Wind power in Canada
| Electricity generation in Canada |
|---|
 |
Wind power has a history in Canada dating back many decades, particularly on prairie farms. As of June 2015, wind power generating capacity was 10,204 megawatts (MW), providing about 4% of Canada's electricity demand.[1] The Canadian Wind Energy Association has outlined a future strategy for wind energy that would reach a capacity of 55,000 MW by 2025, meeting 20% of the country’s energy needs.[2]
Overview

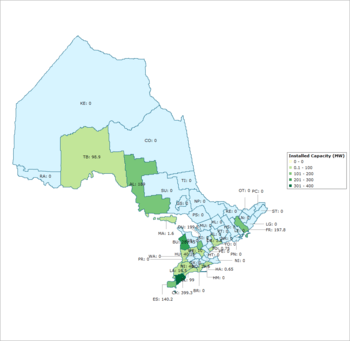
Early development of wind energy in Canada was located primarily in Ontario, Quebec, and Alberta. Throughout the late 1990s and early years of the 21st Century every Canadian province has pursued wind power to supplement their provincial energy grids. Alberta built the first commercial wind farm in Canada in 1993. British Columbia was the last province to add wind power to its grid with the completion of the Bear Mountain Wind Park in November 2009.[4] With increasing population growth, Canada has seen wind power as a way to diversify energy supplies away from traditional reliance on fossil fuel burning thermal plants and heavy reliance on hydroelectricity in some provinces. In provinces like Nova Scotia, where only 12% of electricity comes from renewable sources,[5] the development of wind energy projects will provide a measure of electricity security that some jurisdictions are lacking. In the case of British Columbia, wind energy will help close the electricity deficit that the province is facing into the 2010s and help reduce the reliance on importing power from other jurisdictions that may not use renewable energy sources. An additional 2,004 megawatts of wind power is to come on stream in Quebec between 2011 and 2015. The new energy will cost 10.5 cents per kilowatt-hour, a price described as "highly competitive".[6]
| Province/Territory | June 2015 Installed Capacity (MW)[3] |
|---|---|
| Alberta | 1471 |
| British Columbia | 489 |
| Manitoba | 258 |
| New Brunswick | 294 |
| Newfoundland and Labrador | 55 |
| Northwest Territories | 9 |
| Nova Scotia | 392 |
| Ontario | 3927 |
| Prince Edward Island | 204 |
| Québec | 2883 |
| Saskatchewan | 221 |
| Yukon | 1 |
| Total | 10204 |
Wind hybrid projects
Contributors to the main power grid are Wind-Diesel and Wind-Hydrogen. One Canadian example is the community of Ramea, Newfoundland and Labrador that initially used a Wind-Diesel system and is now being converted to Wind-Hydrogen technology.[7]
Wind power industry
Canadian industry has started to supply major components for Wind Tower projects, Mitsubishi Hitachi Power Systems Canada, Ltd. being one example.
Public opinion

In a survey conducted by Angus Reid Strategies in October 2007, 89 per cent of respondents said that using renewable energy sources like wind or solar power was positive for Canada, because these sources were better for the environment. Only 4 per cent considered using renewable sources as negative since they can be unreliable and expensive.[8]
According to a Saint Consulting survey in April 2007, wind power was the alternative energy source most likely to gain public support for future development in Canada, with only 16% opposed to this type of energy. By contrast, 3 out of 4 Canadians opposed nuclear power developments.[9]
Despite this general support for the concept of wind power in the public at large, local opposition often exists, primarily from residents concerned about visual and light pollution, noise or reduced property values. The construction of wind turbines has a negative effect on rural communities, owing to the fact that landowners who receive payments to allow wind turbines on their land are seen as sellouts who are unconcerned with the windmills' effect on their neighbours. Public opposition has had the desired effect in some cases, aborting or delaying construction of windmills. This opposition has been described as a case of NIMBYism.[10]
Complicating matters further is wind energy's association with high electricity costs in Ontario. Due to increasing hydro prices some attribute to the Green Energy Act, many Ontarians are turning to alternative sources of energy to meet their needs, such as propane and the burning of wood.[11]
Several wind farms in Canada have become tourist attractions,[12] to the surprise of the owners.
