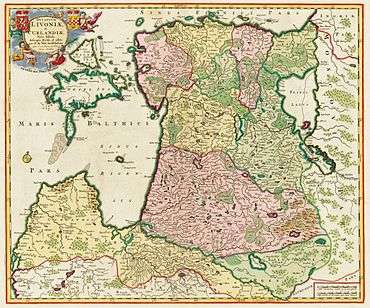
Swedish Livonia
| Swedish Livonia | ||||||||||||
| Svenska Livland | ||||||||||||
| Dominion of the Swedish Empire | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
 Baltic provinces of Swedish Empire in the 17th century. | ||||||||||||
| Capital | Riga | |||||||||||
| Languages | Swedish, Estonian, Latvian, Livonian, Low German (Latin as lingua franca) | |||||||||||
| Religion | Lutheranism | |||||||||||
| Government | Dominion | |||||||||||
| King of Sweden | ||||||||||||
| • | 1611–1632 | Gustav II Adolf | ||||||||||
| • | 1720–1751 | Frederick I | ||||||||||
| Governor-General | ||||||||||||
| • | 1622–1628 | Jacob De la Gardie | ||||||||||
| • | 1696–1702 | Erik Dahlberg | ||||||||||
| Legislature | Diet | |||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||
| • | Conquered by Sweden | 1621 | ||||||||||
| • | Truce of Altmark | 25 September 1629 | ||||||||||
| • | Treaty of Oliva | 23 April 1660 | ||||||||||
| • | Great Northern War | 1700–1721 | ||||||||||
| • | Conquered by Russia | 1713 | ||||||||||
| • | Treaty of Nystad | 30 August 1721 | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Swedish Livonia (Swedish: Svenska Livland) was a dominion of the Swedish Empire from 1629 until 1721. The territory, which constituted the southern part of modern Estonia (including the island of Ösel ceded by Denmark after the Treaty of Brömsebro) and the northern part of modern Latvia (the Vidzeme region), represented the conquest of the major part of the Polish-Lithuanian Duchy of Livonia during the 1600–1629 Polish-Swedish War. Parts of Livonia and the city of Riga were under Swedish control as early as 1621 and the situation was formalized in Truce of Altmark 1629, but the whole territory was not ceded formally until the Treaty of Oliva in 1660. The minority part of the Wenden Voivodeship retained by the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was renamed the Inflanty Voivodeship ("Livonian Principality"), which today corresponds to the Latgale region of Latvia.
Riga was the second largest city in the Swedish Empire at the time. Together with other Baltic Sea dominions, Livonia served to secure the Swedish dominium maris baltici. In contrast to Swedish Estonia, which had submitted to Swedish rule voluntarily in 1561 and where traditional local laws remained largely untouched, the uniformity policy was applied in Swedish Livonia under Karl XI of Sweden: serfdom was abolished, peasants were offered education as well as military, administrative or ecclesiastical careers, and nobles had to transfer domains to the king in the Great Reduction.
The territory in turn was conquered by the Russian Empire during the Great Northern War and, following the Capitulation of Estonia and Livonia in 1710, formed the Governorate of Livonia. Formally, it was ceded to Russia in the Treaty of Nystad in 1721, together with Swedish Estonia and Swedish Ingria.
Governors-General
The dominion was ruled by appointed Governors-General, but retained its own diet.
- Jacob De la Gardie (1622–1628)
- Gustaf Horn (1628–1629)
- Johan Skytte (1629–1633)
- Nils Assersson Mannersköld (1633–1634)
- Bengt Oxenstierna (1634–1643)
- Herman Wrangel (1643)
- Erik Eriksson Ryning (1644)
- Gabriel Bengtsson Oxenstierna (1645–1647)
- Magnus Gabriel De la Gardie (1649–1651)
- Gustaf Horn (1652–1653)
- Magnus Gabriel De la Gardie (1655–1657)
- Axel Lillie (1661)
- Bengt Oxenstierna (1662–1665)
- Clas Åkesson Tott (the younger) (1665–1671)
- Fabian von Fersen (1671–1674)
- Krister Klasson Horn (1674–1686)
- Jacob Johan Hastfer (1687–1695)
- Erik Dahlberg (1696–1702)
- Carl Gustaf Frölich (1702–1706)
- Adam Ludwig Lewenhaupt (1706–1709)
- Henrik Otto Albedyll (1709)
- Niels Jonsson Stromberg af Clastorp (1709–1710)
|
Military
Swedish infantry and cavalry regiments
- Infantry regiments
- Garnisonsregementet i Riga (Garrison Regiment in Riga)
- Guvenörsregementet i Riga (Governor's Regiment in Riga)
- Livländsk infanteribataljon I (Livonian Infantry Battalion I)
- Livländsk infanteribataljon II (Livonian Infantry Battalion II)
- Livländsk infanteribataljon III (Livonian Infantry Battalion III)
- Livländsk infanteribataljon IV (Livonian Infantry Battalion IV)
- Livländskt infanteriregemente I (Livonian Infantry Regiment I)
- Livländskt infanteriregemente II (Livonian Infantry Regiment II)
- Livländskt infanteriregemente III (Livonian Infantry Regiment III)
- Livländskt infanteriregemente IV (Livonian Infantry Regiment IV)
- Livländskt infanteriregemente V (Livonian Infantry Regiment V)
- Cavalry regiments
- Laurentzens fridragoner (Wolter Wolfgang Laurentzen's Free Dragoons)
- Lewenhaupts frikompani (Adam Ludwig Lewenhaupt's Free Company)
- Adelsfanan i Livland och Ösel (Livonian and Öselian Banner of Nobles)
- Livländsk dragonskvadron I (Livonian Dragoon Squadron I)
- Livländsk dragonskvadron II (Livonian Dragoon Squadron II)
- Livländskt dragonregemente I (Livonian Dragoon Regiment I)
- Livländskt dragonregemente II (Livonian Dragoon Regiment II)
- Öselska lantdragonskvadronen (Öselian County Dragoon Squadron)
Temporary cavalry regiments:
- Livländska ståndsdragonbataljonen (Livonian Rank Dragoon Battalion)
- Öselska ståndsdragonbataljonen (Ösel Rank Dragoon Battalion)
See also
- Rise of Sweden as a Great Power
- Swedish Empire
- Realm of Sweden
- Duchy of Estonia (1561–1721)
- Estonia under Swedish rule
- Bishopric of Ösel-Wiek
References
- Andrejs Plakans, A Concise History of the Baltic States, Cambridge University Press, 2011, pp. 105ff.
Coordinates: 56°58′00″N 24°08′00″E / 56.9667°N 24.1333°E