School Lands
School Lands are land grants established in support of education. Support for public education in the United States predates the constitution; two years before the adoption of the United States Constitution of 1787, the Congress of the Confederation provided support for public schooling by establishing the land grants in the Land Ordinance of May 20, 1785[1] which granted Section 16 (one square mile) of every township to be used for public education: "There shall be reserved the Lot No. 16, of every township, for the maintenance of public schools within said township."[2][3]

In the land ordinance, the township is not a civil township but a surveying unit: a six mile by six mile square, divided into 36 one square mile sections. The one square mile Section 16 is located near the center of the township. (For states surveyed under the federal rectangular system, survey townships and civil townships usually have the same boundaries, but there are many exceptions.)[4]
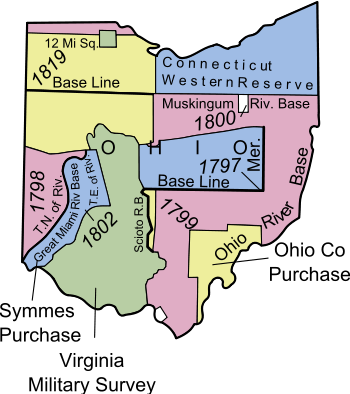
The School Lands are part of the Ohio Lands,[4] comprising land grants in Ohio from the United States federal government for public schools. According to the Official Ohio Lands Book,[4] "by 1920, 73,155,075 acres of public land had been given by the federal government to the public land states in support of public schooling."
In the Land Ordinance of 1785 provision was also made by land grant for higher education (the College Lands).
References
- ↑ A compilation of laws, treaties, resolutions, and ordinances: of the general and state governments, which relate to lands in the state of Ohio; including the laws adopted by the governor and judges; the laws of the territorial legislature; and the laws of this state, to the years 1815-16. G. Nashee, State Printer. 1825. p. 534. page 17.
- ↑ "Ohio Lands: A Short History Part 5". Retrieved 10 March 2011.
- ↑ John Kilbourne (1907). "The Public Lands of Ohio". In Henry Howe. Historical Collections of Ohio ... an Encyclopedia of the State. 1 (The Ohio Centennial ed.). The State of Ohio. School lands, page 132. (Volume 1 originally published in 1847 as Historical Collections of Ohio.)
- 1 2 3 George W. Knepper. "The Official Ohio Lands Book" (PDF). Retrieved 10 March 2011.
|chapter=ignored (help) page 56.
- Henry Howe (1849). Historical collections of Ohio: containing a collection of the most interesting facts, traditions, biographical sketches, anecdotes, etc., relating to its general and local history: with descriptions of its counties, principal towns and villages. Bradley & Anthony. p. 599. School lands, page 562.
See also
- Ohio Lands
- Ohio Company of Associates
- Northwest Territory
- Land Ordinance of 1785
- College Lands
- Survey township