Suture (joint)
| Suture (joint) | |
|---|---|
 Side view of the skull. | |
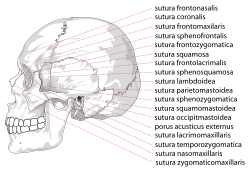 Human skull side suturas right | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Sutura |
| TA | A03.1.02.001 |
| FMA | 7493 |
A suture is a type of fibrous joint which only occurs in the skull (or "cranium"). The bones are bound together by Sharpey's fibres. A tiny amount of movement is permitted at sutures, which contributes to the compliance and elasticity of the skull. These joints are synarthroses.[1] It is normal for many of the bones of the skull to remain unfused at birth. The fusion of the skull's bones at birth is known as craniosynostosis. The term "fontanelle" is used to describe the resulting "soft spots". The relative positions of the bones continue to change during the life of the adult (though less rapidly), which can provide useful information in forensics and archaeology. In old age, cranial sutures may ossify (turn to bone) completely.[2] The joints between the teeth and the joint between the mandible and the cranium, the temporomandibular joint, form the only non-sutured joints in the skull.
Types of sutures
- Squamous sutures
- Plane sutures - edges of the bones are flush with each other as in a normal butt joint
- Limbous sutures - edges are bevelled so the plane of the suture is sloping as in a mitre joint
- Schindylesis - formed by two bones fitting into each other similar to a bridle joint
- Denticulate sutures - the edges slot into each other as in a finger joint
- Serrate sutures - similar to a denticulate suture but the interlocking regions are serrated rather than square.
List of sutures
Most sutures are named for the bones they articulate, but some have special names of their own.
Primarily visible from the side (norma lateralis)
- Coronal suture - between the frontal and parietal bones
- Lambdoid suture - between the parietal and occipital bones and continuous with the occipitomastoid suture
- Occipitomastoid suture - between the occipital and temporal bones and continuous with the lambdoid suture
- Sphenofrontal suture
- Sphenoparietal suture
- Sphenosquamosal suture
- Sphenozygomatic suture
- Squamosal suture - between the parietal and the temporal bone
- Zygomaticotemporal suture
- Zygomaticofrontal suture
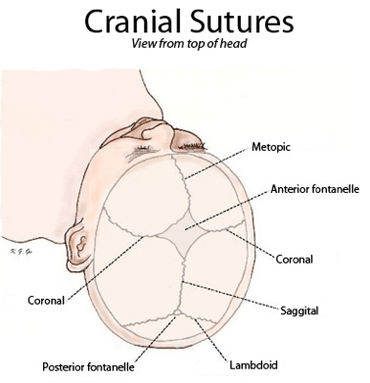
Primarily visible from front (norma frontalis) or above (norma verticalis)
- Frontal suture / Metopic suture - between the two frontal bones, prior to the fusion of the two into a single bone
- Sagittal suture - along the midline, between parietal bones
Primarily visible from below (norma basalis) or inside
Gallery
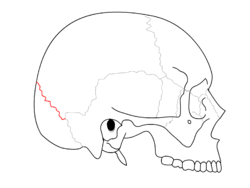 Lambdoid suture
Lambdoid suture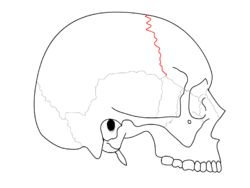 Coronal suture
Coronal suture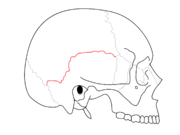 Squamosal suture
Squamosal suture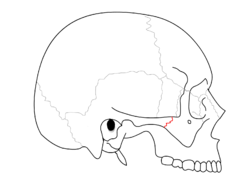 Zygomaticotemporal suture
Zygomaticotemporal suture Sagittal suture.
Sagittal suture.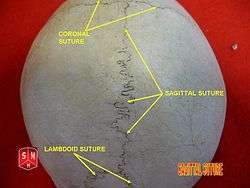 Sagittal suture.
Sagittal suture.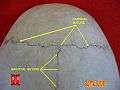 Sagittal suture.
Sagittal suture.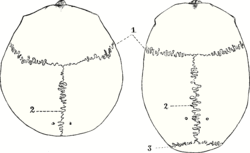 Top view of cranial suture.
Top view of cranial suture.
References
- ↑ "Module - Introduction to Joints". Archived from the original on 2007-12-17. Retrieved 2008-01-29.
- ↑ Harth, Sebastian; Obert, Martin; Ramsthaler, Frank; Reuss, Christina; Traupe, Horst; Verhoff, Marcel (2009). "Estimating age by assessing the ossification degree of cranial sutures with the aid of Flat-Panel-CT". Legal Medicine (Tokyo). Elsevier. 11 (Supp.1): S186–S189. doi:10.1016/j.legalmed.2009.01.091. PMID 19261532. Retrieved 5 February 2016.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Cranial sutures. |
- MedlinePlus Encyclopedia 002320
- Age at Death Estimation from Cranial Suture Closures
- Cranial suture closure and its implications for age estimation
- http://commons.bcit.ca/biology/articulations/fibrous.html