Worshippers Way
Worshippers Way or Prayers Road in Hebron, West Bank is a road linking the Israeli settlement of Kiryat Arba with the Cave of the Patriarchs and with the Jewish settlements in Hebron. The road is used by Israelis and tourists who visit the Cave and the Old City of Hebron. Palestinians are denied vehicular use of the road. The road was expanded after an ambush near Kiryat Arba that took place in November 2002. The expansion required that adjacent Palestinian land be expropriated, which resulted in a legal battle. A number of buildings of architectural and historical value, dating back to the Mamluk-Ottoman period, were also expropriated and destroyed.
Names
The Worshippers route has been given numerous names and variants of names, such as "Worshipper's Way", "Worshipers' Way", "Worshippers' Path", etcetera. Before the Israeli High Court the route was called "prayers' path"[1] and "Worshippers' Way".[2] Settlers called the western Prayers Road "Simtat Eretz" and the eastern Prayers Road "Tsir ha-Metpolelim Street".
The name Worshippers Way or Prayers Road is sometimes also used for the north-south route between Kiryat Arba/Givat Ha'avot and the Cave of the Patriarchs.[3]
Background
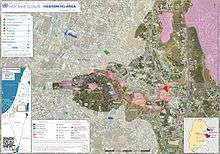
Kiryat Arba is an Israeli settlement at the outskirts of Hebron, just outside the eastern municipality border. It is located close to the Cave of the Patriarchs, and six Jewish settlements south of the Old City of Hebron. Kiryat Arba has more than 7,500 residents, while the settlements in Hebron as of 2005 house some 600 settlers, secured by about 1,500 soldiers.[4] Kiryat Arba was built at the edge of the area which the 1967 Allon Plan envisioned as being annexed to Israel, while Hebron itself would be part of an enclave with Palestinian self-rule.
Originally, the settlers used a route running from the northern entrance via Al-Shuhada Street (which was closed to Palestinians) to the Cave of the Patriarchs. This road, connecting all the Jewish locations in Hebron, is known by Israelis as "Tzir Zion Road", or "Route of Zion", and was closed to Palestinian traffic in 2001,[5] after two Israeli settlers were killed. In August 2009, the route was reopened to 80 local Palestinian families.[6]
Following an ambush near Kiryat Arba in 2002, in which 12 Israeli soldiers and security guards were killed, Israel wanted to build a road directly connecting the southern gate of Kiryat Arba with the Cave.
Plans after the 2002 Hebron ambush
One day after the 2002 Hebron ambush, Zvi Katzover, the head of Kiryat Arba, called on the government to "clean up the area" between Kiryat Arba and the Tomb of the Patriarchs and to destroy the hundreds of Palestinian homes along this short stretch of road.[7] The next day, Prime Minister Ariel Sharon said that the opportunity that now presents itself in the wake of the attack ... must be exploited to establish new facts on the ground.[7] He said that ″a window of opportunity existed in the coming 48 hours to establish a "compact" zone of Jewish territorial contiguity between Kiryat Arba and the Jewish enclave in the heart of Hebron, including the Tomb of the Patriarchs″. Already in 1996, Sharon had presented a plan for a Jewish zone from Kiryat Arba to Tel Rumeida and Beit Hadassah, including the ancient Karaite and Sephardi cemeteries.[8] Housing and Construction Minister Natan Sharansky supported the plan to link the settlements and build settlement contiguity.[9]
Tourism Minister Yitzhak Levy ordered his ministry to speed up its preparations for a "tourism promenade" between Kiryat Arba and the Tomb of the Patriarchs.[8] The plan envisioned a Jewish settlers–only promenade consisting of an open promenade in an area that was not built up, and an "alley promenade" through the southern edge of the old town of Hebron, among ancient buildings with cultural, historical, archaeological and architectural values.[10]
The Kiryat Arba Council and the council of settlers in Hebron's Jewish enclave announced a plan to build 1,000 housing units between Kiryat Arba and the Tomb of the Patriarchs, in the area in which the ambush had taken place. Housing and Construction Minister Natan Sharansky supported the plan and ordered his ministry's workers to review the possibility of expropriating lands in the city and using them for Jewish residential purposes.[11]
