Hop (protein)
| STIP1 | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
|||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | STIP1, HEL-S-94n, HOP, IEF-SSP-3521, P60, STI1, STI1L, stress induced phosphoprotein 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 605063 MGI: 109130 HomoloGene: 4965 GeneCards: STIP1 | ||||||||||||||||
| Genetically Related Diseases | |||||||||||||||||
| attention deficit hyperactivity disorder[1] | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||||||||
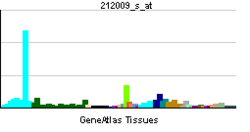  | |||||||||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||||||
| Entrez | |||||||||||||||||
| Ensembl | |||||||||||||||||
| UniProt | |||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | |||||||||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 11: 64.19 – 64.2 Mb | Chr 19: 7.02 – 7.04 Mb | |||||||||||||||
| PubMed search | [2] | [3] | |||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
Hop, occasionally written HOP, is an abbreviation for Hsp70-Hsp90 Organizing Protein. It functions as a co-chaperone which reversibly links together the protein chaperones Hsp70 and Hsp90.[4]
Hop belongs to the large group of co-chaperones, which regulate and assist the major chaperones (mainly heat shock proteins). It is one of the best studied co-chaperones of the Hsp70/Hsp90-complex. It was first discovered in yeast and homologues were identified in human, mouse, rat, insects, plants, parasites, and virus. The family of these proteins is referred to as STI1 (stress inducible protein) and can be divided into yeast, plant, and animal STI1 (Hop).
Synonyms
|
|
Gene
The gene for human Hop is located on chromosome 11q13.1 and consists of 14 exons.
Structure
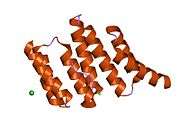
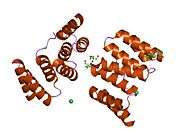
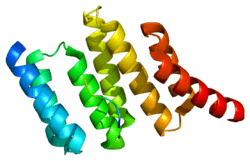
STI proteins are characterized by some structural features: All homologues have nine tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR) motifs, that are clustered into domains of three TPRs. The TPR motif is a very common structural feature used by many proteins and provides the ability of directing protein-protein interactions. Crystallographic structural information is available for the N-terminal TPR1 and the central TPR2A domains in complex with Hsp90 resp. Hsp70 ligand peptides.[5]
Function
The main function of Hop is to link Hsp70 and Hsp90 together. But recent investigations indicate that it also modulates the chaperone activities of the linked proteins and possibly interacts with other chaperones and proteins. Apart from its role in the Hsp70/Hsp90 "chaperone machine" it seems to participate in other protein complexes too (for example in the signal transduction complex EcR/USP and in the Hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase complex, which enables the viral replication). It acts as a receptor for prion proteins too.[6][7] Hop is located in diverse cellular regions and also moves between the cytoplasm and the nucleus.
Interactions
Hop (protein) has been shown to interact with PRNP[8] and Heat shock protein 90kDa alpha (cytosolic), member A1.[9][10]
References
- ↑ "Diseases that are genetically associated with STIP1 view/edit references on wikidata".
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Odunuga OO, Longshaw VM, Blatch GL (2004). "Hop: more than an Hsp70/Hsp90 adaptor protein". BioEssays. 26 (10): 1058–68. doi:10.1002/bies.20107. PMID 15382137.
- ↑ Scheufler C, Brinker A, Bourenkov G, Pegoraro S, Moroder L, Bartunik H, Hartl FU, Moarefi I (2000). "Structure of TPR Domain–Peptide Complexes". Cell. 101 (2): 199–210. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80830-2. PMID 10786835.
- ↑ Martins VR, Graner E, Garcia-Abreu J, de Souza SJ, Mercadante AF, Veiga SS, Zanata SM, Neto VM, Brentani RR (1997). "Complementary hydropathy identifies a cellular prion protein receptor". Nat Med. 3 (12): 1376–1382. doi:10.1038/nm1297-1376. PMID 9396608.
- ↑ Zanata SM, Lopes MH, Mercadante AF, Hajj GN, Chiarini LB, Nomizo R, Freitas AR, Cabral AL, Lee KS, Juliano MA, de Oliveira E, Jachieri SG, Burlingame A, Huang L, Linden R, Brentani RR, Martins VR (2002). "Stress-inducible protein 1 is a cell surface ligand for cellular prion that triggers neuroprotection". EMBO J. 21 (13): 3307–3316. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdf325. PMC 125391
 . PMID 12093732.
. PMID 12093732. - ↑ Zanata SM, Lopes MH, Mercadante AF, Hajj GN, Chiarini LB, Nomizo R, Freitas AR, Cabral AL, Lee KS, Juliano MA, de Oliveira E, Jachieri SG, Burlingame A, Huang L, Linden R, Brentani RR, Martins VR (July 2002). "Stress-inducible protein 1 is a cell surface ligand for cellular prion that triggers neuroprotection". EMBO J. 21 (13): 3307–16. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdf325. PMC 125391
 . PMID 12093732.
. PMID 12093732. - ↑ Scheufler C, Brinker A, Bourenkov G, Pegoraro S, Moroder L, Bartunik H, Hartl FU, Moarefi I (April 2000). "Structure of TPR domain-peptide complexes: critical elements in the assembly of the Hsp70-Hsp90 multichaperone machine". Cell. 101 (2): 199–210. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80830-2. PMID 10786835.
