Socialist Party of Serbia
Socialist Party of Serbia Социјалистичка Партија Србије Socijalistička Partija Srbije | |
|---|---|
 | |
| President | Ivica Dačić |
| Deputy president | Aleksandar Antić |
| Honorary president | Milutin Mrkonjić |
| Founder | Slobodan Milošević and Milutin Mrkonjić |
| Founded | 17 July 1990 |
| Preceded by | League of Communists of Serbia |
| Headquarters |
Studentski trg 15 Belgrade |
| Membership (2014) | 200,000[1] |
| Ideology |
Left-wing nationalism Social democracy Democratic socialism |
| Political position | Centre-left[2] to Left-wing[3] |
| European affiliation | None |
| International affiliation | None |
| Colours | Red |
| National Assembly |
21 / 250 |
| Assembly of Vojvodina |
8 / 120 |
| City Assembly of Belgrade |
11 / 110 |
| Website | |
|
www | |
The Socialist Party of Serbia (Serbian: Социјалистичка партија Србије, СПС / Socijalistička partija Srbije, SPS) is a political party in Serbia that identifies iterlf as a democratic socialist[4] and social democratic party.[5] During the rule of its leader Slobodan Milošević (and after), the party utilised some nationalist rhetoric and themes,[6][7][8] and has therefore been labelled a Serbian nationalist[9] party, although the SPS has never identified itself as such.[10][11][12]
History
The Socialist Party of Serbia was founded in 1990 as a merger between the League of Communists of Serbia, led by Slobodan Milošević, and the Socialist Alliance of the Working People of Serbia, led by Radmila Anđelković.[13]
Its membership from its foundation in 1990 to 1997 involved many elements of the social strata of Serbia, including: state administrators, including business management elites of state-owned enterprises; employees in the state-owned sector; less privileged groups farmers; and dependants (the unemployed and pensioners).[14] From 1998 to 2000, its membership included: apparatchiks at administrative and judicial levels; the nouveau riche, whose business success was founded solely from their affiliation with the regime; top army and police officials and a large majority of the police force.[15] Following its foundation, the SPS demanded strict loyalty to its leader, Milošević, by top party officials and any sign of independence from such loyalty led to expulsion from the party. Anyone who went against policy as defined by the party leadership could face sanctions or expulsion.[16]
The SPS during the Milošević era, has been accused by opposition of using an authoritarian style of rule and allowing a criminal economy to exist in Serbia including personal profiteering by the Milošević family from illegal business transactions in the arms trade, cigarettes and oil, although this illegal business was caused by the UN sanctions, and none of accusations for personal profiteering were ever proven at the court.[17] Opposition media to the SPS or Milošević's administration were harassed by threats; media members involved were fired or arrested; independent media faced high fines mostly by Ministry of information led by the Serbian Radical Party's Aleksandar Vučić; state-sponsored paramilitaries seized radio equipment of opposition supporters; and in April 1999, the owner and distributor of the most popular daily newspaper in Serbia was killed, and although it was never proven on court that murder had any connections to SPS, opposition media and parties claimed so, but couldn't prove it even after they came to power.[18] The SPS maintained the Communist era policy of maintaining connection with official trade unions; however, independent trade unions faced hostility and their activists were brutalized by police while in custody.[18]
The party won the first elections in Serbia with 194 out of 250 seats and 77.6% of the popular vote.[19] From 1992 it governed in coalition with other parties – initially with the Serbian Radical Party, and from 1993 with the New Democracy Party. They also contested elections in coalition with Yugoslav Left, a party led by Milošević's wife Mirjana Marković.
With the ousting of Milošević in 2000, the party became a part of the opposition. In the 2003 Serbian general elections, the party won 7.6% of the popular vote and 22 out of 250 seats in the National Assembly of Serbia. In 2004, however, its candidate in the presidential election, Ivica Dačić, placed fifth with 3.6% of the vote.
In 2007 parliamentary elections, the Socialist Party of Serbia won 16 seats with 227,580 or 5.64% of votes. It formed a sole parliamentary group, with Ivica Dačić as president and Žarko Obradović as vice-president. It won 14 seats outright while a single seat was given to its new partner, the Movement of Veterans of Serbia and non-partisan Borka Vučić, who became the transitional speaker, also received a seat.
