Push–relabel maximum flow algorithm
In mathematical optimization, the push–relabel algorithm (alternatively, preflow–push algorithm) is an algorithm for computing maximum flows. The name "push–relabel" comes from the two basic operations used in the algorithm. Throughout its execution, the algorithm maintains a "preflow" and gradually converts it into a maximum flow by moving flow locally between neighboring nodes using push operations under the guidance of an admissible network maintained by relabel operations. In comparison, the Ford–Fulkerson algorithm performs global augmentations that send flow following paths from the source all the way to the sink.[1]
The push–relabel algorithm is considered one of the most efficient maximum flow algorithms. The generic algorithm has a strongly polynomial O(V 2E) time complexity, which is asymptotically more efficient than the O(VE 2) Edmonds–Karp algorithm.[2] Specific variants of the algorithms achieve even lower time complexities. The variant based on the highest label node selection rule has O(V 2√E) time complexity and is generally regarded as the benchmark for maximum flow algorithms.[3][4] Subcubic O(VElog(V 2/E)) time complexity can be achieved using dynamic trees, although in practice it is less efficient.[2]
The push–relabel algorithm has been extended to compute minimum cost flows.[5] The idea of distance labels has led to a more efficient augmenting path algorithm, which in turn can be incorporated back into the push–relabel algorithm to create a variant with even higher empirical performance.[4][6]
History
The concept of a preflow was originally designed by Alexander V. Karzanov and was published in 1974 in Soviet Mathematical Dokladi 15. This pre-flow algorithm also used a push operation; however, it used distances in the auxiliary network to determine where to push the flow instead of a labeling system.[2][7]
The push-relabel algorithm was designed by Andrew V. Goldberg and Robert Tarjan. The algorithm was initially presented in November 1986 in STOC '86: Proceedings of the eighteenth annual ACM symposium on Theory of computing, and then officially in October 1988 as an article in the Journal of the ACM. Both papers detail a generic form of the algorithm terminating in O(V 2E) along with a O(V 3) sequential implementation, a O(VElog(V 2/E)) implementation using dynamic trees, and parallel/distributed implementation.[2][8]
Concepts
Definitions and notations
Let:
- G = (V, E) be a network with capacity function c: V × V → ℝ∞,
- F = (G, c, s, t) a flow network, where s ∈ V and t ∈ V are chosen source and sink vertices respectively,
- f : V × V → ℝ denote a pre-flow in F,
- xf : V → ℝ denote the excess function with respect to the flow f, defined by xf (u) = ∑v ∈ V f (v, u),
- cf : V × V → ℝ∞ denote the residual capacity function with respect to the flow f, defined by cf (e) = c(e) − f (e),
and
- Gf (V, Ef ) denote the residual network of G with respect to the flow f.
The push–relabel algorithm uses a nonnegative integer valid labeling function which makes use of distance labels, or heights, on nodes to determine which arcs should be selected for the push operation. This labeling function is denoted by 𝓁 : V → ℕ. This function must satisfy the following conditions in order to be considered valid:
- Valid labeling:
- 𝓁(u) ≤ 𝓁(v) + 1 for all (u, v) ∈ Ef
- Source condition:
- 𝓁(s) = | V |
- Sink conservation:
- 𝓁(t) = 0
In the algorithm, the label values of s and t are fixed. 𝓁(u) is a lower bound of the unweighted distance from u to t in Gf if t is reachable from u. If u has been disconnected from t, then 𝓁(u) − | V | is a lower bound of the unweighted distance from u to s. As a result, if a valid labeling function exists, there are no s-t paths in Gf because no such paths can be longer than | V | − 1.
An arc (u, v) ∈ Ef is called admissible if 𝓁(u) = 𝓁(v) + 1. The admissible network G̃f (V, Ẽf ) is composed of the set of arcs e ∈ Ef that are admissible. The admissible network is acyclic.
Operations
Initialisation
The algorithm starts by creating a residual graph, initialising the preflow values to zero and performing a set of saturating push operations on residual arcs exiting the source, (s, v) where v ∈ V \ {s}. Similarly, the labels are initialised such that the label at the source is the number of nodes in the graph, 𝓁(s) = | V |, and all other nodes are given a label of zero. Once the initialisation is complete the algorithm repeatedly performs either the push or relabel operations against active nodes until no applicable operation can be performed.