- ↑ Johnson BD, Schumacher RJ, Ross ED, Toft DO (February 1998). "Hop modulates Hsp70/Hsp90 interactions in protein folding". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (6): 3679–86. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.6.3679. PMID 9452498.
Further reading
- Rasmussen HH, van Damme J, Puype M, Gesser B, Celis JE, Vandekerckhove J (1993). "Microsequences of 145 proteins recorded in the two-dimensional gel protein database of normal human epidermal keratinocytes". Electrophoresis. 13 (12): 960–9. doi:10.1002/elps.11501301199. PMID 1286667.
- Honoré B, Leffers H, Madsen P, Rasmussen HH, Vandekerckhove J, Celis JE (1992). "Molecular cloning and expression of a transformation-sensitive human protein containing the TPR motif and sharing identity to the stress-inducible yeast protein STI1". J. Biol. Chem. 267 (12): 8485–91. PMID 1569099.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Bonaldo MF, Lennon G, Soares MB (1997). "Normalization and subtraction: two approaches to facilitate gene discovery". Genome Res. 6 (9): 791–806. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.791. PMID 8889548.
- Dittmar KD, Pratt WB (1997). "Folding of the glucocorticoid receptor by the reconstituted Hsp90-based chaperone machinery. The initial hsp90.p60.hsp70-dependent step is sufficient for creating the steroid binding conformation". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (20): 13047–54. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.20.13047. PMID 9148915.
- Dittmar KD, Demady DR, Stancato LF, Krishna P, Pratt WB (1997). "Folding of the glucocorticoid receptor by the heat shock protein (hsp) 90-based chaperone machinery. The role of p23 is to stabilize receptor.hsp90 heterocomplexes formed by hsp90.p60.hsp70". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (34): 21213–20. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.34.21213. PMID 9261129.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, Suyama A, Sugano S (1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–56. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- Zou J, Guo Y, Guettouche T, Smith DF, Voellmy R (1998). "Repression of heat shock transcription factor HSF1 activation by HSP90 (HSP90 complex) that forms a stress-sensitive complex with HSF1". Cell. 94 (4): 471–80. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81588-3. PMID 9727490.
- Scanlan MJ, Gordan JD, Williamson B, Stockert E, Bander NH, Jongeneel V, Gure AO, Jäger D, Jäger E, Knuth A, Chen YT, Old LJ (1999). "Antigens recognized by autologous antibody in patients with renal-cell carcinoma". Int. J. Cancer. 83 (4): 456–64. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(19991112)83:4<456::AID-IJC4>3.0.CO;2-5. PMID 10508479.
- Scheufler C, Brinker A, Bourenkov G, Pegoraro S, Moroder L, Bartunik H, Hartl FU, Moarefi I (2000). "Structure of TPR domain-peptide complexes: critical elements in the assembly of the Hsp70-Hsp90 multichaperone machine". Cell. 101 (2): 199–210. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80830-2. PMID 10786835.
- Hernández MP, Chadli A, Toft DO (2002). "HSP40 binding is the first step in the HSP90 chaperoning pathway for the progesterone receptor". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (14): 11873–81. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111445200. PMID 11809754.
- Brinker A, Scheufler C, Von Der Mulbe F, Fleckenstein B, Herrmann C, Jung G, Moarefi I, Hartl FU (2002). "Ligand discrimination by TPR domains. Relevance and selectivity of EEVD-recognition in Hsp70 x Hop x Hsp90 complexes". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (22): 19265–75. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109002200. PMID 11877417.
- Zanata SM, Lopes MH, Mercadante AF, Hajj GN, Chiarini LB, Nomizo R, Freitas AR, Cabral AL, Lee KS, Juliano MA, de Oliveira E, Jachieri SG, Burlingame A, Huang L, Linden R, Brentani RR, Martins VR (2002). "Stress-inducible protein 1 is a cell surface ligand for cellular prion that triggers neuroprotection". EMBO J. 21 (13): 3307–16. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdf325. PMC 125391
 . PMID 12093732.
. PMID 12093732. - Hernández MP, Sullivan WP, Toft DO (2002). "The assembly and intermolecular properties of the hsp70-Hop-hsp90 molecular chaperone complex". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (41): 38294–304. doi:10.1074/jbc.M206566200. PMID 12161444.
- Abbas-Terki T, Briand PA, Donzé O, Picard D (2003). "The Hsp90 co-chaperones Cdc37 and Sti1 interact physically and genetically". Biol. Chem. 383 (9): 1335–42. doi:10.1515/BC.2002.152. PMID 12437126.
- Imai Y, Soda M, Murakami T, Shoji M, Abe K, Takahashi R (2004). "A product of the human gene adjacent to parkin is a component of Lewy bodies and suppresses Pael receptor-induced cell death". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (51): 51901–10. doi:10.1074/jbc.M309655200. PMID 14532270.
- Longshaw VM, Chapple JP, Balda MS, Cheetham ME, Blatch GL (2004). "Nuclear translocation of the Hsp70/Hsp90 organizing protein mSTI1 is regulated by cell cycle kinases". J. Cell. Sci. 117 (Pt 5): 701–10. doi:10.1242/jcs.00905. PMID 14754904.
- Rush J, Moritz A, Lee KA, Guo A, Goss VL, Spek EJ, Zhang H, Zha XM, Polakiewicz RD, Comb MJ (2005). "Immunoaffinity profiling of tyrosine phosphorylation in cancer cells". Nat. Biotechnol. 23 (1): 94–101. doi:10.1038/nbt1046. PMID 15592455.