XSS 10
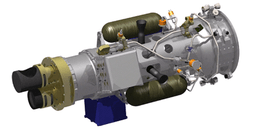 XSS-10 computer model | |
| Mission type | Technology |
|---|---|
| Operator | AFRL |
| COSPAR ID | 2003-005B |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Manufacturer | Boeing |
| Launch mass | 28 kilograms (62 lb) |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | January 29, 2003, 18:06:00 UTC |
| Rocket | Delta II 7925-9.5 |
| Launch site | Cape Canaveral SLC-17B |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric |
| Regime | Low Earth |
| Eccentricity | 0.020384971 |
| Perigee | 518.0 kilometers (321.9 mi) |
| Apogee | 805.0 kilometers (500.2 mi) |
| Inclination | 39.75& degrees |
| Period | 98.0 minutes |
XSS-10 (eXperimental Small Satellite 10) was a small, low-cost micro-spacecraft developed by the U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory’s Space Vehicles Directorate to test technology for line-of-sight guidance of spacecraft.[1] The project was initiated at AFRL by Program Manager David Barnhart [2] and completed by Georgia Tech Research Institute engineer Thom Davis.[3] The project was declared a success shortly after launch.[4]

Spent upper stage of the Delta II launch vehicle imaged by the XSS 10 satellite
References
- ↑ Banke, Jim (2003-01-30). "Air Force XSS-10 Micro-Satellite Mission a Success". Space.com. Archived from the original on May 13, 2008. Retrieved 2008-07-28.
- ↑ David A. Barnhart et al, “XSS-10 Micro-satellite Demonstration,” AIAA-1998-5298, AIAA Defense and Civil Space Programs Conference and Exhibit, Huntsville, AL, Oct. 28-30, 1998
- ↑ "Big plans for small satellites". Historical archive. Georgia Tech Research Institute. Retrieved 2012-10-26.
- ↑ Sanders, Jane M (2003-08-11). "The Little Engine That Could". Research Horizons. Georgia Institute of Technology. Retrieved 2012-10-26.
External links
- XSS Micro-Satellite at Boeing.com
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/11/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.