Solar power in Canada
| Electricity generation in Canada |
|---|
 |
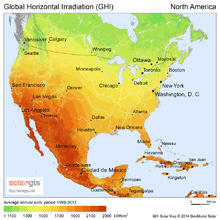
Canada has plentiful solar energy resources, with the most extensive resources being found in southern British Columbia, Ontario, Quebec and the Prairies. The territories have a smaller potential, and less direct sunlight, because of their higher latitude.[1]
Historically, the main applications of solar energy technologies in Canada have been non-electric active solar system applications for space heating, water heating and drying crops and lumber. In 2001, there were more than 12,000 residential solar water heating systems and 300 commercial/ industrial solar hot water systems in use. These systems presently comprise a small fraction of Canada’s energy use, but some government studies suggest they could make up as much as five per cent of the country’s energy needs by the year 2025.[1]
Photovoltaic (PV) cells are increasingly used as standalone units, mostly as off-grid distributed electricity generation to power remote homes, telecommunications equipment, oil and pipeline monitoring stations and navigational devices. The Canadian PV market has grown quickly and Canadian companies make solar modules, controls, specialized water pumps, high efficiency refrigerators and solar lighting systems.[1]
One of the most important uses for PV cells is in northern communities, many of which depend on high-cost diesel fuel to generate electricity. Since the 1970s, the federal government and industry has encouraged the development of solar technologies for these communities. Some of these efforts have focused on the use of hybrid systems that provide power 24 hours a day, using solar power when sunlight is available, in combination with another energy source.[1]
By region
Ontario
With the introduction of a Feed-in tariff (FIT) in 2009, Ontario became a global leader for solar energy projects. The program was the first of its kind in North America. Thanks to the FIT program, Ontario was the home of what was temporarily the largest solar farm in the world (in October 2010) until surpassed by larger farms in China and India. Located in Sarnia, Ontario, the 97 megawatt[2] Sarnia Photovoltaic Power Plant can power more than 12,000 homes.[3] The most recent concentrated solar thermal power and storage technologies were barred from the FIT. The reason offered was that the technologies are not proven in Ontario climate.
The FIT program is intended for installations over 10 kW, while the microFIT program is to encourage the development of micro-scale renewable energy projects, such as residential solar photovoltaic (PV) installations. The microFIT program provides a rate of $0.802/kWh for rooftop mounted solar panels.[4] On July 2, 2010 the microFIT's program rate (for ground-mounted systems only) was lowered to $0.642/kWh by the Ontario Power Authority (OPA).[5] This new rate means consumers investing in solar energy through the Ontario microFIT Program will experience a drop in profit margin from a 25% range to 10%.[6] On April 5, 2012 the rate was reduced to $0.549/kWh.[7] The 2012 target is for 50 MW to be installed.[8] As of August 7, 2012, 9,764 applications for the FIT have been submitted, totaling 8,504 MW. 1,757 applications have been submitted for the microFIT program, totaling 16 MW.[9] Ontario plans to end coal generation by 2014.[10]
The 23.4 MW Arnprior Solar Generating Station was built in 2009, and is expected to expand to 80 MW.[11]
A 68 megawatt solar farm is in Sault Ste. Marie, and a 100 megawatt solar farm is planned for Kingston, Ontario.[12][13]
Ontario is expected to reach 2,650 MW of solar PV by 2015.[14]
As of October 2013, Ontario's solar energy installations contribute less than 0.4% of the province's energy needs.[15]
Statistics
| Year | Σ Installed (MWp) | Δ Installed (MWp) | Generation (GWh) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1992 | 0.96 | ||
| 1993 | 1.23 | 0.2 | |
| 1994 | 1.51 | 0.3 | |
| 1995 | 1.86 | 0.4 | |
| 1996 | 2.56 | 0.7 | |
| 1997 | 3.38 | 0.8 | |
| 1998 | 4.47 | 1.1 | |
| 1999 | 5.83 | 1.3 | |
| 2000 | 7.15 | 1.4 | |
| 2001 | 8.83 | 1.6 | |
| 2002 | 10.00 | 1.2 | |
| 2003 | 11.83 | 1.8 | |
| 2004 | 13.88 | 2.1 | |
| 2005 | 16.75 | 2.85 | |
| 2006 | 20.48 | 3.75 | |
| 2007 | 25.77 | 5.3 | |
| 2008 | 32.72 | 6.9 | |
| 2009 | 94.57 | 61.87 | |
| 2010 | 281.13 | 186.43 | |
| 2011 | 558.29 | 297 | 400 |
| 2012 | 765.97 | 268 | |
| 2013 | 1,210.48 | 444.51 | |
| 2014 | 1,843.08 | 632.60 |
See also
- Solar power by country
- Feed-in tariff program in Canada
- Green Energy Act 2009
- Renewable energy in Canada
- Wind power in Canada
- Geothermal power in Canada
- Hydroelectricity in Canada
- Renewable energy by country
References
- 1 2 3 4 Solar power in Canada
- ↑ Large-scale photovoltaic power plants ranking 1 - 50
- ↑ "Enbridge completes Sarnia solar farm". CBC News. 4 October 2010.
- ↑ Ontario microFIT Program FAQ
- ↑ "Ontario Power Authority Cuts Solar Rates". CBC News. 16 July 2010.
- ↑ "Ontario microFIT Program - Ottawa Solar Power". 8 September 2011.
- ↑ FIT Price Schedule
- ↑ Program Overview
- ↑ Bi-Weekly Report
- ↑ Ontario’s Electricity System
- ↑ EDF Commissions 23.4-MW Arnprior Solar Plant
- ↑ Going big on solar energy
- ↑ Kingston & Loyalist Township
- ↑ Paul Gipe (23 March 2011). "Ontario's //Solar PV Installations May Surpass California in 2011". Renewable Energy World.
- ↑ "Supply Overview - IESO". 17 January 2014.
- ↑ collected data from article growth of photovoltaics
- ↑ Global Market Outlook for Photovoltaics 2013-2017
- ↑ National Survey Report of PV Power Applications in Canada 2014