In the 2008 parliamentary election, the SPS and the Party of United Pensioners of Serbia (PUPS) have strengthened their links by forming a coalition, on which United Serbia and Movement of Veterans of Serbia were present. The coalition won 23 seats with 313,896 or 7.58 percent of votes. SPS and its coalition partners entered post-election coalition with the For a European Serbia group.
In 2010, SPS introduced a new program, declares to be democratic leftists, opposing populism, racialism and privatization, advocating Socialism of the 21st century, including elements of liberalism and social justice.[20]
The SPS is a senior coalition member with the Serbian Progressive Party in the Serbian government, since 2012.
Policies
The SPS was formed as a coalition of the League of Communists of Serbia and the Socialist Alliance of Working People of Serbia, and Slobodan Milošević was elected its present. As the successor of the League of Communists, the party became the most dominant in Serbia; Milošević as President of the SPS was able to wield considerable power and influence in the government and the public and private sectors.[21] Milošević came to power promising the strengthening of Serb influence in Yugoslavia by reducing the autonomy of the provinces of Kosovo and Vojvodina within Serbia,[22][23] and had demanded a one-member-one vote system for the League of Communists of Yugoslavia which would have given a numerical majority to the Serbs. This course was a factor in the splintering of the Yugoslav Communist party, and caused the Serbian communist elite to take part in the creation of the Socialist Party of Serbia.
The political programme of the SPS has stated its intention to develop "Serbia as a socialist republic, founded on law and social justice."[24] The party made economic reforms outside of Marxist ideology such as recognizing all forms of property and intended a progression to a market economy while at the same time advocating some regulation for the purposes of "solidarity, equality, and social security".[24] In power however, the party enacted policies that were negative to workers rights, such as ending the Communists' worker participation programs. Beginning in its political programme of 1992, the SPS has supported a mixed economy, stating: "the Socialist Party of Serbia advocates a modern, mixed economy representing a synthesis of those elements of liberal and socialist models that have so far proved to be successful in the history of modern society and in our own development."[25] The SPS advocated the transition from a planned economy to a mixed economy, with both public and private sectors.[26]
The party endorsed the equality of all the Yugoslav peoples and ethnic minorities on the principle of full equality.[24]
Nationalist activity
From 1990 to 1993, the party endorsed supporting the Serbs in Bosnia & Herzegovina and Croatia who wished to remain in Yugoslavia.[27] As Croatia and Bosnia declared independence, the involvement by the SPS as a ruling party in Belgrade had become more devoted to helping the external Serbs run their own independent entities. The SPS was in coalition with the nationalist Serbian Radical Party (SRS) at the time.[27] Milošević responded to press questions of whether the Serbian government approved the Bosnian Serbs, by claiming that the Serbian government did not directly support the Srpska government or Serb military forces of Bosnia and Herzegovina in their war but claimed that Serbs had the right to self-determination. Fellow SPS member and government official Borisav Jović - in the 1995 BBC Documentary "The Death of Yugoslavia" - denied this and claimed Milošević did endorse the transfer of Bosnian Serb federal army forces to the Bosnian Serb Army in 1992 to help achieve Serb independence from the Alija Izetbegović government of Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Upon the Republic of Macedonia seceding in 1991, the Milošević government declared Macedonians an "artificial nation" and Serbia allied with Greece against the Republic of Macedonia, even suggesting a partition of the Republic of Macedonia between the FRY and Greece.[28] Subsequent interviews with government officials involved in these affairs revealed that Milošević planned to arrest the Republic of Macedonia's political leadership and replace it with politicians loyal to Serbia. Milošević demanded the self-determination of Serbs in the Republic of Macedonia.[28]
In 1998, five years after a split between the SPS and the Radicals, the party returned to its more successful coalition with the Serbian Radical Party as Kosovo-Albanian separatism was on the rise.[27]
The Helsinki Committee for Human Rights in Serbia reported that in reaction to the 2008 declaration of Kosovo independence, SPS leader Ivica Dačić said he would call for a ban on all political parties and NGOs in Serbia which would recognise Kosovo independence.[29]
Deviation from nationalism
The SPS is direct successor to the Serbian communists so party membership has never been exclusive to Serbs; as such, the SPS has contained non-Serb figures such as Rrahman Morina (ethnic Albanian); and ethnic Hungarians Verona Ádám Bokros and Mihalj Kertes.[30] In addition, the party engaged in discussions with Croatian and Bosnian leaders, particularly during the early stages of the Yugoslav wars. The SPS, unlike the right-wing nationalist Serbian Radical Party, also joined other parties in negotiations with ethnic Kosovo-Albanian politicians to resolve outstanding disputes and stop the Kosovo War.[31] The SPS however was unwilling to grant secession of any territory from FR Yugoslavia which formed in 1992.
