S7 Airlines
 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Founded | May 1992 (as Siberia Airlines) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hubs | |||||||
| Focus cities | |||||||
| Frequent-flyer program | S7 Priority | ||||||
| Alliance | Oneworld | ||||||
| Fleet size | 66 (incl Globus Airlines) | ||||||
| Destinations | 87 | ||||||
| Company slogan | Freedom to choose | ||||||
| Headquarters | Novosibirsk, Russia, Russia | ||||||
| Key people | Vladimir Obyedkov, General Director | ||||||
| Employees | 3,000 [1] | ||||||
| Website | s7.ru | ||||||
PJSC Siberia Airlines (Russian: ПАО «Авиакомпания "Сибирь"» "PАО Aviakompania Sibir"), operating as S7 Airlines, is an airline headquartered in Novosibirsk Oblast, Russia,[2][3] with offices in Moscow.[4] As of 2008, it was Russia's biggest domestic airline.[5] Its main bases are Domodedovo International Airport and Tolmachevo Airport.
History
What is now S7 Airlines started in 1957 as "the Tolmachevo united squadron" of the General Directorate of Civil Aviation of the USSR. After the Soviet Union disintegration and during 1990's Russian economic reforms a state-run "Siberia Airlines" was created based on the squadron in 1992 and later privatized in 1994. The same year Siberia was assigned an IATA airline code. Siberia Airlines was rebranded S7 Airlines in 2006.


In 1997, Siberia Airlines tried to buy Vnukovo Airlines, to make Moscow its next main hub, but this didn't eventuate.
After the 1998 Russian financial crisis, Vnukovo Airlines was heading towards bankruptcy, and Siberia Airlines advised it to merge, but Vnukovo refused. In 1999, Siberia Airlines signed a document for the Vnukovo Airlines take-over, in the event the airline ceased operations due to insolvency. S7 Airlines began merging with Vnukovo Airlines in 2001. S7 Airlines had acquired all the aircraft from Vnukovo Airlines including Tupolev Tu-154, Tupolev Tu-204-100 and Ilyushin Il-86.
In 2001, the airline absorbed Baikal Airlines and then in 2004, the airline absorbed Chelyabinsk Airlines and Enkor.[6] In 2002, S7 Airlines (then known as Siberia Airlines) painted all Vnukovo Airlines fleet with Siberia Airlines livery and the airline began its service from Moscow-Vnukovo, but after some time it shifted all the flights, including the charters from Moscow-Sheremetyevo, to Moscow-Domodedovo.
The first western aircraft, Airbus A310s, were acquired in 2004. In summer 2004, during the Farnborough Airshow, the company signed a memorandum of understanding to purchase 50 of the new Sukhoi Russian Regional Jet, with the first plane to be delivered in 2007. However, the airline subsequently dropped its plans to order this aircraft, citing that the aircraft's changed specifications no longer met its requirements.[7]
In line with an IATA resolution, from December 2006 the airline began to publish its fares for international destinations originating in Russia in euros, rather than US dollars. This resulted in a fare increase, as the conversion rate used was 1 euro = 1 US dollar. Fuel surcharges were also published in euros. Its domestic fares were still to be shown in the local currency.[8] Also in December 2006, the airline became the second Russian air carrier to complete, and pass, the IATA International Safety Audit (IOSA), which is the first global air safety standard. On 27 September 2007, OAO Sibir Airlines /S7 Airlines/ received an official notice of IATA when the carrier was entered in the register of operators IOSA.[9]
It was announced in April 2007 that a new division had been set up within the airline, called Globus. This division was to focus on charter flights for tourists to foreign holiday destinations. Initially, the aircraft for this division would be drawn from the mainline fleet, but during 2010–2014, 10 Boeing 737–800 aircraft were leased with an all-economy layout, with the option for a further 10 aircraft.[10]
On 29 May 2007, the airline announced a proposed order for 15 Boeing 787 Dreamliners scheduled for delivery in 2014, with an option for 10 additional aircraft.[11] However, the order was officially cancelled on 29 January 2009, with S7 stating that it was considering the possibility of taking the aircraft under a leasing scheme.[12]
As of November 2008, all Soviet-made aircraft had left the fleet.[13]
In November 2015, S7 Airlines made an offer to acquire a majority stake in bankrupt Transaero. However, the proposal was rejected by shareholders.[14]
S7 joined the Oneworld alliance in 2010.[15]
In 2016, American band OK Go partnered with S7 to film a "zero-g" music video, Upside Down & Inside Out, aboard a reduced gravity aircraft.[16][17]
Destinations
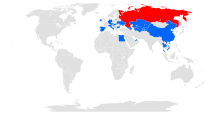

S7 has operated scheduled passenger flights to destinations in Russia, as well as international services to Armenia, Austria, Azerbaijan, Bulgaria, PR China, Cyprus, Czech Republic, France, Georgia, Germany, Hong Kong, Ireland, Italy, Japan, Kazakhstan, Korea (South), Kyrgyzstan, Moldova, Montenegro, Spain, Tajikistan, Thailand, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan and the United Arab Emirates.
