Zhao (state)
| State of Zhao | ||||||||||
| 趙 | ||||||||||
| Kingdom | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
 | ||||||||||
| Capital | Jinyang (initially) Handan (later) | |||||||||
| Religion | Chinese folk religion ancestor worship | |||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | |||||||||
| Historical era | Warring States period | |||||||||
| • | Partition of Jin | 403 BC | ||||||||
| • | Conquered by Qin | 222 BC | ||||||||
| Currency | spade money other ancient Chinese coinage | |||||||||
| ||||||||||
| Zhao | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
"Zhao" in seal script (top), Traditional (middle), and Simplified (bottom) Chinese characters | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 趙 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simplified Chinese | 赵 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Zhao (Chinese: 趙; Old Chinese: *[d]rewʔ) was one of the seven major states during the Warring States period of ancient China. At the beginning of the Warring States Period, Zhao was one of the weakest states but gained strength during the reign of King Wuling of Zhao: by the end of the period, Zhao was the only state strong enough to oppose the mighty Qin.
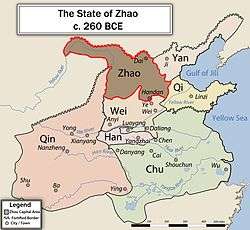
Its territory included areas in modern Inner Mongolia, Hebei, Shanxi and Shaanxi provinces. The state of Zhao bordered the Xiongnu (Huns), the states of Qin, Wei and Yan. Its capital was Handan (邯郸), suburb of modern-day Handan City in Hebei.
Origins and ascendancy
At the end of the Spring and Autumn Period, the state of Jin was divided up between three powerful ministers, the Zhao family patriarch being one of them. In BC 403, the king of Zhou formally recognized the existence of the State of Zhao along with two other States, Han and Wei, marking the start of the Warring States Period.
At the onset of the Warring States period, Zhao was one of the weaker states. Despite its extensive territory, its northern border was frequently subject to harassment by the Xiongnu and by other northern nomadic peoples. At the same time, surrounded by strong states and lacking the military strength of Wei or the prosperity of Qi, Zhao became an asset in the struggle between those two states; this struggle came to a climax in 354 BC, when Wei invaded Zhao and Zhao had to seek aid from Qi. The resulting Battle of Guiling, a major victory for Qi, lessened the southern threat to Zhao.
Zhao remained relatively weak until the military reforms of King Wuling of Zhao (325-299 BC). The soldiers of Zhao were ordered to dress like their Xiongnu neighbours and to replace war chariots with cavalry archers. This proved a brilliant reform: with advanced technology of the Chinese states and nomadic tactics, the cavalry of Zhao became a powerful force, allowing Zhao to match Qin during the middle decades of the era.
Zhao demonstrated its enhanced military prowess by conquering the State of Zhongshan in 295 BC after a prolonged war, and annexing territory from its neighbors Wei, Yan and Qin. The cavalry of Zhao occasionally intruded into the state of Qi in campaigns against the state of Chu.
Several brilliant military commanders of the period appeared concurrently, including Lian Po, Zhao She (趙奢) and Li Mu. Lian Po proved instrumental in defending against the Qin. Zhao She (趙奢) was most active in the east; he led the invasion of Yan state. Li Mu defended Zhao from the Xiongnu and later from Qin.
Fall of Zhao
By the end of the Warring States Period, Zhao was the only state strong enough to oppose the powerful Qin state. An alliance with Wei begun in 287 BC against Qin ended in defeat at Huayang in 273 BC. The struggle then culminated in the bloodiest battle of the whole period, the Battle of Changping in 260 BCE. The troops of Zhao were completely defeated by Qin. Although the forces of Wei and Chu saved Handan from a follow-up siege by the victorious Qin, Zhao would never recover from the huge loss of men in the battle.
In 229 BCE, invasions led by the Qin general Wang Jian were opposed by Li Mu and his subordinate officer Sima Shang (司馬尚) until 228 BCE. According to some accounts, King Youmiu, ordered the execution of Li Mu and relieved Sima Shang from his duties, due to faulty advice from disloyal court officials and Qin infiltrators.
In 228 BCE, Qin captured King Youmiu and conquered Zhao. Prince Jia, the stepbrother of King Qian, was proclaimed King Jia at Dai and led the last Zhao forces against the Qin. The regime lasted until 222 BCE, when the Qin army captured him and defeated his forces at Dai.
In 154 BCE, an unrelated Zhao (赵), headed by Liu Sui (劉遂), the Prince of Zhao kingdom, participated in the unsuccessful Rebellion of the Seven States (Chinese: 七国之乱) against the newly installed second emperor of the Han dynasty.
Culture and society
Before Qin unified China, each state had its own customs and culture. According to the Yu Gong or Tribute of Yu, composed in the 4th or 5th century BC and included in the Book of Documents, there were nine distinct cultural regions of China, which are described in detail in this book. The work focuses on the travels of the titular sage, Yu the Great, throughout each of the regions. Other texts, predominantly military, also discussed these cultural variations.[1]
One of these texts was The Book of Master Wu, written in response to a query by Marquis Wu of Wei on how to cope with the other states. Wu Qi, the author of the work, declared that the government and nature of the people were reflective of the terrain they live in. Of Zhao, he said:
The Han and the Zhao are gentle people. Their populations are weary from war and experienced in arms, but they have little regard for their generals. The soldiers' salaries are meager and their officers have no strong commitment to their countries. Although their troops are experienced, they cannot be expected to fight to the death. To defeat them, we must concentrate large numbers of troops in our attacks to present them with certain peril. When they counterattack, we must be prepared to defend our positions vigorously and make them pay dearly. When they retreat, we must pursue and give them no rest. This will grind them down.
List of Zhao rulers
- Marquess Xian (獻侯), personal name Huan (浣), ruled 424 BC–409 BC
- Marquess Lie (烈侯), personal name Ji (籍), son of previous, ruled 409 BC–387 BC, noted for several reforms
- Marquess Jing (敬侯), personal name Zhang (章), son of previous, ruled 387 BC–375 BC
- Marquess Cheng (成侯), personal name Zhong (種), son of previous, ruled 375 BC–350 BC
- Marquess Su (肅侯), personal name Yu (語), son of previous, ruled 350 BC–326 BC
- King Wuling (武靈王), personal name Yong (雍), son of previous, ruled 326 BC–Spring 299 BC
- King Huiwen (惠文王), personal name He (何), son of previous, ruled Spring 299 BC–266 BC
- King Xiaocheng (孝成王), personal name Dan (丹), son of previous, ruled 266 BC–245 BC
- King Daoxiang (悼襄王), personal name Yan (偃), son of previous, ruled 245 BC–236 BC
- King Youmiu (幽繆王), personal name Qian (遷), son of previous, ruled 236 BC–228 BC
- King Jia of Dai (代王), personal name Jia (嘉), half-brother of previous, ruled 228 BC–222 BC
Zhao in astronomy
There is two opinions about the representing star of Zhao in Chinese astronomy. The opinions are :
- Zhao is represented with the star Lambda Herculis in asterism Left Wall, Heavenly Market enclosure .,[2] and also represented with two stars 26 Capricorni (趙一 Zhao yī, English: the First Star of Zhao) and 27 Capricorni (趙二 Zhao èr, English: the Second Star of Zhao) in asterism Twelve States, Girl mansion.[3] (see Chinese constellation).
- Zhao is represented with the star Lambda Herculis,[4] and also represented with star "m Capricorni".[5]
See also
- The kingdoms of Former Zhao and Later Zhao of the Sixteen Kingdoms
.svg.png)