In contrast to right-wing nationalist sentiment and contrary to the wishes of the early nationalist enthusiasts of the SPS, the party did not pursue a policy in which it would absorb Montenegro as the Kingdom of Serbia had done to the Kingdom of Montenegro in 1918. The plan was for Montenegro to continue to function alongside Serbia with all local affairs governed internally. In addition, at the Anti-bureaucratic revolutions, conducted whilst SFR Yugoslavia was active, the demonstrations in Kosovo and Vojvodina (as well as Montenegro) stopped short of calling for their respective entities to be abolished, they instead concentrated on ousting the authorities to replace them with pro-SPS loyalists. Right-wing Serbian nationalists in turn conceive no such Serbian state in which internal entities be granted self-rule.
Despite the bitterness towards the Macedonian nation whose locals rejected Serbian ethnicity, the SPS which governed FR Yugoslavia recognised the Republic of Macedonia in 1996. Four years before this milestone however, JNA troops and remnants of Belgrade's central government had peacefully and voluntarily left Macedonia.[32]
These policies adopted by the SPS created an uneasy relationship with the Radicals, a characteristic which culminated between 1993 and 1998 when the two parties had split and SRS leader Vojislav Šešelj even found himself imprisoned for a time. In this crucial period, the SPS broke away from the coalition with the Radicals and officially opposed the Bosnian Serb government of Radovan Karadžić by passing economic sanctions against it, as Karadžić was opposing peace initiatives and the party criticised the discriminatory nationalism of Karadžić's administration.[27] In 1995, Slobodan Milošević signed the Dayton Agreement on behalf of the Bosnian Serbs to end the Bosnian war and this infuriated the SRS and Serbian nationalists - relations between Milošević and Radovan Karadžić and other Bosnian Serb politicians had already soured by this point. For having signed the Dayton Agreement, Šešelj branded Milošević the "worst traitor in Serbian history".[33]
Meanwhile, the very union itself between the Radicals and the SPS was the subject of controversy among Serbian nationalists, World War II Chetnik commander Momčilo Đujić,[34] who granted the title of Vojvoda (Duke) to Šešelj in 1989, went as far as to revoke the Radical leader's honorary status for his association with Milošević. The former United States ambassador to Yugoslavia Warren Zimmermann admitted Milošević was not a genuine nationalist, but claimed nevertheless he was "an opportunist".[35]
Presidents of the Socialist Party of Serbia (1990–present)
| # | President | Born–Died | Term start | Term end | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Slobodan Milošević |  | 1941–2006 | 17 July 1990 | 24 May 1991 |
| 2 | Borisav Jović |  | 1928– | 24 May 1991 | 24 October 1992 |
| 3 | Slobodan Milošević[nb 1] |  | 1941–2006 | 24 October 1992 | 11 March 2006 (died in office) |
| 4 | Ivica Dačić[nb 2] |  | 1966– | 11 March 2006 | Incumbent |
Acting leaders during the incarceration of Milošević
Milošević was incarcerated at the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia (ICTY) from 2001 to 2006. Ref:[36]
