Telbivudine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Tyzeka |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a607045 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | J05AF11 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | Low (3.3% in vitro) |
| Metabolism | Nil |
| Biological half-life | 40 to 49 hours (terminal phase) |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Synonyms |
1-(2-deoxy-β-L-ribofuranosyl)-5-methyluracil β-L-2-deoxythymidine β-L-thymidine (LdT) 1-[(2S,4R,5S)-4-hydroxy-5-hydroxymethyltetrahydrofuran-2-yl]-5-methyl-1H-pyrimidine-2,4-dione |
| CAS Number |
3424-98-4 |
| PubChem (CID) | 159269 |
| DrugBank |
DB01265 |
| ChemSpider |
140081 |
| UNII |
2OC4HKD3SF |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL374731 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.125.511 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H14N2O5 |
| Molar mass | 242.23 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
Telbivudine is an antiviral drug used in the treatment of hepatitis B infection. It is marketed by Swiss pharmaceutical company Novartis under the trade names Sebivo (Europe) and Tyzeka (United States). Clinical trials have shown it to be significantly more effective than lamivudine or adefovir, and less likely to cause resistance.[1][2][3] However, HBV signature resistance mutation M204I (a change from methionine to isoleucine at position 204 in the reverse transcriptase domain of the hepatitis B polymerase) or L180M+M204V have been associated with Telbivudine resistance.[4]
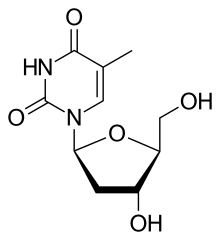
Telbivudine is a synthetic thymidine β-L-nucleoside analogue; it is the L-isomer of thymidine. Telbivudine impairs hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA replication by leading to chain termination. It differs from the natural nucleotide only with respect to the location of the sugar and base moieties, taking on an levorotatory configuration versus a dextrorotatory configuration as do the natural deoxynucleosides.[5] It is taken orally in a dose of 600 mg once daily with or without food.
References
- ↑ Lai CL, Leung N, Teo EK, et al. (2005). "A 1-year trial of telbivudine, lamivudine, and the combination in patients with hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B". Gastroenterology. 129 (2): 528–36. doi:10.1016/j.gastro.2005.05.053. PMID 16083710.
- ↑ Lai CL, Gane E, Liaw YF, et al. (2007). "Telbivudine versus lamivudine in patients with chronic hepatitis B". N Engl J Med. 357 (25): 2576–88. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa066422. PMID 18094378.
- ↑ Chan HL, Heathcote EJ, Marcellin P, et al. (4 December 2007). "Treatment of hepatitis B e antigen positive chronic hepatitis with telbivudine or adefovir: a randomized trial". Ann Intern Med. 147 (11): 745–54. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-147-11-200712040-00183. PMID 17909201.
- ↑ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2762437/
- ↑ Safety and efficacy of telbivudine for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B. "NCBI". Retrieved 16 July 2016.
External links
- Tyzeka official website run by Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
- Telbivudine entry in RxList
- Sebivo Summary of Product Characteristics (from the EMEA website)