Codeshare agreements
S7 codeshares with the following airlines:[15]
Fleet
Current fleet
_(6441118793).jpg)
_FRA_30JUN13_(9201617860).jpg)

As of March 2016, the S7 Airlines fleet consists of the following aircraft:[18][19]
| Aircraft | In Service | Orders | Passengers | Notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Y | Total | ||||
| Airbus A319-100 | 20 | — | — | 144 | 144 | One in oneworld livery[19] |
| Airbus A320-200 | 19 | 3[20] | 8 | 150 | 158 | |
| Airbus A320neo | — | 3 | TBA | Russian launch customer Enter into service 2017[21] | ||
| Airbus A321-200 | 6 | 4 | 8 | 189 | 197 | |
| Airbus A321neo | — | 5 | TBA | Russian launch customer Enter into service 2017[21] | ||
| Boeing 737-800 | 19 | 6 | 12 | 154 | 166 | Operated by Globus Airlines One in oneworld livery[19] |
| 8 | 168 | 176 | ||||
| Boeing 737 MAX 8 | — | 9 | TBA | Russian launch customer Enter into service September 2018.[22] | ||
| Boeing 767-300ER | 2 | — | 18 | 222 | 240 | To be phased out in 2017 To be replaced by Airbus A321neo[23] |
| 12 | 240 | 252 | ||||
| Embraer E170 | — | 17 | TBA | Entry into service 2016[24] | ||
| Total | 66 | 47 | ||||
Fleet history


At different times, the S7 Airlines fleet has consisted of the following aircraft:[25]
| Aircraft | Years of Operation |
Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Airbus A310-200 | 2004—2010 | 5 now stored |
| Airbus A310-300 | 2004—2014 | 3 now stored, one written off |
| Airbus A319-100 | 2006— | |
| Airbus A320-200 | 2008— | One sold to Armavia, 9 still in operation Currently, the youngest aircraft in the fleet. |
| Antonov An-24 | 1992—2000 | Received from Aeroflot, used for domestic flights |
| Boeing 737–400 | 2006—2008 (In S7) 2008—2015 (in Globus) |
transferred to Globus Airlines, then retired. |
| Boeing 737–500 | 2005—2009 | Replaced Tupolev Tu-154B-2. 3 sold to Air Ivoire and 7 to Aero Contractors |
| Boeing 737–800 | 2008— | Currently, all operated by Globus Airlines. |
| Boeing 767-300ER | 2008— | Currently, the oldest aircraft in the fleet. Replaced Ilyushin Il-86 Planned to be replaced in 2017 by Airbus A321neo. |
| Ilyushin Il-86 | 1992—2008 | 1 sold to Ural Airlines, 5 were in the fleet since 1992, other from Vnukovo Airlines. Replaced by Boeing 767-300ER |
| Tupolev Tu-154B-2 | 1992—2004 | All written off in 2004 |
| Tupolev Tu-154M | 1992—2009 (in S7) 2009 (in Globus) |
3 transferred to Globus Airlines, 2 written off, 2 stored. Replaced by Airbus A320 and Boeing 737-800 |
| Tupolev Tu-204-100 | 1992—2005 | All incorporated from Vnukovo Airlines, replaced by Airbus A310 |
Incidents and accidents
- On 4 October 2001, Siberia Airlines Flight 1812, a Tupolev Tu-154M, registration RA-85693, en route from Tel Aviv to Novosibirsk crashed into the Black Sea off Sochi, after being hit with a S-200V surface-to-air missile fired as part of a Ukrainian Air Defense exercise staged off Cape Opuk (or Chuluk) in Crimea. All 78 people on board were killed.[26]
- On 24 August 2004, Siberia Airlines Flight 1047, a Tupolev Tu-154B2, registration RA-85556, en route from Moscow to Sochi exploded and crashed due to a terrorist bombing near Rostov-on-Don, Russia, killing all 46 people on board.
