Lake Eyre
| Kati Thanda–Lake Eyre | |
|---|---|
|
Composite Landsat 7 satellite image using shortwave infrared, near-infrared, and blue wavelengths | |
|
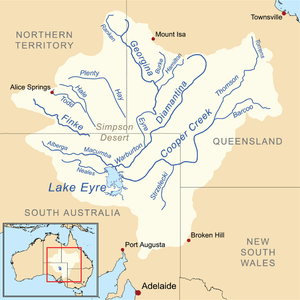
A map of the Lake Eyre basin, with the lake at bottom left | |
| Location | Northern South Australia |
| Coordinates | 28°22′S 137°22′E / 28.367°S 137.367°ECoordinates: 28°22′S 137°22′E / 28.367°S 137.367°E |
| Lake type | Endorheic |
| Primary inflows | Warburton River |
| Primary outflows | evaporation |
| Basin countries | Australia |
| Surface area | 9,500 km2 (3,668 sq mi) (max) |
| Average depth | 1.5 m (5 ft) (every 3 years), 4 m (13 ft) (every decade) |
| Surface elevation |
−9 m (−30 ft) (shoreline when full); −15 m (−49 ft) (lowest point when empty) |
Lake Eyre (/ˈɛər/ AIR), officially known as Kati Thanda–Lake Eyre,[1] contains the lowest natural point in Australia, at approximately 15 m (49 ft) below sea level (AHD), and, on the rare occasions that it fills, is the largest lake in Australia covering 9,500 km2 (3,668 sq mi). The shallow endorheic lake is the depocentre of the vast Lake Eyre basin and is found in Northern South Australia, some 700 km (435 mi) north of Adelaide.
When the lake is full, it has the same salinity level as the sea, but as the lake dries up and the water evaporates, salinity increases.
The lake was named in honour of Edward John Eyre, who was the first European to see it, in 1840. The lake's official name was changed in December 2012 to combine the name "Lake Eyre" with the indigenous name, Kati Thanda.[1] Native title over the lake and surrounding region is held by the Arabana people.[2]
Geography
Kati Thanda–Lake Eyre is located in the deserts of central Australia, in northern South Australia. The Lake Eyre Basin is a large endorheic system surrounding the lakebed, the lowest part of which is filled with the characteristic salt pan caused by the seasonal expansion and subsequent evaporation of the trapped waters. Even in the dry season there is usually some water remaining in Kati Thanda–Lake Eyre, normally collecting in over 200 smaller sub-lakes within its margins. The lake was formed by aeolian processes after tectonic upwarping occurred to the south subsequent to the end of the Pleistocene epoch.[3]
During the rainy season the rivers from the north-east part of the Lake Eyre Basin (in outback (south-west and central) Queensland) flow towards the lake through the Channel Country. The amount of water from the monsoon determines whether water will reach the lake and if it does, how deep the lake will get. The average rainfall in the area of the lake is 100 to 150 millimetres (3.9 to 5.9 in) per year.[3]
The −15 m (−49 ft) altitude usually attributed to Kati Thanda–Lake Eyre refers to the deepest parts of the lake floor, in Belt Bay and the Madigan Gulf. The shoreline lies at −9 m (−30 ft).[4] The lake is the area of maximum deposition of sediment in the Lake Eyre Basin.[5]
Lake Eyre is divided into two sections which are joined by the Goyder Channel. These are known as Lake Eyre North, which is 144 kilometres (89 mi) in length and 65 kilometres (40 mi) wide, and Lake Eyre South, which measures 65 by 24 kilometres (40 by 15 mi).[6] The salt crusts are thickest (up to 50 cm (20 in)) in the southern Belt Bay, Jackboot Bay and Madigan Gulf sub-basins of Lake Eyre North.[7]
Since 1883, proposals have been made to flood Lake Eyre with seawater brought to the basin via a canal or pipeline. The purpose was, in part, to increase evaporation and thereby increase rainfall in the region downwind of an enlarged Lake Eyre.[8] Due to the basin's low elevation below sea level and the region's high annual evaporation rate (between 2,500 and 3,500 millimetres (98 and 138 in)[9]), such schemes have generally been considered impractical as it is likely that accumulation of salt deposits would rapidly block the engineered channel.[10]
Salinity
The salinity in the lake increases as the 450 mm (18 in) salt crust dissolves over a period of six months of a major flood resulting in a massive fish kill. When over 4 m (13 ft) deep the lake is no more salty than the sea, but salinity increases as the water evaporates, with saturation occurring at about a 500 mm (20 in) depth. The lake takes on a pink hue when saturated due to the presence of beta-carotene pigment caused by the algae Dunaliella salina.