Expansion
Two weeks after the ambush, on 29 November 2002,[12] the Israel Defense Forces (IDF) issued a sequestration order to seize Palestinian lands and demolish a number of buildings under "Decree Number 61/02/T to Expropriate Property". Contradictory to the original promenade plan, 22 buildings of architectural and historical value, dating back to the Mamluk-Ottoman period would be demolished in the old town of Hebron "for military needs". A 730 meters long and 6 to 12 meters wide corridor was planned on 8.2 dunams expropriated land, about a quarter of which in the old town of Hebron.[10] According to the High Court, the total width of the alley was originally planned to amount 8 meters. Thirteen buildings along the south–western part of the route were to be demolished, and a concrete wall was to be built along the north–eastern part of the route.[1]
According to the American administration and Israeli sources close to the planning, the aim of the expropriation of the land and the building of the promenade was to create territorial contiguity between Kiryat Arba and Hebron.[10]
On 1 December 2002, the IDF posted warrants to seize and demolish 15 Palestinian properties, with the plan to widen the road.[13] On 8 December 2002, the IDF started the expansion of the road with a large truck and bulldozers, while a work stoppage order, issued by the High Court, ordered not to demolish Palestinian buildings adjacent to areas planned for the new promenade.[14]
On 11 December 2002, the Municipality of Hebron and Palestinian landowners issued a petition (HCJ 10497/02) at the High Court against the sequestration.[10] Another petition (HCJ 10356/02) was issued by Israeli conscientious objectors of Yesh Gvul. Following the petitions and remarks of the court, the plan was adapted; the width of the promenade would be smaller, and only 3 of the 13 houses demolished. The houses were already abandoned for years after the army had declared the area a closed military zone.[15]
In February 2003, the High Court prohibited the demolition of the 22 houses from to the Mamluk-Ottoman period. According to UNESCO, eventually three of them were destroyed and eleven others damaged.[16]
In its decision of 4 March 2004, the High Court stipulated that praying in the Tomb was part of the constitutional right to freedom of religion and worship for the residents of the area. It even stated that ″The freedom of religion is a constitutional basic right of the individual, of a status even higher than other constitutional human rights″. The Court decided that the right to freedom of religion and worship for the settlers of Kiryat Arba, including a save route to the Tomb, prevailed over the right to private property for the Palestinian landowners. It found that the ″relative impingement upon property rights of the property owners along the route, which was limited to a minimum″ justified the expropriation of the Palestinian lands.[1]
After the High Court decision, on 7 May 2004, the IDF ordered the demolition of 11 houses in the Wadi Al-Nassara and Haret Jaber neighborhoods, and the confiscation of 700 square meters of Palestinian land close to the Ibrahimi Mosque belonging to the Waqf, all located in the area between Kiryat Arba and the Mosque.[17] On 10 August, the Israeli Army demolished the houses, dating back to the Ottoman and Mamluk periods.[18][19]
Third route, Dana Way
In 2004, settlers built a cement path in the Wadi al Hussein (Wadi a-Nasara) from the southwestern entrance of Kiryat Arba to the Worshippers Way,[20][21] called "Dana Way". Initially, the State ordered to remove the path, but the IDF ignored the orders. When the Palestinian land owners went to the Israeli High Court (HCJ) in 2007, the State first declared that the path would be demolished, but later said it was needed for military reasons. The IDF declared that it was a military security road, also used by worshippers as a pedestrian path.[22] In May 2010, the land owners received a land seizure order, which in effect legalized the already existing dirt road.[20][21]
On 1 February 2012, the High Court ruled on a petition against the 2010 land seizure order and approved the path, based on security reasons, as a more secure alternative to Worshippers Way.[2]