| # | Name | Born–Died | Term start | Term end | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Živadin Jovanović |  | 1938– | 7 April 2001 | 24 December 2001 |
| 2 | Mirko Marjanović |  | 1937–2006 | 24 December 2001 | 23 August 2002 |
| 3 | Bogoljub Bjelica |  | 1956–2013 | 23 August 2002 | 18 January 2003 |
| 4 | Ivica Dačić |  | 1966– | 18 January 2003 | 11 March 2006 |
Electoral results
Parliamentary elections
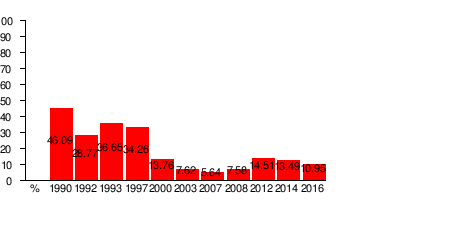
| Year | Popular vote | % of popular vote | # of seats | Seat change | Notes | Government |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 2,320,587 | 46.09% | 194 / 250 |
|
government | |
| 1992 | 1,359,086 | 28.77% | 101 / 250 |
|
government | |
| 1993 | 1,576,287 | 36.65% | 123 / 250 |
|
government | |
| 1997 | 1,418,036 | 34.26% | 85 / 250 |
|
Coalition with JUL-ND | government |
| 2000 | 515,845 | 13.76% | 37 / 250 |
|
opposition | |
| 2003 | 291,341 | 7.62% | 22 / 250 |
|
gov′t support | |
| 2007 | 227,580 | 5.64% | 16 / 250 |
|
opposition | |
| 2008 | 313,896 | 7.58% | 11 / 250 |
|
Coalition with PUPS-JS-PVS | government |
| 2012 | 567,689 | 14.51% | 24 / 250 |
|
Coalition with PUPS-JS-PVS | government |
| 2014 | 484,607 | 13.49% | 25 / 250 |
|
Coalition with PUPS-JS | government |
| 2016 | 413,770 | 10.95% | 21 / 250 |
|
Coalition with JS-ZS | government |
Presidential elections
| Election year | # | Candidate | 1st round votes | % | 2nd round votes | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 | Slobodan Milošević | 3,285,799 | 65.34% | — | — | |
| 1997 | Milan Milutinović | 1,665,822 | 43.70% | 2,181,808 | 59.23% | |
| 2004 | Ivica Dačić | 125,952 | 4.04% | — | — | |
| 2008 | Milutin Mrkonjić | 245,889 | 5.97% | — | — | |
| 2012 | Ivica Dačić | 556,013 | 14.23% | — | — |
Accusations of illegal activities
Critics have accused the SPS of involvement with organised crime, blackmail, political assassinations (most notably Serbian President Ivan Stambolić), supporting paramilitary formations during the Yugoslav Wars, and profiteering from illicit drug and oil trade.[37] The party received 1,000,000 barrels (160,000 m3) worth of oil vouchers in the United Nations Oil-for-Food Programme.[38]
Relations to other parties
Until the final dissolution of a federal Yugoslav state in 2006, the Socialist Party of Serbia held close ties with the Yugoslav Left, a coalition of left-wing and communist factions led by Miloševićs wife. The SPS has held close ties with the various political parties led by Momir Bulatović who had been installed as President of Montenegro with Milosević's aide, the SPS supported the Democratic Party of Socialists of Montenegro until Bulatović's ousting in 1998, Socialist People's Party of Montenegro under Bulatović from 1998 until his ousting in 2000, and the last one to be led by Bulatović is the People's Socialist Party of Montenegro. The SPS holds ties with a branch party in the Republic of Srpska in Bosnia & Herzegovina, the Socialist Party of Republika Srpska which was founded in 1993.[39] After the Dayton Accord, this party became a major opponent to the regime of Radovan Karadžić.[40] In the short-lived enclave Serb state of the Republic of Serbian Krajina in Croatia, the SPS supported the Serbian Party of Socialists and particularly the election bid of Milan Martić for President of Serbian Krajina in 1993.
