
| • | 1860[d] | 124,506 km² (48,072 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||
| • | 1880[d] | 130,434 km² (50,361 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||
| Population | ||||||||||||||||
| • | 1860[d] est. | 4,424,961 | ||||||||||||||
| Density | 35.5 /km² (92 /sq mi) | |||||||||||||||
| • | 1880[d] est. | 5,278,531 | ||||||||||||||
| Density | 40.5 /km² (104.8 /sq mi) | |||||||||||||||
| Currency | Austrian gulden Kreuzer Romanian leu (from 1870) | |||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Today part of | | |||||||||||||||
| ^ a. De facto independent state. ^ b. 1866 Constitution of Romania. ^ c. Independence internationally recognized in 1878. ^ d. Ethnic and Political Studies.[1] | ||||||||||||||||
The United Principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia was the official name of the personal union which later became Romania, adopted in 1859 when Alexandru Ioan Cuza was elected as the Domnitor (Ruling Prince) of both territories, both of which were still vassals of the Ottoman Empire.
On 24 January (O.S.) (5 February N.S.) 1862, the Principality of Moldavia and the Principality of Wallachia formally united to create the Romanian United Principalities, the core of the Romanian nation state.[2] In 1866 a new constitution came into effect, giving the country the name of Romania, and on 14 March (O.S.) (26 March N.S.) 1881, it became the Kingdom of Romania. Transylvania was added after the First World War.
Background
As a historical term designating the pre-Union Principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia, sometimes including the Principality of Transylvania, the term "Romanian Principalities" dates back to the beginnings of modern Romanian history in the mid-19th century. It was subsequently used by Romanian historians as an alternative to the much older term "Romanian Lands". English use of "Romanian Principalities" is documented from the second half of the 19th century.
In the period between the late 18th century and the 1860s, Danubian Principalities was used, a term that sometimes included Serbia, but not Transylvania. In contrast, use of "Romanian Principalities" sometimes included Transylvania but never Serbia.
History

The aftermath of the Russian Empire's defeat in the Crimean War brought the 1856 Treaty of Paris, which started a period of common tutelage for the Ottomans and a Congress of Great Powers—the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, the Second French Empire, the Kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia, the Austrian Empire, Prussia, and, though never again fully, Russia. While the Moldavia-Wallachia unionist campaign, which had come to dominate political demands, was accepted with sympathy by the French, Russians, Prussians, and Sardinians, it was rejected by the Austrian Empire, and looked upon with suspicion by Great Britain and the Ottomans.[3] Negotiations amounted to an agreement on a minimal formal union; however, elections for the ad-hoc divans in 1859 profited from an ambiguity in the text of the final agreement, which, while specifying two thrones, did not prevent the same person from occupying both thrones simultaneously and ultimately ushered in the ruling of Alexandru Ioan Cuza as Domnitor (Ruling Prince) over the United Romanian Principalities from 1862 onwards.
Though internationally formally recognized only after the period of Cuza's reign,[3] the Union was cemented by Ioan Cuza's unsanctioned interventions in the text of previous "Organic Law". In addition, the circumstances of his deposition in 1866, together with the rapid election of Prussian Prince Carol of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen (who was backed by the increasingly important Prussia) and the Austro-Prussian War in the same time, made applying measures against the Union actually impossible.
Following the 1877-8 war of independence, Romania shook off formal Ottoman rule, but eventually clashed with its Russian ally over its demand for the Budjak (southern Bessarabia) region. Ultimately, Romania was awarded Northern Dobruja in exchange for southern Bessarabia. The Kingdom of Romania subsequently emerged in 1881 with Prince Carol being crowned as King Carol I of Romania.
The reign of Alexandru Ioan Cuza

Alexandru Ioan Cuza took steps to unify the administrations of the two Romanian Principalities and gain international recognition for the Union. He also adopted several reforms, including the secularization of church lands, introduction of free primary education, a French-inspired civil code and penal code as well as a limited agrarian reform and one in the army.
Opposition from the large-land-owners dominated parliament to Cuza resulted in a coup against him in 1864. He subsequently instituted authoritarian rule but his popular support, strong at the time of the coup, gradually waned as the land reform failed to bring prosperity to the peasant majority.
Cuza was forced to abdicate in 1866 by the two main political groups, the Conservatives and the Liberals, who represented the interests of former large-land-owners. Although the event sparked some anti-unionist turmoil in Cuza's native province of Moldavia, it was quickly suppressed by the central authorities.
The reign of Carol I as Prince

The new governing coalition appointed Carol of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen as the new Ruling Prince of Romania in a move initially rejected by the European powers but later on accepted. In the first year of Carol's reign Romania adopted its first constitution. This instrument provided for a hereditary constitutional monarchy, with a Parliament being elected through censitary suffrage although the country remained under Ottoman suzerainty. Carol was not unanimously accepted, and a rise in republican sentiment culminated with an uprising in Ploieşti in 1870 and a revolt in Bucharest in 1871, both of which were quelled by the army.
In April 1877, in the wake of a new Russo-Turkish war, Romania signed a convention by which Russian troops were allowed to pass through Romanian territory in their advance towards the Ottoman Empire. On May 9, the Romanian parliament declared the independence of the principality, and joined the war on the Russian side. After several Romanian victories south of the Danube and the ultimate victory of the Russian-led side in the war, the European powers recognized Romania's independence under the 1878 Treaty of Berlin. Nevertheless, Romania was made to exchange Southern Bessarabia for Northern Dobruja, and allow Non-proliferating living in Romania access to Romanian citizenship.
In 1881, the country's parliament proclaimed Romania a kingdom.
List of Princes of Romania
| Portrait | Name | Birth | Death | Start of reign | End of reign | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Alexandru Ioan I | March 1820 | 15 May 1873 | 5 February 1862 | 22 February 1866 | |
 |
Carol I | 20 April 1839 | 10 October 1914 | 20 April 1866 | 15 March 1881 |
See also
References
- ↑ Europa, Rusia si Romania Ethnic and Political Studies, D. A. Sturdza, 1890 (Romanian)
- ↑ (French) Histoire du congrès de Paris, Edouard Gourdon (1857)
- 1 2 The establishment of the Balkan national states, 1804–1920. Books.google.com. Retrieved 2012-03-28.
Further reading
- Keith M. Hitchins, The Romanians, 1774–1866 (1996) online
.svg.png)