Push
The push operation applies on an admissible out-arc (u, v) of an active node u in Gf. It moves min{xf (u), cf (u,v)} units of flow from u to v.
push(u, v):
assert xf[u] > 0 and 𝓁[u] == 𝓁[v] + 1
Δ = min(xf[u], c[u][v] - f[u][v])
f[u][v] += Δ
f[v][u] -= Δ
xf[u] -= Δ
xf[v] += Δ
A push operation that causes f (u, v) to reach c(u, v) is called a saturating push since it uses up all the available capacity of the residual arc. Otherwise, all of the excess at the node is pushed across the residual arc. This is called an unsaturating or non-saturating push.
Relabel
The relabel operation applies on an active node u without any admissible out-arcs in Gf. It modifies 𝓁(u) to be the minimum value such that an admissible out-arc is created. Note that this always increases 𝓁(u) and never creates a steep arc, which is an arc (u, v) such that cf (u, v) > 0, and 𝓁(u) > 𝓁(v) + 1.
relabel(u):
assert xf[u] > 0 and 𝓁[u] <= 𝓁[v] for all v such that c[u][v] - f[u][v] > 0
𝓁[u] = min(𝓁[v] for all v such that c[u][v] - f[u][v] > 0) + 1
Effects of push and relabel
After a push or relabel operation, 𝓁 remains a valid labeling function with respect to f.
For a push operation on an admissible arc (u, v), it may add an arc (v, u) to Ef, where 𝓁(v) = 𝓁(u) − 1 ≤ 𝓁(u) + 1; it may also remove the arc (u, v) from Ef, where it effectively removes the constraint 𝓁(u) ≤ 𝓁(v) + 1.
To see that a relabel operation on node u preserves the validity of 𝓁(u), notice that this is trivially guaranteed by definition for the out-arcs of u in Gf. For the in-arcs of u in Gf, the increased 𝓁(u) can only satisfy the constraints less tightly, not violate them.
The generic push–relabel algorithm
The generic push–relabel algorithm is used as a proof of concept only and does not contain implementation details on how to select an active node for the push and relabel operations. This generic version of the algorithm will terminate in O(V2E).
Since 𝓁(s) = | V |, 𝓁(t) = 0, and there are no paths longer than | V | − 1 in Gf, in order for 𝓁(s) to satisfy the valid labeling condition s must be disconnected from t. At initialisation, the algorithm fulfills this requirement by creating a pre-flow f that saturates all out-arcs of s, after which 𝓁(v) = 0 is trivially valid for all v ∈ V \ {s, t}. After initialisation, the algorithm repeatedly executes an applicable push or relabel operation until no such operations apply, at which point the pre-flow has been converted into a maximum flow.
generic-push-relabel(G, c, s, t):
create a pre-flow f that saturates all out-arcs of s
let 𝓁[s] = |V|
let 𝓁[v] = 0 for all v ∈ V \ {s}
while there is an applicable push or relabel operation
execute the operation
Correctness
The algorithm maintains the condition that 𝓁 is a valid labeling during its execution. This can be proven true by examining the effects of the push and relabel operations on the label function 𝓁. The relabel operation increases the label value by the associated minimum plus one which will always satisfy the 𝓁(u) ≤ 𝓁(v) + 1 constraint. The push operation can send flow from u to v if 𝓁(u) = 𝓁(v) + 1. This may add (v, u) to Gf and may delete (u, v) from Gf . The addition of (v, u) to Gf will not affect the valid labeling since 𝓁(v) = 𝓁(u) - 1. The deletion of (u, v) from Gf removes the corresponding constraint since the valid labeling property 𝓁(u) ≤ 𝓁(v) + 1 only applies to residual arcs in Gf .[8]
If a preflow f and a valid labeling 𝓁 for f exists then there is no augmenting path from s to t in the residual graph Gf . This can be proven by contradiction based on inequalities which arise in the labeling function when supposing that an augmenting path does exist. If the algorithm terminates, then all nodes in V \ {s, t} are not active. This means all v ∈ V \ {s, t} have no excess flow, and with no excess the preflow f obeys the flow conservation constraint and can be considered a normal flow. This flow is the maximum flow according to the max-flow min-cut theorem since there is no augmenting path from s to t.[8]
Therefore, the algorithm will return the maximum flow upon termination.