Criticism
Human rights organization HaMoked criticized the role of the High Court as supporting the Israeli state in institutionalizing the presence of the settlers in the territory, which is illegal under international law. While international law forbids to destroy or seize the enemy's property if not necessary for imperative operational military needs, the state argued that the expanded road was needed for the safety of the settlers; the state itself, however, was party to the illegal presence of the settlers. HaMoked blamed the Court for accepting, without a "second guess", the state's and the army's assertion that the road was not meant to create Jewish territorial contiguity, but was based purely on security considerations and was meant to protect the lives of the worshippers using the road.[15]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 HCJ 10356/02 and HCJ 10497/02, Petition for an Order Nisi and an Interlocutory Injunction. High Court of Justice, 4 March 2004
- 1 2 HCJ 4331/10–Petition for Order Nisi and Interim Injunction. High Court of Justice, 1 February 2012. On
- ↑ Settlers get three more months on ′Worshipers' Way′. Dan Izenberg, Jerusalem Post, 17 January 2008
- ↑ Special Focus: The Closure of Hebron’s Old City. OCHAoPt, July 2005. PDF
- ↑ Israel lets Palestinians use Hebron road for first time in 8 years.Reuters/Haaretz, 2 August 2009
- ↑ Settlers, MKs protest reopening of Zion Route. Tovah Lazaroff, Jerusalem Post, 2 August 2009
- 1 2 PM calls for territorial continuity from Kiryat Arba to Hebron. Haaretz, 17 November 2002
- 1 2 PM demands `quick' changes in Hebron for Jewish control. Haaretz, 18 November 2002
- ↑ Sharon threatens to expand Hebron enclave. Conal Urquhart, The Guardian, 18 November 2002
- 1 2 3 4 Pernicious promenade. Esther Zandberg, Haaretz, 12 December 2002
- ↑ Hebron settlers plan to build 1,000 units in new neighborhood. Amos Harel and Nadav Shragai, Haaretz, 19 November 2002
- ↑ Note: The English translation of the petitions judgment under the numbers HCJ 10356/02 and HCJ 10497/02 mentions the date of 29 November 2003, but speaks of an order nisi in the petitions on 18 December 2002. It is unclear if there was a new Order in 2003.
- ↑ Israel issues warrants to seize Palestinian property in Hebron. Associated Press, 2 December 2002
- ↑ IDF starts work on Hebron promenade. Haaretz, 10 December 2002
- 1 2 Demolition of Palestinian houses in Hebron to ease the daily life of settlers: HCJ 10356/02 Haas v. IDF Commander in the West Bank (judgement rendered March 4, 2004). Yossi Wolfson, HaMoked: Center for the Defence of the Individual, 1 December 2012
- ↑ Progress report on the protection of the Palestinian cultural and natural heritage, par. 24. UNESCO, July 2005
- ↑ Israel Orders Demolition of 11 Houses and Land Seizure in Hebron. AFP/Reuters, 7 May 2004
- ↑ The Israeli Colonization activities in the Palestinian Territories during the 3ed quarter of 2004, section Israeli Violations in Hebron Governorate. POICA, 31 August 2004
- ↑ Geopolitical Status in Hebron Governorate, p. 11. LRC (Jerusalem), December 2006
- 1 2 Israeli Colonists Attempts to Open a Road. POICA, 27 May 2013
- 1 2 OPT: Protection of civilians. Weekly report 19–25 May 2010, par. Israeli authorities continue to issue demolition orders. OCHA, 27 May 2010 (the source refers to the ambush near Kiryat Arba, on 15 November 2002).
- ↑ Using "security grounds" to legalize illegal settler building: HCJ 4331/10 City of Hebron v. State of Israel (judgment rendered February 1, 2012). Yotam Ben Hillel, HaMoked–Center for the Defence of the Individual, 30 December 2012
External links
- Israeli " Prayers" Road" built on ruins of ancient Palestinian houses in the old city of Hebron. POICA, 7 September 2004 (This page contains maps that are rotated upside down!)
- Israeli Colonists Attempts to Open a Road. POICA, 27 May 2013
- A one-way road. Jennifer Peterson, The Palestine Report/Media Monitors Network, 20 December 2002
- Destroying History. Ahmad Sub Laban, Palestine Report, 1 September 2004
- ‘They have two roads on our land already, why do they need a third…?’. ISM, 27 June 2013
- Updates on settler road expansion,. Christian Peacemaker Teams, 27 June 2013
- Map of the Hebron center