Rakhadrak Hermitage
| Rakhadrak Hermitage | |
|---|---|
 Rakhadrak Hermitage. | |
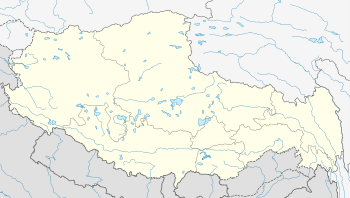 Rakhadrak Hermitage Location within Tibet | |
| Coordinates | 29°42′11″N 91°08′43″E / 29.70306°N 91.14528°E |
| Monastery information | |
| Location | Lhasa Prefecture, Tibet, China |
| Type | Tibetan Buddhist |
| Colleges | Part of Sera Monastery |
Rakhadrak Hermitage (Ra kha brag ri khrod) is a historical hermitage, belonging to the Sera Monastery. It is located to the northeast of Sera and to the north of Lhasa in Tibet Autonomous Region.[1] It is located just up the mountain from the Keutsang Hermitage.
History
The historical fame of the hermitage is two-fold. One is that Tsongkhapa created his great classic treatise known as “The Essence of Eloquence that Distinguishes Between the Provisional and Definitive Meaning of the Scriptures (Drang nges legs bshad snying po)”. The second aspect is that a letter known as “bearers of the golden letter” (gser yig pa) was formally handed over to Tsongkhapa here, brought by a delegation from the Emperor of China. The letter was an invitation from the Chinese Emperor to Tsongkhapa to visit his court in China.[2]
In the 18th century, the hermitage was also established by Sgrub khang dge legs rgya mtsho (1641–1713) as a formal monastic institution with twelve fully ordained monks. The hermitage is also part of the “Sixth-Month Fourth-Day” (drug pa tshe bzhi) pilgrimage circuit. Another account (oral account) attributes building of the hermitage in the 17th century to a student of the Fifth Dalai Lama (Da lai bla ma sku phreng lnga pa).[2]
It is said that the mother of the Fifth Dalai Lama (Da lai bla ma sku phreng lnga pa) was the hermitage’s benefactor.[1] Under her patronage the upper temple complex was built as a formal monastery. However, it has also been inferred that the compound wall precincts (with housing complex) of the upper temple was built in the seventeenth century first, with financial support from the members of Dalai Lama’s court. During subsequent periods, the hermitage probably came under the control of the Sgrub khang dge legs rgya mtsho when it became a popular monastery.[2]
Structure

The hermitage was built in two segments – the upper and the lower. The lower part, which has an orange hut, had a compound wall where caves of Tsongkhapa (1357–1419), Rgyal tshab rje (1364–1432) and Mkhas grub rje (1385–1438) existed. The “Ganden Feast of the 25th” (dga’ ldan lnga mchod), a commemoration of the death-date of Tsongkhapa, used to be observed here at a small hut. This tradition was initiated by Byams chen chos rje (1354–1435), the founder of Sera who lived in the small hut. A small kitchen and a large building (residence for monks) are also seen to the north of the compound wall.[3]
The upper part of the hermitage had also a compound where the main temple, a kitchen, a bla ma’s residence, rooms for visiting Sera monks existed. A temple to Tsongkhapa was also located here, which had thousands of small pressed-clay tablets (tsa tsa) of him.[3]
Post revolution period
The hermitage was destroyed during the Cultural Revolution of 1959. In the 1980s, Sera took control of the hermitage complex. However, rebuilding activity has been sporadic and monastic rituals are not held. Two monks of Sera monastery keep it open for pilgrims.[2]
References
- 1 2 "Rakhadrak Hermitage" (pdf). The Tibetan & Himalayan Library. Retrieved 2010-03-03.
- 1 2 3 4 "Sera Monastery". history. The Tibetan and Himalayan Library. Retrieved 2010-03-05.
- 1 2 "Sera Monastery". Location and layout. The Tibetan and Himalayan Library. Retrieved 2010-03-05.
External links
| Part of a series on |
| Tibetan Buddhism |
|---|
 |
|
Practices and attainment |
|
History and overview |
|