- On 9 July 2006, S7 Airlines Flight 778, an Airbus A310 carrying 193 passengers and 10 crew members, suffered a landing accident at the Irkutsk International Airport in Siberia. The jet failed to decelerate on landing, overran the runway and crashed into a concrete barricade. 124 people died.[27][28]
Subsidiaries
Sibir Technics LCC is a subsidiary of S7, located on the grounds of Tolmachevo Airport.[29]
See also
References
- ↑ https://www.oneworld.com/news-information/oneworld-fact-sheets/oneworld-at-a-glance/
- ↑ "Talk to Us." S7 Airlines. Retrieved on 21 June 2010. "Legal Department, S7 AIRLINES, Ob-2, Novosibirsk Region, 633102, Russia "
- ↑ Головной офис Россия 633104 Обь-4 Новосибирская обл (in Russian). S7 Airlines. Retrieved 4 October 2009.
- ↑ "Headquarters." S7 Airlines. Retrieved on 4 October 2009. Archived 2 May 2012 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Russian airline growth slows from over 20% to under 5%; S7 extends lead over Aeroflot in domestic market". anna.aero. PPS Publications. 3 October 2008. Retrieved 18 May 2013.
- ↑ Artem Fetisov On the Mend, November 1, 2006, Air Transport World (subscription required)
- ↑ Flight Global, 7 February 2006
- ↑ "IATA converts fares to euros" (Press release). S7 Airlines. 2006-11-15. Retrieved 17 November 2010.
- ↑ "S7 Airlines Successfully Completed IATA Operational Safety Audit and was Awarded IOSA Certificate" (Press release). S7 Airlines. 2 October 2007. Retrieved 17 November 2010.
- ↑ "S7 Сharter начнёт эксплуатацию самолётов нового поколения Boeing 737–800" (in Russian). S7 Airlines. Retrieved 17 November 2010.
- ↑ Announcement by Boeing of Dreamliner order 29 May 2007.
- ↑ Zaitsev, Tom (2009-01-29). "S7 confirms 787 cancellation but considers lease instead". Flight Global. Retrieved 17 November 2010.
- ↑ "Флот S7" (in Russian). S7 Airlines.
- ↑ ch-aviation.com - S7's Filev fails in bid to acquire control of Transaero 4 November 2015
- 1 2 "Profile on S7 Airlines". CAPA. Centre for Aviation. Archived from the original on 2016-10-31. Retrieved 2016-10-31.
- ↑ Sage, Alyssa (2016-02-11). "Watch: OK Go Filmed a Music Video Entirely in Zero Gravity". Variety. Retrieved 2016-02-12.
- ↑ "Upside Down and Inside Out FAQ & Credits".
- ↑ ch-aviation.com - S7 Airlines retrieved 7 December 2015
- 1 2 3 "Our Fleet". s7.ru. S7 Airlines. Retrieved 25 October 2016.
- ↑ airbus.com - Orders & deliveries retrieved 7 December 2015
- 1 2 "Russia's S7 Airlines to lease A321neo, A320neo from ALC". ch-aviation. 8 April 2016. Retrieved 20 May 2016.
- ↑ "S7 Group станет первым российским покупателем лайнеров Boeing нового поколения". «Ведомости» (Vedomosti). 21 September 2016. Retrieved 21 September 2016.
- ↑ "S7 Airlines расширила парк узкофюзеляжных самолетов А321". ATO.ru. Авиатранспортное обозрение. 31 May 2016. Retrieved 31 May 2016.
- ↑ "Компания S7 купит у Embraer на поставку 17 самолетов". Interfax. 21 October 2016. Retrieved 21 October 2016.
- ↑ Sibir Airlines S7 Fleet | Airfleets aviation. Airfleets.net. Retrieved on 2010-11-16.
- ↑ "Aircraft accident Tupolev 154M RA-85693 Adler, Russia [Black Sea]". Aviation Safety Network. Retrieved 22 June 2014.
- ↑ Passenger plane crashes in Russia BBC News 9 July 2006
- ↑ '150 dead' in Russian jet crash CNN, 8 July 2006
- ↑ "Sibir Technics." S7 Airlines. Retrieved on 21 June 2010. Archived 5 May 2012 at the Wayback Machine.
External links
![]() Media related to S7 Airlines at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to S7 Airlines at Wikimedia Commons
- Official website (Mobile) (English) (Chinese) (Russian)