WZ551
| Type 92/WZ551 IFV | |
|---|---|
|
A WZ551 APC | |
| Type |
Infantry fighting vehicle Armored personnel carrier |
| Place of origin | People's Republic of China |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1995-present |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Jiang Hong [WZ551B] at NORINCO Vehicle Research Institute; institute 201 (中国北方车辆研究所 China Vehicles Research Institute) and Institute 202 |
| Manufacturer | Norinco, at Factory 256 (西南车辆制造厂Southwest Vehicles Factories) |
| Specifications | |
| Weight | 12.5 tonnes |
| Length | 6.63 m |
| Width | 2.80 m |
| Height | 2.80 m |
| Crew | 3 + 9 passengers |
|
| |
| Armor | Welded steel |
Main armament | 25 mm autocannon |
Secondary armament |
12.7 mm heavy machine gun[1] 7.62 mm coaxial machine gun |
| Engine |
8-cylinder, turbo-charged, air-cooled diesel 320 hp |
| Suspension | Independent wheel |
Operational range | 800 km |
| Speed | 85 km/h |
The WZ551 (AKA the ZSL92 [2] is a Chinese wheeled armored personnel carrier. It is actually consisted of two families of vehicles with official designations in the People's Liberation Army as Type 90 and Type 92. Roughly 900 WZ551s are in service with the PLA,[3] where they are used by light mechanized infantry units. WZ551s have been exported to Algeria, Bosnia, Sri Lanka, Nepal and Pakistan.
Design
Produced by Norinco, the WZ551 first appeared in 1984, but the Chinese military were not satisfied with its performance, and the design had to be modified. Modification is mostly concentrated on improving the chassis. The improved WZ551A entered service in 1995 as the Type 92 IFV and Type 92A APC.
It has a crew of three men, and is fully amphibious, being driven in the water by shrouded propellers.
The IFV version is equipped with a 25 mm cannon and a 7.62 mm coaxial machine gun in a closed turret and it can carry 9 passengers. The APC version has only a 12.7 mm machine gun but can carry 11 passengers. Additional versions include anti-tank missile, command, self-propelled artillery, air defense and armored recovery vehicles.
Type 90
Type 90 first appeared on the National Day of the People's Republic of China parade in 1984, and it is the basic version of WZ551. During its service, it was discovered that the vehicle was underpowered and the cross country capability at high altitude terrain was not sufficient enough to meet the requirement. As a result, the planned 4 x 4 and 8 x 8 variants were canceled, and resources were concentrate on the improvement effort. However, the planned export version designated as ZSL-90 (also the industrial designation) was continued, and the vehicle was used as chassis for a variety weaponry platforms, such as command vehicle, ATGW carrier, self-propelled AAA, and ambulance.
The most distinct visual difference between Type 90 and its successor Type 92 is that for Type 90, the distance between the first pair and the second pair of wheels is greater than the distance between the second pair and the third pair of wheels, while for Type 92, the distance is the same for all. Despite being used as a common chassis for many different platforms, the total number of vehicles of all types entering Chinese service is small due to its inherent problem, and with the exception of the basic APC version, no other versions of ZSL-90 is known to be exported due to the same reason.
NGV-1
NGV-1 is the successor of Type 90. It was discovered that the cross country mobility was not the only thing that needed to be improved for WZ551, firepower was also in need for improvement. The original Chinese manually operated 25-mm gun initially mounted on WZ551 proved to be incapable of penetrating the armor plate of most of Soviet armored vehicles, and a more power small caliber gun that was able to defeat Soviet armor was needed, and China turned to west for help because its own technologies and industrial capabilities back in the 1980s could not fill the need in the required time.
A deal was made with French firm GIAT to incorporate a GIAT 25-mm autocannon as the primary weapon for WZ551 and the work on the redesign of WZ551 begun in China even before the French gun was delivered. Due to the urgent need to meet the schedule, the GIAT 25-mm autocannon was airlifted to China, as opposed to delivery via cargo ships, the usual practice at the time. The development was completed and received state certification in October 1988, and the new vehicle was named as NGV-1, with N for Norinco, G for GIAT and V for vehicle. The remotely operated 25-mm autocannon was eventually reverse engineered in China after France withdrew from the program after 1989, and used to upgrade Type 92, another development of WZ551.
Type 92

The redesigned ZSL-92 or Type 92 solved the problems of its predecessor Type 90 and was first revealed to the public in 1986, and entered Chinese service on larger scale than its predecessor. Just like Type 90, Type 92 is also used as a common chassis for many different weaponry platforms, such as command vehicle, ATGW carrier, self-propelled AAA, and ambulance. Additionally, the canceled 4 x 4 and 8 x 8 versions were realized in Type 92 program. The industrial designation VN2A is also used for the export version of Type 92, following earlier practice. The chassis of Type 92 comes in three variations:
- the 4X4 APC looks like the VAB, used mostly by the Chinese police, but also used as self-propelled SAM chassis.
- the 6X6 APC or MICV. This was the baseline and also the first of the series.