Floods
Typically a 1.5 m (5 ft) flood occurs every three years, a 4 m (13 ft) flood every decade, and a fill or near fill a few times a century. The water in the lake soon evaporates with a minor or medium flood drying by the end of the following summer. Most of the water entering the lakes arrives via Warburton River.[3]
In strong La Niña years the lake can fill. Since 1885 this has occurred in 1886–1887, 1889–1890, 1916–1917, 1950, 1955, 1974–1977,[11] and 1999-2001,[12] with the highest flood of 6 m (20 ft) in 1974. Local rain can also fill Kati Thanda–Lake Eyre to 3–4 m (9.8–13.1 ft) as occurred in 1984 and 1989. Torrential rain in January 2007 took about six weeks to reach the lake but put only a small amount of water into it.[13]
When recently flooded the lake is almost fresh and native freshwater fish, including bony bream (Nematolosa erebi), the Lake Eyre Basin sub-species of golden perch (Macquaria ambigua) and various small hardyhead species (Craterocephalus spp.) can survive in it.
2009 to 2011

The 2009 Lake Eyre flood peaked at 1.5 m (5 ft) deep in late May, which is a quarter of its maximum recorded depth of 6 m (20 ft). 9 km3 (2 cu mi) of water crossed the Queensland–South Australian border with most of it coming from massive floods in the Georgina River. However, owing to the very low rainfall in the lower reaches of these rivers (contrasting with heavy rainfall in the upper catchments)[14] the greater proportion soaked into the desert or evaporated en route to the lake, leaving less than 4 km3 (0.96 cu mi) in the lake which covered an area of 800 km2 (309 sq mi) or 12% of the total. As the flood did not start filling the lake's deepest point (Belt Bay) until late March, little bird life appeared preferring instead to nest in the upper reaches of the Lake Eyre Basin, north of Birdsville, where large lakes appeared in January as a result of monsoonal rain.
The high rainfall in summer 2010 sent flood water into the Diamantina, Georgina and Cooper Creek catchments of the Lake Eyre basin, with the Cooper Creek reaching the lake for the first time since 1990. The higher rainfall has prompted many different birds to migrate back to the area for breeding.[15]
Heavy local rain in early March 2011 in the Stuart Creek and Warriner catchments filled Lake Eyre South, with Lake Eyre North about 75 per cent covered with water firstly from the Neales and Macumba Rivers, and later from the Warburton River.[16]
2015 to 2016
In late 2015, water began flowing into Lake Eyre following heavy rain in the north-east of the state.[17]
Yacht club
The Lake Eyre Yacht Club is a dedicated group of sailors who sail on the lake's floods, including recent trips in 1997, 2000, 2001, 2004, 2007 and 2009.[18] A number of 6 m (20 ft) trailer sailers sailed on Kati Thanda–Lake Eyre in 1975, 1976, and 1984 when the flood depth reached 3–6 m (9.8–19.7 ft). In July 2010 The Yacht Club held its first regatta since 1976 and its first on Lake Killamperpunna, a freshwater lake on Cooper Creek. The Cooper had reached Kati Thanda–Lake Eyre for the first time since 1990.
When the lake is full, a notable phenomenon is that around midday the surface can often become very flat. The surface then reflects the sky in a way that leaves both the horizon and water surface virtually impossible to see. The commodore of the Lake Eyre Yacht Club has stated that sailing during this time has the appearance of sailing in the sky.
Land speed record attempts
Kati Thanda–Lake Eyre has been a site for various land speed record attempts on its salt flats, especially those by Donald Campbell with the Bluebird-Proteus CN7.[19]
Wildlife
Phytoplankton in the lake includes Nodularia spumigena and a number of species of Dunaliella.[3]
Birds
Birds such as pelicans and banded stilts are drawn to a filled lake from southern coastal regions of Australia, and from as far afield as Papua New Guinea. During the 1989—90 flood it was estimated that 200,000 pelicans, 80% of Australia's total population, came to feed & roost at Lake Eyre.[20] Scientists are presently unable to determine how such birds appear able to detect the filling of the lake, even when hundreds or thousands of miles away from the basin.[21]
Protected area status
Statutory
The extent of the lake is covered by two protected areas declared by the Government of South Australia - the Kati Thanda-Lake Eyre National Park and the Elliot Price Conservation Park.[22]
Non-statutory
Wetlands
Lake Eyre is on the list of wetlands of national importance known as A Directory of Important Wetlands in Australia.[23]
Important bird area
Lake Eyre has been identified by BirdLife International as an Important Bird Area (IBA) known as the Lake Eyre Important Bird Area because, when flooded, it supports major breeding events of the Banded stilt and Australian pelican, as well as over 1% of the world populations of Red-necked avocets, Sharp-tailed sandpipers, Red-necked stints, Silver gulls and Caspian terns.[24]
See also
References
- 1 2 "New name adopted for outback Lake Eyre". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 19 December 2012. Retrieved 19 December 2012.