The SPS wants to join the Socialist International. In May 2008, Ivica Dačić travelled to Athens to meet President of Socialist International George Papandreou. During this meeting, Papandreou said that Socialist International was ready to initiate the process for the SPS's membership.[41] However, there is still some opposition within Socialist International to inviting the SPS, notably from the Social Democratic Party of Bosnia and Herzegovina.[42] while Jelko Kacin claimed that Democratic Party (Serbia) president Boris Tadic lied about not blocking SPS from joining Socialist International.[43]
As of 2012, SPS continues to seek closer ties with Europe's social democratic and socialist parties, and has hinted that it might consider apologising for its role in the 1990s wars.[44]
Positions held
Major positions held by Socialist Party of Serbia members:
| President of Serbia | Years |
|---|---|
| Slobodan Milošević | 1990–1997 |
| Milan Milutinović | 1997–2002 |
| President of the National Assembly of Serbia | Years |
| Slobodan Unković | |
| Aleksandar Bakočević | 1991–1993 |
| Zoran Lilić | |
| Zoran Aranđelović | 1993–1994 |
| Dragan Tomić | 1994–2001 |
| Slavica Đukić Dejanović | 2008–2012 |
| Prime Minister of Serbia | Years |
| Dragutin Zelenović | |
| Radoman Božović | 1991–1993 |
| Nikola Šainović | 1993–1994 |
| Mirko Marjanović | 1994–2000 |
| Milomir Minić | 2000–2001 |
| Ivica Dačić | 2012–2014 |
| Mayor of Belgrade | Years |
| Milorad Unković | 1991–1993 |
| Slobodanka Gruden | 1993–1994 |
| Nebojša Čović | 1994–1997 |
| President of the Government of Vojvodina | Years |
| Jovan Radić | 1990–1991 1991–1992 |
| Radoman Božović | |
| Koviljko Lovre | 1992–1993 |
| Boško Perošević | 1993–2000 |
| Damnjan Radenković |
See also
Bibliography
- Branković, Srbobran (2002). András Bozóki; John T. Ishiyama, eds. The Yugoslav "Left" Parties: Continuities of Communist Tradition in the Milošević Era. The Communist Successor Parties of Central and Eastern Europe. M. E. Sharpe. pp. 206–223.
References
- Notes
- Footnotes
- ↑ "507118-Naprednjacka-knjizica-na-ceni Naprednjačka knjižica na ceni" (in Serbian). Novosti.
- ↑ Dragojević, Mila (2014). The Politics of Social Ties: Immigrants in an Ethnic Homeland. Ashgate. p. 90.
- ↑ http://www.b92.net/eng/news/politics.php?yyyy=2008&mm=01&dd=11&nav_id=46866
- ↑ Alan John Day, Roger East, Richard Thomas. A political and economic dictionary of Eastern Europe. First Edition. Cambridge International Reference on Current Affairs, Ltd, 2002, p. 544.
- ↑ Thompson, Wayne C. (2013). Nordic, Central, and Southeastern Europe 2013. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 444.
- ↑ Pavlaković, Vjeran (2005). Serbia Transformed? Political Dynamics in the Milošević Era and After. Serbia since 1989. University of Washington Press. p. 17.
- ↑ Prošić-Dvornić, Mirjana (2000). Apocalyptic Thought and Serbian Identity: Mythology, Fundamentalism, Astrology and Soothsaying as Part of Political Propaganda. Ethnologia Balkanica. 4. p. 166.
- ↑ Miller, Nicholas (2005). Serbia and Montenegro. Eastern Europe: An Introduction to the People, Land, and Culture. 3. ABC-CLIO. p. 560.
- ↑ Janusz Bugajski (1995). Ethnic Politics in Eastern Europe: A Guide to Nationality Policies, Organizations, and Parties. M.E. Sharpe. p. 466. ISBN 978-0-7656-1911-2.
- ↑ Janusz Bugajski. Political Parties of Eastern Europe: A Guide to Politics in the Post-Communist Era. Armonk, New York, USA: Center for Strategic and International Studies, 2002, p. 399.
- ↑ Christiane Lemke, Gary Marks. The crisis of socialism in Europe. Duke University Press, 1992, p. 101.
