Republic XF-91 Thunderceptor
| XF-91 Thunderceptor | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Role | Prototype interceptor aircraft |
| Manufacturer | Republic Aviation |
| First flight | 9 May 1949 |
| Status | Canceled |
| Number built | 2 |
| Unit cost | |
| Developed from | Republic F-84 Thunderjet |
The Republic XF-91 Thunderceptor (originally designated XP-91) was a mixed-propulsion prototype interceptor aircraft, developed by Republic Aviation. The aircraft would use a jet engine for most flight, and a cluster of four small rocket engines for added thrust during climb and interception. The design was largely obsolete by the time it was completed due to the rapidly increasing performance of contemporary jet engines, and only two prototypes were built. One of these was the first US fighter to exceed Mach 1 in level flight.
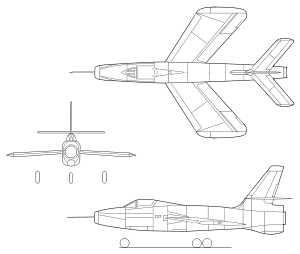
A unique feature of the Thunderceptor was its unusual inverse tapered wing, in which the chord length increased along the wing span from the root to the tip, the opposite of conventional swept wing designs. This was an attempt to address the problem of pitch-up, a potentially deadly phenomenon that plagued early high-speed models. The Thunderceptor's design meant the entire wing stalled smoothly, more like a straight-wing design.
Design and development

During the development of the XP-84, Republic, under the guidance of Alexander Kartveli looked at the installation of rockets to fighters. The company was inspired by German wartime aircraft: the rocket-powered Messerschmitt Me 163 and the experimental rocket-boosted turbojet Messerschmitt Me 262C Heimatschützer (home protector) series of interceptor prototypes.
The Thunderceptor design was one of two swept-wing modifications based on the original Republic F-84 Thunderjet, the other being the Republic F-84F Thunderstreak which was developed later. A serious problem with most swept wing designs of the era was dangerous performance at low speeds and high angle of attack. The stagnant airflow over the wing tended to "slide" towards the wingtips, which caused them to stall before the rest of the wing. In this situation the center of lift would rapidly shift forward relative to the center of mass, pitching the nose up and leading to an even greater angle of attack or, in extreme cases, end-over-end tumbling of the aircraft. Aircraft caught in this regime would often stall and crash, and a rash of such accidents with the North American F-100 Super Sabre led to the term "Sabre dance". The most famous incident was the loss of an F-100C Super Sabre during an attempted emergency landing at Edwards AFB, California on 10 January 1956 which was caught by film cameras set up for an unrelated test. The pilot fought to retain control as he rode the knife-edge of the flight envelope but fell off on one wing, hit the ground and exploded with fatal results.
The Thunderceptor's most notable design feature was intended to address this problem. The wings were built to have considerably more chord (distance from the leading edge to the trailing edge) at the tip than root, allowing them to generate more lift. This neatly addressed the problem of Sabre dance by delaying the point of stall on the tip to that of the entire wing. A side-effect of this design was that the tips had more internal room, so the landing gear was mounted to retract outwards with the wheels lying in the wingtips, using two smaller wheels in a tandem arrangement for each main gear strut, instead of one larger one. Another design change was the ability to vary the angle of incidence of the wing as a whole, tilting it up for low speed operations during takeoff and landing, and then "leveling it off" for high-speed flight and cruise. This allowed the fuselage to remain closer to level while landing, greatly improving visibility.
In keeping with its intended role as an interceptor, the nose was redesigned to incorporate a radar antenna, forcing the air intake for the engine to be moved from its original nose-mounted position to a new intake below it. The fuselage was otherwise very similar to the F-84's. The first prototype did not include the radome, although this was fitted to the second prototype.
Testing and evaluation

