Sahara Sea
The Sahara Sea was the name of a hypothetical macro-engineering project which proposed flooding portions of the Sahara Desert with waters from the Atlantic Ocean or Mediterranean Sea. The goal of this unrealized project was to create an inland sea that would cover the substantial areas of the Sahara Desert which lie below sea level, bringing humid air, rain and agriculture deep into the desert.
The possibility of such a project was raised several times by different scientists and engineers during the late 19th century and early 20th century, primarily from European colonial powers in Africa.[1][2] The concept of a flooded Sahara was also featured in novels of the time.[3]
History
19th century
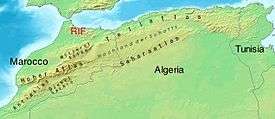
In 1877, British engineer Donald Mackenzie was the first to propose a Sahara Sea be created. Mackenzie proposed cutting a channel from Cape Juby in southern Morocco to a large basin and plain known as El Djouf.[1][4][5] This basin was approximately 61 metres (200 ft) below sea level at its deepest, and would have created an inland sea 155,400 square kilometres (60,000 sq mi) in area. Indeed, geological evidence suggested that this basin had previously been connected to the Atlantic Ocean via a channel near Sakiet el-Hamra.[1] It was further proposed that this inland sea, if augmented with an inland canal, could provide access to the Niger River.[1][5] Mackenzie acknowledged that other desert basins in present-day Tunisia and Algeria shared below-sea-level profiles similar to those observed at El Djouf.[5] These basins contained seasonally dry salt lakes, known as chotts.
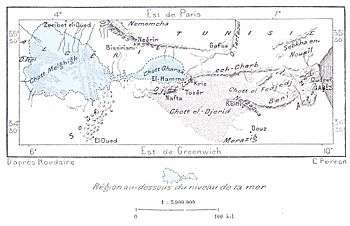
François Elie Roudaire, a French geographer, and Ferdinand de Lesseps, a diplomat influential in the creation of the Suez Canal, proposed this area for the creation of an inland sea in 1878. Roudaire and de Lesseps proposed that a channel be cut from the Gulf of Gabès in the Mediterranean to the Chott el Fejej[6] which would allow the sea to drain into these basins. They were not specific in the area such a sea would cover (although subsequent analyses suggested that it would be considerably smaller than Mackenzie's proposal at only 8,000 square kilometres (3,100 sq mi) in area), but argued that the new inland sea would improve the quality of weather on the European continent.[1][2][7] The estimated cost of the Roudaire project was $30,000,000 at the time.[7]
While Roudaire and de Lesseps were optimistic about the weather effects that such an inland sea would produce in Europe, others were not as hopeful. Alexander William Mitchinson argued that flooding substantial areas would create disease-ridden swamps.[1][8] Others were critical of the feasibility of the project or the proposal to join the sea at El Djouf with the sea in what is now Tunisia and Algeria.[1] The project was ultimately rejected by the French Government and funding was withdrawn when surveys revealed that many areas were not below sea level as had been believed.[2][9]
20th century
The proposal to create a Sahara Sea was revived in the early 1900s by French professor Etchegoyen. Around 1910, Etchegoyen proposed that a longer and deeper channel could be constructed. He argued that such a sea could be a boon for colonization and could potentially produce an inland sea half the size of the Mediterranean. This proposal was considered by the French government but also rejected. Critics noted that, while some parts of the Sahara Desert were indeed below sea level, much of the Sahara Desert was above sea level. This, they said, would produce an irregular sea of bays and coves; it would also be considerably smaller than estimates by Etchegoyen suggested.[1]
A proposal similar to that of Roudaire and de Lesseps was raised by members of Operation Plowshare, an American idea to use nuclear explosives in civil engineering projects such as the Qattara Depression Project.[10]
It was also suggested that nuclear explosives might be detonated to create a channel from the Mediterranean to the chotts of Tunisia.[9][11] This proposal was abandoned,[9] however, with the signing of various treaties prohibiting peaceful nuclear explosions.[10]
Appearances in literature
The notion of a Sahara Sea has been featured several times in literature, most notably in Jules Verne's last novel, Invasion of the Sea, which directly referred to the plan of Roudaire and de Lesseps.[3] The idea of a flooded Sahara Desert also occurs in The Secret People by John Wyndham.
Other desert flooding projects
Since the late 19th century there have been proposals to connect Lake Eyre in the South Australian desert to the ocean via canal.[12]
In 1905, engineers working on an irrigation canal in southern California accidentally released the waters of the Colorado River into a formerly dry basin, creating a large saline lake known as the Salton Sea. Although the lake has shrunk considerably since its creation, it remains the largest lake in the state of California.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Spinage, Clive Alfred (2012). African Ecology: Benchmarks and Historical Perspectives. Springer Geography (Illustrated ed.). New York: Springer. ISBN 3642228712. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- 1 2 3 McKay, Donald Vernon (1943). "Colonialism in the French geographical movement 1871-1881". Geographical Review. American Geographical Society. 33 (2): 214–232. doi:10.2307/209775. JSTOR 209775.
- 1 2 Taves, Brian. "Review of Invasion of the Sea". North American Jules Verne Society. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ↑ Cust, R. (1884). "The railway over the Sahára from Algeria to the Senegál and the destruction of Colonel Flatters". Journal of the Royal United Service Institution. Royal United Services Institute for Defence Studies. 28 (77): 839–856. doi:10.1080/03071848409424351. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- 1 2 3 Mackenzie, Donald (1877). The flooding of the Sahara: an account of the proposed plan for opening Central Africa to commerce and civilization from the north-west coast, with a description of Soudan and western Sahara, and notes of ancient manuscripts, &c. London: Sampson Low, Marston, Searle, & Rivington. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ↑ Hill, Christopher L. (2008). National History and the World of Nations: Capital, State, and the Rhetoric of History in Japan, France, and the United States. Durham, NC: Duke University Press. ISBN 0822343169. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- 1 2 Plummer, Harry Chapin (1913). "A Sea in the Sahara". National Waterways: A Magazine of Transportation. National Rivers and Harbors Congress. 1 (2): 131–138. Retrieved 16 December 2012.
- ↑ Mitchinson, Alexander William (1881). The expiring continent: A narrative of travel in Senegambia, with observations on native character, the present condition and future prospects of Africa and colonisation. London: W. H. Allen & Co. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- 1 2 3 Jacobs, Daniel (2009). The Rough Guide to Tunisia. London: Penguin. ISBN 1405384557. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ↑ Jousiffe, Ann (2010). Tunisia. Globetrotter: Guide and Map Series (4th ed.). London: New Holland Publishers. ISBN 1845378644. Retrieved 16 December 2012.
- ↑ "Bradfields Hydraulic Dreaming".