Proposed future strategies
Wind farms on crown land
Some rural communities want Alberta to grant companies the right to develop wind farms on leased Crown land.[13]
Wind Vision 2025
In 2008, the Canadian Wind Energy Association (CanWEA), a non-profit trade association, outlined a future strategy for wind energy that would reach a capacity of 55,000 MW by 2025, fulfilling 20% of the country’s energy needs. The plan, Wind Vision 2025, could create over 50,000 jobs and represent around CDN$165 million annual revenue. If achieved, CanWEA’s target would make the country a major player in the wind power sector and would create around CDN$79 billion of investment. It would also save an estimated 17 megatonnes of greenhouse gas emissions annually.[2]
Current support schemes
Ontario's Large Renewable Procurement
The LRP is an important tool of Ontario’s commitment to reach the province's 2025 target for renewable energy to comprise about 50% of Ontario's installed capacity. Projects of more than 10 MW of capacity are eligible to obtain a 20-year contract through a price competitive auction.[14] [15]
- LRP I: concluded in April 2016, with the execution of 299.5 onshore wind contracts.
- LRP II: kicked off on July 29, 2016 with the launch of the Request for Qualifications (RFQ), and with the aim of allocating up to 600 MW of onshore wind, and 50 MW of technological upgrades of existing renewable energy facilities. However, this round was suspended on September 27, 2016.
See also
- Electricity sector in Canada
- Energy policy of Canada
- List of wind farms in Canada
- Renewable energy in Canada
- Solar power in Canada
- Geothermal power in Canada
- Hydroelectricity in Canada
- Renewable energy commercialization
- Science and technology in Canada
- Renewable energy by country
- V2G
- Melancthon EcoPower Centre
- Association of Power Producers of Ontario
References
- ↑ Canwea (May 1, 2014). "Powering Canada's Future" (PDF). Canwea.
- 1 2 Wind Vision 2025
- 1 2 Canadian Wind Farms
- ↑ Bear Mountain Wind Park
- ↑ "Nova Scotia Power is generating cleaner, greener energy" (PDF). Nova Scotia Power website. Archived from the original (pdf) on March 18, 2009. Retrieved 2007-12-16.
- ↑ Quebec picks 15 wind-power projects
- ↑ Introduction of Hydrogen Technologies to Ramea Island
- ↑ Canadians favour energy sources that are better for the environment
- ↑ Wind power developments are least likely to be opposed by Canadians – Nuclear power opposed by most
- ↑ "Windmills vs. NIMBYism". The Star. Toronto. 2008-10-20.
- ↑ http://www.windconcernsontario.ca/in-ontario-green-living-means-propane/
- ↑ Young, Kathryn (2007-08-03). "Canada wind farms blow away turbine tourists". Edmonton Journal. Retrieved 2008-09-06.
- ↑ Rural communities want Alberta to allow wind power farms on leased Crown land
- ↑ Large Renewable Procurement, IESO, retrieved 28 September 2016
- ↑ Renewable Energy Development Process, Ontario's Ministry of Energy, retrieved 28 September 2016
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Wind power in Canada. |
- Renewable energy players opt to network
- Canadian Wind Energy Association
- Association of Power Producers of Ontario
- The Great Lakes May Soon be Home to Offshore Wind
- The Ontario Sustainable Energy Association
- Canadian Wind Atlas by Environment Canada
- Wind turbine production would boost troubled manufacturing
- The BC Sustainable Energy Association
- "Where is my Electricity Coming From at this Hour? (if I lived in Ontario)" (Canadian Nuclear Society, with data from IESO)
- Ontario Wind Turbine Noise Health Report Prepared by HGC Engineering Acoustical Consultants