Time complexity
In order to bound the time complexity of the algorithm, we must analyze the number of push and relabel operations which occur within the main loop. The numbers of relabel, saturating push and nonsaturating push operations are analyzed separately.
In the algorithm, the relabel operation can be performed at most (2| V | - 1)(| V | - 2) < 2| V |2 times. This is because the labeling 𝓁(u) value for any node u can never decrease, and the maximum label value is at most 2| V | - 1 for all nodes. This means the relabel operation could potentially be performed 2| V | - 1 times for all nodes V \ {s, t} (i.e. | V | - 2). This results in a bound of O(V 2) for the relabel operation.
Each saturating push on an admissible arc (u, v) removes the arc from Gf . For the arc to be reinserted into Gf for another saturating push, v must first be relabeled, followed by a push on the arc (v, u), then u must be relabeled. In the process, 𝓁(u) increases by at least two. Therefore, there are O(V) saturating pushes on (u, v), and the total number of saturating pushes is at most 2| V || E |. This results in a time bound of O(VE) for the saturating push operations.
Bounding the number of nonsaturating pushes can be achieved via a potential argument. We use the potential function Φ = ∑[u ∈ V ∧ xf (u) > 0] 𝓁(u) (i.e. Φ is the sum of the labels of all active nodes). It is obvious that Φ is | V | initially and stays nonnegative throughout the execution of the algorithm. Both relabels and saturating pushes can increase Φ. However, the value of Φ must be equal to 0 at termination since there cannot be any remaining active nodes at the end of the algorithm's execution. This means that over the execution of the algorithm, the nonsaturating pushes must make up the difference of the relabel and saturating push operations in order for Φ to terminate with a value of 0.
The relabel operation can increase Φ by at most (2| V | - 1)(| V | - 2). A saturating push on (u, v) activates v if it was inactive before the push, increasing Φ by at most 2| V | - 1. Hence, the total contribution of all saturating pushes operations to Φ is at most (2| V | - 1)(2| V || E |). A nonsaturating push on (u, v) always deactivates u, but it can also activate v as in a saturating push. As a result, it decreases Φ by at least 𝓁(u) − 𝓁(v) = 1. Since relabels and saturating pushes increase Φ, the total number of nonsaturating pushes must make up the difference of (2| V | - 1)(| V | - 2) + (2| V | - 1)(2| V || E |) ≤ 4| V |2| E |. This results in a time bound of O(V 2E) for the nonsaturating push operations.
In sum, the algorithm executes O(V 2) relabels, O(VE) saturating pushes and O(V 2E) nonsaturating pushes. Data structures can be designed to pick and execute an applicable operation in O(1) time. Therefore, the time complexity of the algorithm is O(V 2E).[1][8]
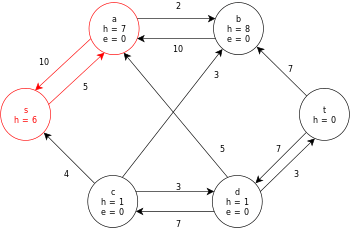
Example
The following is a sample execution of the generic push-relabel algorithm, as defined above, on the following simple network flow graph diagram.
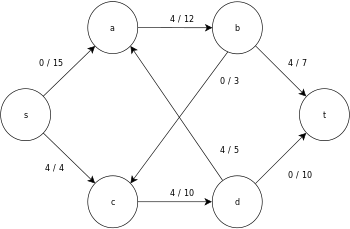
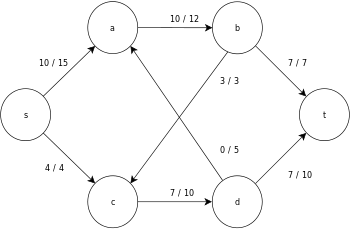
In the example, the h and e values denote the label 𝓁 and excess xf , respectively, of the node during the execution of the algorithm. Each residual graph in the example only contains the residual arcs with a capacity larger than zero. Each residual graph may contain multiple iterations of the perform operation loop.
| Algorithm Operation(s) | Residual Graph |
|---|---|
| Initialise the residual graph by setting the preflow to values 0 and initialising the labeling. | 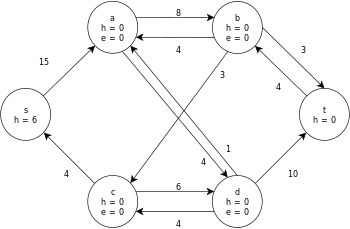 |
| Initial saturating push is performed across all preflow arcs out of the source, s. |  |
| Node a is relabeled in order to push its excess flow towards the sink, t.