- ↑ "Federal Court awards native title over Lake Eyre". ABC News. Australia. 23 May 2012. Retrieved 2 January 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 O'Sullivan, Patrick; C. S. Reynolds (2008). The Lakes Handbook: Lake Restoration and Rehabilitation, Volume 2. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 233–235. ISBN 1405141107. Retrieved 23 December 2012.
- ↑ Lake Eyre. International Lake Environment Committee. Retrieved 29 March 2012.
- ↑ Laity, Julie J. (2009). Deserts and Desert Environments. John Wiley & Sons. p. 112. ISBN 1444300741. Retrieved 20 December 2012.
- ↑ Rafferty, John P. (2007). Lakes and Wetland. The Rosen Publishing Group. p. 186. ISBN 1615303200. Retrieved 20 December 2012.
- ↑ Dulhunty, J.A. (1990): Lake Eyre, In: M.J. Tyler, C.R. Twidale, M. Davis and C.B. Walker, Natural History of the North East Deserts. Royal Society of South Australia Inc. Pp. 101-4. ISBN 0-9596627-5-8
- ↑ Badescu, V., Cathcart, R.B., Bolonkin, A.A., Paulescu, M. and Gravila, P. (2013) Macro-engineering Australia's Lake Eyre with imported seawater. International Journal of Environment and Sustainable Development 12: 264-284.
- ↑ Badman, F.J. (1991): Introduction. In: F.J. Badman, B.K. Arnold and S.L. Belt, A Natural History of the Lake Eyre Region. The South Australian National Parks and Wildlife Service's Northern Consultative Committee. P 1. ISBN 0 646 07183 1
- ↑ The Plan To Fill Lake Eyre TROVE: The Sydney Morning Herald, 27 May 1954. Retrieved 8 February 2016.
- ↑ Allen, Robert J.; The Australasian Summer Monsoon, Teleconnections, and Flooding in the Lake Eyre Basin; published 1985 by Royal Geographical Society of Australasia, S.A. Branch; ISBN 0-909112-09-6
- ↑ Australian Bureau of Meteorology; Annual Climate Summary (2000)
- ↑ "Lake Eyre flooding attracts yachting club interest". ABC News. Australia. 8 March 2007. Retrieved 8 March 2007.
- ↑ Australian Annual Climate Summary 2009
- ↑ Lake Eyre floods again, Australian Geographic, 15 July 2010
- ↑ "Flooding and storms fill outback lake". ABC News. Australia. 9 March 2011. Retrieved 29 March 2012.
- ↑ "Lake Eyre begins filling with water after soaking rains". ABC News. Retrieved 2016-01-04.
- ↑ Welcome to the Lake Eyre Yacht Club. Retrieved 29 March 2012.
- ↑ John Pearson (author). Bluebird and the Dead Lake.
- ↑ TCR, White (2005). Why Does the World Stay Green?: Nutrition and Survival of Plant-eaters. Csiro Publishing. p. 88. ISBN 0643099816. Retrieved 20 December 2012.
- ↑ Birds set to return to Lake Eyre to breed as inland lakes fill with water ABC News, 6 January 2016. Accessed 6 January 2016.
- ↑ "Kati Thanda-Lake Eyre National Park Map" (PDF). Department of Environment, Water and Natural Resources. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ↑ Eyles, Kathy (2001). A Directory of important wetlands in Australia (PDF) (3 ed.). Environment Australia. p. 78. ISBN 978-0-642-54721-7. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
- ↑ "Important Bird Areas factsheet: Lake Eyre". Birdata. Birdlife International. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Lake Eyre. |
- NASA Earth Observatory pages on Lake Eyre:
- Fluctuations of Lake Eyre, South Australia - 5 December 2002 Accessed 5 February 2014.
- Lake Eyre, South Australia - 24 March 2003 Accessed 5 February 2014.
- Lake Eyre Filling Peaks - 21 June 2009 Accessed 5 February 2014.
- Lake Eyre Yacht Club website Accessed 5 February 2014.
- Samela Harris: Lake Eyre pelican mystery Accessed 5 February 2014.
- Dr Vincent Kotwicki: Floods of Lake Eyre Accessed 5 February 2014.
- Salt, an award-winning documentary about Lake Eyre by filmmaker Murray Fredericks