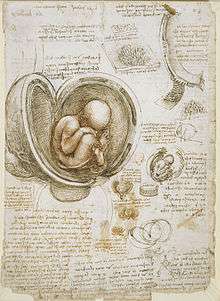
Studies of the Fetus in the Womb
|
The fetus in the womb The female external genitalia and five views of the fetus in the womb | |
| Artist | Leonardo da Vinci |
|---|---|
| Year | c.1510–12/13 |
| Type | Black chalk, sanguine, pen, ink wash on paper |
| Location | Royal Collection, United Kingdom |
Studies of the Fetus in the Womb are two colored annotated sketches by Leonardo da Vinci made in 1510–1512/13. The studies correctly depict the human fetus in its proper position inside the dissected uterus.[1] Da Vinci depicted the uterus with one chamber, in contrast to theories that the uterus had multiple chambers which many believed divided fetuses into separate compartments in the case of twins.[1] Da Vinci also correctly drew the uterine artery and the vascular system of the cervix and vagina.[1]
Preparation and the studies
Da Vinci studied human embryology with the help of anatomist Marcantonio della Torre and saw the fetus within a cadaver.[1] The first study, measuring 30.5×22 cm, shows the fetus in a breech position inside a dissected uterus. Da Vinci mistakenly depicted the cotyledons in the vascular walls of the human uterus that he had previously found in a cow uterus.[2] The other study, measuring 30.3×22 cm, shows female external genitalia, the supposed arrangement of abdominal muscles on the top right and fetus from different angles. The tablet at the top contains an Italian inscription: "Dimanda la moglie di Biagin Crivelli come il cappone alleva le oua della ghallina essendo lui imbricato" ("Ask Biagino Crivelli's wife how the capon rears and hatches the eggs of hens when he is unplucked").[3] Da Vinci theorized that the umbilical cord was responsible for taking the fetus’ urine outside of the uterus.[1]
Provenance
The studies were initially bequeathed to Francesco Melzi. In c. 1582–90 they were bought from his heirs by Pompeo Leoni and by 1630 they belonged to Thomas Howard, 2nd Earl of Arundel. Since 1690 the studies are housed in the Royal Collection, United Kingdom.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Hilary Gilson. "Leonardo da Vinci's Embryological Drawings of the Fetus". The Embryo Project Encyclopedia. Retrieved 6 Aug 2015.
- ↑ Leonardo (da Vinci), Kenneth David Keele, Jane Roberts (1983). Leonardo Da Vinci: Anatomical Drawings from the Royal Library, Windsor Castle. Metropolitan Museum of Art. p. 78. ISBN 0870993623.
- ↑ Leonardo Da Vinci: Anatomical Drawings from the Royal Library, Windsor Castle, p. 75