The excess at a is then pushed to b then d in two subsequent saturating pushes; which still leaves a with some excess. | |
 | |
| Once again, a is relabeled in order to push its excess along its last remaining positive residual (i.e. push the excess back to s).
The node a is then removed from the set of active nodes. | |
 | |
| Relabel b and then push its excess to t and c. |  |
| Relabel c and then push its excess to d. |  |
| Relabel d and then push its excess to t. |  |
| This leaves the node b as the only remaining active node, but it cannot push its excess flow towards the sink.
Relabel b and then push its excess towards the source, s, via the node a. | |
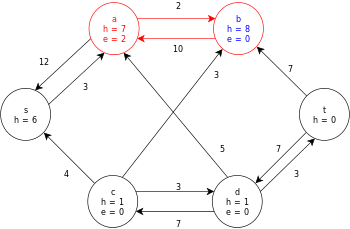 | |
| Push the last bit of excess at a back to the source, s.
There are no remaining active nodes. The algorithm terminates and returns the maximum flow of the graph (as seen above). | |
 |
The example (but with initial flow of 0) can be run here interactively.
Practical implementations
While the generic push–relabel algorithm has O(V 2E) time complexity, efficient implementations achieve O(V 3) or lower time complexity by enforcing appropriate rules in selecting applicable push and relabel operations. The empirical performance can be further improved by heuristics.
"Current-arc" data structure and discharge operation
The "current-arc" data structure is a mechanism for visiting the in- and out-neighbors of a node in the flow network in a static circular order. If a singly linked list of neighbors is created for a node, the data structure can be as simple as a pointer into the list that steps through the list and rewinds to the head when it runs off the end.
Based on the "current-arc" data structure, the discharge operation can be defined. A discharge operation applies on an active node and repeatedly pushes flow from the node until it becomes inactive, relabeling it as necessary to create admissible arcs in the process.
discharge(u):
while xf[u] > 0
if current-arc[u] has run off the end of neighbors[u]
relabel(u)
rewind current-arc[u]
else
let (u, v) = current-arc[u]
if (u, v) is admissible
push(u, v)
let current-arc[u] point to the next neighbor of u
Active node selection rules
Definition of the discharge operation reduces the push–relabel algorithm to repeatedly selecting an active node to discharge. Depending on the selection rule, the algorithm exhibits different time complexities. For the sake of brevity, we ignore s and t when referring to the nodes in the following discussion.
FIFO selection rule
The FIFO push–relabel algorithm[2] organizes the active nodes into a queue. The initial active nodes can be inserted in arbitrary order. The algorithm always removes the node at the front of the queue for discharging. Whenever an inactive node becomes active, it is appended to the back of the queue.
The algorithm has O(V 3) time complexity.
Relabel-to-front selection rule
The relabel-to-front push–relabel algorithm[1] organizes all nodes into a linked list and maintains the invariant that the list is topologically sorted with respect to the admissible network. The algorithm scans the list from front to back and performs a discharge operation on the current node if it is active. If the node is relabeled, it is moved to the front of the list, and the scan is restarted from the front.
The algorithm also has O(V 3) time complexity.
Highest label selection rule
The highest-label push–relabel algorithm[9] organizes all nodes into buckets indexed by their labels. The algorithm always selects an active node with the largest label to discharge.