- the 8x8 variant
105 mm Assault Gun
In 2001 a self-propelled assault gun based on the WZ-551 was disclosed.[4]
120 mm Self Propelled Mortar
In 2001 a self-propelled mortar based on the WZ-551 was disclosed.[4]
122 mm Self Propelled Howitzer
This was based on a lengthened chassis.[4]
YT ADS
In 2005, another mobile land based air defense variant of TY-90 was revealed to the Chinese public, named as YT ADS, short for Yi-Tian (倚天, meaning leaning on the sky) Air Defense System. YT ADS is a development of earlier LS ADS designed to specifically address the shortcomings of the latter, namely, the insufficient armor protection, lack of amphibious capability and radar. Like its predecessor LS ADS, the system is also developed by Norinco.
Weaponry of YT ADS is similar to that of earlier LS ADS, with the missile configuration remains the same as that of LS ADS, but additionally, there is an extra 12.7 mm heavy machine gun and 3 smoke grenade dischargers as secondary armament for added protection. WZ551 is utilized as the chassis of the YT ADS, giving the system amphibious capability and added protection. Additionally, a light solid state 3-D passive phased array radar is added to the fire control system, just above the original electro-optical fire control system, providing the ADS with greater surveillance range. The radar can be fold down for traveling and transportation.
Specifications:
- Maximum target altitude: 4 km
- Minimum target altitude: 15 meter
- Maximum target range: 6 km
- Minimum target range: 300 meter
- Maximum target speed: > 400 meter / second
- Maximum radar searching range: >20 km
- Maximum radar tracking range: 10 – 12 km
- System reaction time: 6 – 8 seconds
WMZ-551B
This was an upgraded amphibious armored personnel carrier with improved firepower, maneuverability, and reliability.[4]
VN2
Upgraded export variant with 30mm cannon.
Operators
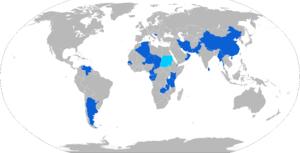
 Algeria - Algerian Army[5]
Algeria - Algerian Army[5] Argentina - Argentine Army: 4[6]
Argentina - Argentine Army: 4[6] Bosnia - Armed Forces of Bosnia and Herzegovina: 10[6]
Bosnia - Armed Forces of Bosnia and Herzegovina: 10[6] Burma - Myanmar Army: 76[6]
Burma - Myanmar Army: 76[6] Burundi - Military of Burundi: Some on order.[6]
Burundi - Military of Burundi: Some on order.[6] Cameroon - Cameroonian Armed Forces
Cameroon - Cameroonian Armed Forces Chad - Chadian Ground Forces: 10
Chad - Chadian Ground Forces: 10 Congo-Brazzaville - Congolese Army[7]
Congo-Brazzaville - Congolese Army[7] Djibouti - Djiboutian Army[8]
Djibouti - Djiboutian Army[8] Gabon - Gabonese Army[7]
Gabon - Gabonese Army[7] Iran - Islamic Republic of Iran Army[5]
Iran - Islamic Republic of Iran Army[5] Kenya - Kenyan Army: 35[6]
Kenya - Kenyan Army: 35[6] Pakistan - Pakistan Army[9]
Pakistan - Pakistan Army[9] People's Republic of China - People's Liberation Army Ground Force - 750 Type 92, 150 Type 92A[3]
People's Republic of China - People's Liberation Army Ground Force - 750 Type 92, 150 Type 92A[3] Nepal - Nepalese Army: 175 [6]
Nepal - Nepalese Army: 175 [6] Niger - Niger Armed Forces: At least one[10]
Niger - Niger Armed Forces: At least one[10] Oman - Omani Royal Guard: 50[6]
Oman - Omani Royal Guard: 50[6] Senegal - Senegal Army: 13[8]
Senegal - Senegal Army: 13[8] Sri Lanka - Sri Lanka Army: 190[6]
Sri Lanka - Sri Lanka Army: 190[6] Sudan - Sudan People's Armed Forces: 10;[6] other Sudanese variants produced under licence.
Sudan - Sudan People's Armed Forces: 10;[6] other Sudanese variants produced under licence. Tanzania - Tanzanian Army: 10[6][7]
Tanzania - Tanzanian Army: 10[6][7] Venezuela - Venezuelan Army[6]
Venezuela - Venezuelan Army[6] Zambia- Zambian Army: 5[6]
Zambia- Zambian Army: 5[6]
See also
References
- ↑ . sinodefence.com http://www.sinodefence.com/army/armour/zsl92specifications.asp. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ Archived January 27, 2009, at the Wayback Machine.
- 1 2 Gaurav Sharma (Spring 2012). "People's Liberation Army Ground Forces Modernisation - An assessment" (pdf). Retrieved 17 January 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 http://www.globalsecurity.org/military/world/china/wz-551.htm
- 1 2 "WZ-551 (Type 90/92) Wheeled Armoured Personnel Carriers". Army Technology. Retrieved 6 July 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 "Trade Registers". Armstrade.sipri.org. Retrieved 2015-01-01.
- 1 2 3 David H. Shinn, Joshua Eisenman. Politics and Government in African States 1960-1985. p. 173.
- 1 2 Binnie, Jeremy (5 April 2016). "Senegal parades new Chinese armour". IHS Jane's 360. London: IHS Jane's. Retrieved 6 April 2016.
- ↑ "WZ-551 (Type 90/92) Wheeled Armoured Personnel Carriers, China". Retrieved 09-03-2013. Check date values in:
|access-date=(help) - ↑ Binnie, Jeremy. "Militant video reveals Niger's Chinese arms | IHS Jane's 360". IHS Jane's 360. London. Retrieved 6 July 2016.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to WZ551. |
.jpg)