The first prototype made its first flight on 9 May 1949, breaking the speed of sound in December 1951. It was later modified with a small radome for gunnery ranging (although not the "full" radome from the second prototype). The second prototype included the full radome and chin-mounted intake, but was otherwise similar. With both the jet and rockets running, the aircraft could reach Mach 1.71. Both prototypes completed 192 test flights over the course of five years.[2]
The second prototype, 46-681, had an engine failure during takeoff from Edwards AFB in the summer of 1951. Republic test pilot Carl Bellinger escaped from the aircraft just as the tail melted off - total flight time was a mere 90 seconds. By the time fire apparatus arrived, driving seven miles across the dry lake bed, the tail section had been reduced to ashes. 46-681 was then fitted with a "V" or "butterfly" tail, and was flight-tested with this configuration. It was later used at Edwards AFB as a crash-crew training simulator, then scrapped.[3]
As an interceptor the Thunderceptor was soon eclipsed by designs from other companies, but like the Thunderceptor none of these would go into production. The United States Air Force decided to wait the short time needed to introduce newer and much more capable designs created as a part of the 1954 interceptor project. The Thunderceptor, like the other interceptor designs of the era, had extremely short flight times on the order of 25 minutes, making them almost useless for protecting an area as large as the United States. The 1954 designs outperformed the XF-91 in speed, range, loiter time, as well as including the radar and fire-control systems needed for night and all-weather operation. The era of the dedicated day fighter-type interceptor was over.
Aircraft disposition

- 46-0680 - Research & Development Gallery at the National Museum of the United States Air Force at Wright-Patterson AFB in Dayton, Ohio.[4]
- 46-0681 - destroyed while testing at Edwards AFB in 1951.[5]
Specifications (XF-91 Thunderceptor)
Data from
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 43 ft 3 in (9.52 m)
- Wingspan: 31 ft 3 in (13.18 m)
- Height: 18 ft 1 in (5.51 m)
- Wing area: 320 ft² (29.73 m²)
- Empty weight: 14,140 lb (6,410 kg)
- Loaded weight: 18,600 lb (8,400 kg)
- Max. takeoff weight: 28,300 lb (12,840 kg)
- Powerplant:
- 1 × General Electric J47-GE-7 (later GE-17) axial-flow turbojet, 5,200 lbf (30,6 kN); 6,900 lbf with afterburning
- 4 × Reaction Motors XLR11-RM-9 rocket, 1,500 lbf (7 kN) each
Performance
- Maximum speed: 984 mph (1,584 km/h)
- Range: 1,170 mi (1,880 km)
- Service ceiling: 50,000 to 55,000 ft (15,200 to 16,800 m)
- Rate of climb: 47,500 ft in 2.5 minutes (14,500 m)
- Wing loading: 58.12 lb/ft² (283 kg/m²)
- Thrust/weight (jet): 0.60
Armament
- Guns: 4 × 20 mm (.79 in) cannon
See also
- Aircraft of comparable role, configuration and era
- Related lists
References
Notes
- ↑ Knaack 1978, p. 309.
- ↑ Yenne 1993, p. 114.
- ↑ Pace 1991, p. 87.
- ↑ "XF-91 Thunderceptor/46-680" National Museum of the United States Air Force. Retrieved: 13 June 2011.
- ↑ "XF-91 Thunderceptor/46-681." Joe Baugher serial numbers. Retrieved: 10 May 2013.
Bibliography
- Jenkins, Dennis R. and Tony R. Landis. Experimental & Prototype U.S. Air Force Jet Fighters. North Branch, Minnesota, USA: Specialty Press, 2008. ISBN 978-1-58007-111-6.
- Knaack, Marcelle Size.Encyclopedia of US Air Force Aircraft and Missile Systems: Volume 1, Post-World War II Fighters, 1945-1973. Washington, D.C.: Office of Air Force History, 1978. ISBN 0-912799-59-5.
- Pace, Steve. Republic XF-91 Thunderceptor Rocket Fighter (Air Force Legends N.210). Simi Valley, California, USA: Steve Ginter Books, 2000. ISBN 0-942612-91-4.
- Pace, Steve. X-Fighters: USAF Experimental and Prototype Fighters, XP-59 to YF-23. St. Paul, Minnesota, USA: Motorbooks International, 1991. ISBN 0-87938-540-5.
- Winchester, Jim. The World's Worst Aircraft: From Pioneering Failures to Multimillion Dollar Disasters. London: Amber Books Ltd., 2005. ISBN 1-904687-34-2.
- Yeager, Chuck and Leo Janos. Yeager: An Autobiography. New York: Bantam Books, 1986. ISBN 0-553-25674-2.
- Yenne, Bill. The World's Worst Aircraft. New York: Dorset Press, 1993. ISBN 0-88029-490-6.
Further reading
- Pace, Steve (2000). Republic XF-91 Thunderceptor. Air Force Legends. Nº210 (First ed.). California, United States: Ginter Books. ISBN 0-942612-91-4. Retrieved 1 February 2015.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Republic XF-91. |
- XF-91 in U.S Centennial of Flight Commission
- Several pictures of the XF-91 46-680
- Interceptor, 1949 - pictures from Flight 1949