The algorithm has O(V 2√E) time complexity. If the lowest-label selection rule is used instead, the time complexity becomes O(V 2E).[3]
Implementation techniques
Although in the description of the generic push–relabel algorithm above, 𝓁(u) is set to zero for each node u other than s and t at the beginning, it is preferable to perform a backward breadth-first search from t to compute exact labels.[2]
The algorithm is typically separated into two phases. Phase one computes a maximum pre-flow by discharging only active nodes whose labels are below n. Phase two converts the maximum preflow into a maximum flow by returning excess flow that cannot reach t to s. It can be shown that phase two has O(VE) time complexity regardless of the order of push and relabel operations and is therefore dominated by phase one. Alternatively, it can be implemented using flow decomposition.[10]
Heuristics are crucial to improving the empirical performance of the algorithm.[11] Two commonly used heuristics are the gap heuristic and the global relabeling heuristic.[2][12] The gap heuristic detects gaps in the labeling function. If there is a label 0 < 𝓁' < | V | for which there is no node u such that 𝓁(u) = 𝓁', then any node u with 𝓁' < 𝓁(u) < | V | has been disconnected from t and can be relabeled to (| V | + 1) immediately. The global relabeling heuristic periodically performs backward breadth-first search from t in Gf to compute the exact labels of the nodes. Both heuristics skip unhelpful relabel operations, which are a bottleneck of the algorithm and contribute to the ineffectiveness of dynamic trees.[4]
Sample implementations
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define NODES 6
#define MIN(X,Y) ((X) < (Y) ? (X) : (Y))
#define INFINITE 10000000
void push(const int * const * C, int ** F, int *excess, int u, int v) {
int send = MIN(excess[u], C[u][v] - F[u][v]);
F[u][v] += send;
F[v][u] -= send;
excess[u] -= send;
excess[v] += send;
}
void relabel(const int * const * C, const int * const * F, int *height, int u) {
int v;
int min_height = INFINITE;
for (v = 0; v < NODES; v++) {
if (C[u][v] - F[u][v] > 0) {
min_height = MIN(min_height, height[v]);
height[u] = min_height + 1;
}
}
};
void discharge(const int * const * C, int ** F, int *excess, int *height, int *seen, int u) {
while (excess[u] > 0) {
if (seen[u] < NODES) {
int v = seen[u];
if ((C[u][v] - F[u][v] > 0) && (height[u] > height[v])){
push(C, F, excess, u, v);
}
else
seen[u] += 1;
} else {
relabel(C, F, height, u);
seen[u] = 0;
}
}
}
void moveToFront(int i, int *A) {
int temp = A[i];
int n;
for (n = i; n > 0; n--){
A[n] = A[n-1];
}
A[0] = temp;
}
int pushRelabel(const int * const * C, int ** F, int source, int sink) {
int *excess, *height, *list, *seen, i, p;
excess = (int *) calloc(NODES, sizeof(int));
height = (int *) calloc(NODES, sizeof(int));
seen = (int *) calloc(NODES, sizeof(int));
list = (int *) calloc((NODES-2), sizeof(int));
for (i = 0, p = 0; i < NODES; i++){
if((i != source) && (i != sink)) {
list[p] = i;
p++;
}
}
height[source] = NODES;
excess[source] = INFINITE;
for (i = 0; i < NODES; i++)
push(C, F, excess, source, i);
p = 0;
while (p < NODES - 2) {
int u = list[p];
int old_height = height[u];
discharge(C, F, excess, height, seen, u);
if (height[u] > old_height) {
moveToFront(p,list);
p=0;
}
else
p += 1;
}
int maxflow = 0;
for (i = 0; i < NODES; i++)
maxflow += F[source][i];
free(list);
free(seen);
free(height);
free(excess);
return maxflow;
}
void printMatrix(const int * const * M) {
int i,j;
for (i = 0; i < NODES; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < NODES; j++)
printf("%d\t",M[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
}
int main(void) {
int **flow, **capacities, i;
flow = (int **) calloc(NODES, sizeof(int*));
capacities = (int **) calloc(NODES, sizeof(int*));
for (i = 0; i < NODES; i++) {
flow[i] = (int *) calloc(NODES, sizeof(int));
capacities[i] = (int *) calloc(NODES, sizeof(int));
}
//Sample graph
capacities[0][1] = 2;
capacities[0][2] = 9;
capacities[1][2] = 1;
capacities[1][3] = 0;
capacities[1][4] = 0;
capacities[2][4] = 7;
capacities[3][5] = 7;
capacities[4][5] = 4;
printf("Capacity:\n");
printMatrix(capacities);