- ↑ Pavlaković, Vjeran (2005), "Serbia Transformed? Political Dynamics in the Milošević Era and After", Serbia since 1989: politics and society under Milošević and after, Seattle, Washington, USA: University of Washington Press, p. 17
- ↑ John Borrell (6 August 1990). "Yugoslavia The Old Demons Arise". Time Magazine.

- ↑ Branković (2002). The Yugoslav "Left" Parties. p. 208.
- ↑ Branković (2002). The Yugoslav "Left" Parties. p. 209.
- ↑ Branković (2002). The Yugoslav "Left" Parties. p. 210.
- ↑ Branković (2002). The Yugoslav "Left" Parties. p. 217.
- 1 2 Branković (2002). The Yugoslav "Left" Parties. p. 216.
- ↑ "Elections in Serbia".
- ↑ Program of Socialist Party of Serbia. http://www.sps.org.rs/documents/PROGRAM%20SPS.pdf
- ↑ Heike Krieger (12 July 2001). The Kosovo Conflict and International Law: An Analytical Documentation 1974-1999. Cambridge University Press. p. 522. ISBN 978-0-521-80071-6.
- ↑ Tove Malloy; Alexander Osipov; Balázs Vizi (23 July 2015). Managing Diversity through Non-Territorial Autonomy: Assessing Advantages, Deficiencies, and Risks. OUP Oxford. p. 76. ISBN 978-0-19-105832-5.
- ↑ Eleftheria Rania Kosmidou (2013). European Civil War Films: Memory, Conflict, and Nostalgia. Routledge. p. 94. ISBN 978-0-415-52320-2.
- 1 2 3 Branković (2002). The Yugoslav "Left" Parties. p. 206.
- ↑ Siniša Malešević. Ideology, legitimacy and the new state: Yugoslavia, Serbia and Croatia. London, England, UK; Portland, Oregon, USA: Frank Cass Publishers, 2002, p. 184-185.
- ↑ Siniša Malešević. Ideology, legitimacy and the new state: Yugoslavia, Serbia and Croatia. London, England, UK; Portland, Oregon, USA: Frank Cass Publishers, 2002, p. 184.
- 1 2 3 4 Branković (2002). The Yugoslav "Left" Parties. p. 213.
- 1 2 Alice Ackermann. Making peace prevail: preventing violent conflict in Macedonia. Syracuse, New York, USA: Syracuse University Press, 2000, p. 72.
- ↑ "Revival of hate speech". Helsinki Committee for Human Rights in Serbia. 30 February 2009. Retrieved 2010-12-31. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ "The Milosevic charge sheet". BBC. 2001-04-02. Retrieved 2007-09-07.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on May 9, 2008. Retrieved May 29, 2008.
- ↑ http://www.ethnopolitics.org/ethnopolitics/archive/volume_I/issue_3/issue_3.pdf
- ↑ http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/special_report/1999/03/99/kosovo_strikes/316198.stm
- ↑ http://www.icty.org/x/cases/slobodan_milosevic/trans/en/021204IT.htm
- ↑ Zimmermann 1996, pp. 25.
- ↑ "Serbian ministries, etc.". rulers.org. B. Schemmel. Retrieved 31 May 2015.
- ↑ Branković (2002). The Yugoslav "Left" Parties. pp. 217–218.
- ↑ "The Beneficiaries of Saddam's Oil Vouchers: The List of 270". The Middle East Media Research Institute (MEMRI). 29 January 2004.
- ↑ Day, Alan J.; East, Roger; Thomas, Richard. 2002. A Political and Economic Dictionary of Eastern Europe. Routledge. P. 544
- ↑ Day, Alan J.; East, Roger; Thomas, Richard. P. 545
- ↑ "Serbian socialist party leader meets head of Socialist International". Southeast European Times. 2008-05-25. Retrieved 2008-06-27.
- ↑ "Protest against SPS SI membership". B92. 2008-06-26. Retrieved 2008-06-27.
- ↑ "Kacin: Tadić sanja svoju istinu" (in Serbian). B92. 27 February 2013.
- ↑ Serbia's deputy PM: 'SPS could apologise for problems in the 90s', European Forum for Democracy and Solidarity, 2012-01-05
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Socialist Party of Serbia. |