printf("Max Flow:\n%d\n", pushRelabel(capacities, flow, 0, 5));
printf("Flows:\n");
printMatrix(flow);
return 0;
}
def relabel_to_front(C, source, sink):
n = len(C) # C is the capacity matrix
F = [[0] * n for _ in xrange(n)]
# residual capacity from u to v is C[u][v] - F[u][v]
height = [0] * n # height of node
excess = [0] * n # flow into node minus flow from node
seen = [0] * n # neighbours seen since last relabel
# node "queue"
nodelist = [i for i in xrange(n) if i != source and i != sink]
def push(u, v):
send = min(excess[u], C[u][v] - F[u][v])
F[u][v] += send
F[v][u] -= send
excess[u] -= send
excess[v] += send
def relabel(u):
# find smallest new height making a push possible,
# if such a push is possible at all
min_height = ∞
for v in xrange(n):
if C[u][v] - F[u][v] > 0:
min_height = min(min_height, height[v])
height[u] = min_height + 1
def discharge(u):
while excess[u] > 0:
if seen[u] < n: # check next neighbour
v = seen[u]
if C[u][v] - F[u][v] > 0 and height[u] > height[v]:
push(u, v)
else:
seen[u] += 1
else: # we have checked all neighbours. must relabel
relabel(u)
seen[u] = 0
height[source] = n # longest path from source to sink is less than n long
excess[source] = Inf # send as much flow as possible to neighbours of source
for v in xrange(n):
push(source, v)
p = 0
while p < len(nodelist):
u = nodelist[p]
old_height = height[u]
discharge(u)
if height[u] > old_height:
nodelist.insert(0, nodelist.pop(p)) # move to front of list
p = 0 # start from front of list
else:
p += 1
return sum(F[source])
References
- 1 2 3 Cormen, T. H.; Leiserson, C. E.; Rivest, R. L.; Stein, C. (2001). "§26 Maximum flow". Introduction to Algorithms (2nd ed.). The MIT Press. pp. 643–698. ISBN 0262032937.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Goldberg, A V; Tarjan, R E (1986). "A new approach to the maximum flow problem". Proceedings of the eighteenth annual ACM symposium on Theory of computing - STOC '86. p. 136. doi:10.1145/12130.12144. ISBN 0897911938.
- 1 2 Ahuja, Ravindra K.; Kodialam, Murali; Mishra, Ajay K.; Orlin, James B. (1997). "Computational investigations of maximum flow algorithms". European Journal of Operational Research. 97 (3): 509. doi:10.1016/S0377-2217(96)00269-X.
- 1 2 3 Goldberg, Andrew V. (2008). "The Partial Augment–Relabel Algorithm for the Maximum Flow Problem". Algorithms - ESA 2008. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. 5193. p. 466. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-87744-8_39. ISBN 978-3-540-87743-1.
- ↑ Goldberg, Andrew V (1997). "An Efficient Implementation of a Scaling Minimum-Cost Flow Algorithm". Journal of Algorithms. 22: 1. doi:10.1006/jagm.1995.0805.
- ↑ Ahuja, Ravindra K.; Orlin, James B. (1991). "Distance-directed augmenting path algorithms for maximum flow and parametric maximum flow problems". Naval Research Logistics. 38 (3): 413. doi:10.1002/1520-6750(199106)38:3<413::AID-NAV3220380310>3.0.CO;2-J.
- ↑ Goldberg, Andrew V.; Tarjan, Robert E. (2014). "Efficient maximum flow algorithms". Communications of the ACM. 57 (8): 82. doi:10.1145/2628036.
- 1 2 3 4 Goldberg, Andrew V.; Tarjan, Robert E. (1988). "A new approach to the maximum-flow problem". Journal of the ACM. 35 (4): 921. doi:10.1145/48014.61051.
- ↑ Cheriyan, J.; Maheshwari, S. N. (1988). "Analysis of preflow push algorithms for maximum network flow". Foundations of Software Technology and Theoretical Computer Science. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. 338. p. 30. doi:10.1007/3-540-50517-2_69. ISBN 978-3-540-50517-4.
- ↑ Ahuja, R. K.; Magnanti, T. L.; Orlin, J. B. (1993). Network Flows: Theory, Algorithms, and Applications (1st ed.). Prentice Hall. ISBN 013617549X.
- ↑ Cherkassky, Boris V.; Goldberg, Andrew V. (1995). "On implementing push-relabel method for the maximum flow problem". Integer Programming and Combinatorial Optimization. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. 920. p. 157. doi:10.1007/3-540-59408-6_49. ISBN 978-3-540-59408-6.
- ↑ Derigs, U.; Meier, W. (1989). "Implementing Goldberg's max-flow-algorithm ? A computational investigation". ZOR Zeitschrift für Operations Research Methods and Models of Operations Research. 33 (6): 383. doi:10.1007/BF01415937.