| Team | Pld | W | L | T | NR | NRR | Pts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | +0.758 | 10 | |
| 6 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 1 | +2.582 | 9 | |
| 6 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 1 | +1.123 | 9 | |
| 6 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 0 | +1.135 | 8 | |
| 6 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 0 | +0.030 | 4 | |
| 6 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 0 | −1.987 | 2 | |
| 6 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | −3.042 | 0 |
2011 Cricket World Cup
|
Official logo of the ICC Cricket World Cup 2011 | |
| Dates | 19 February – 2 April |
|---|---|
| Administrator(s) | International Cricket Council |
| Cricket format | One-Day International |
| Tournament format(s) | Round-robin and Knockout |
| Host(s) |
India Sri Lanka Bangladesh |
| Champions |
|
| Participants | 14 (from 104 entrants) |
| Matches played | 49 |
| Player of the series |
|
| Most runs |
|
| Most wickets |
|
| Official website | ICC Cricket World Cup 2011 |
| UDRS | Yes |
The 2011 ICC Cricket World Cup was the tenth Cricket World Cup. It was played in India, Sri Lanka, and (for the first time) Bangladesh. India won the tournament, defeating Sri Lanka by 6 wickets in the final in Mumbai, thus becoming the first country to win the Cricket World Cup final on home soil.[1][2] India's Yuvraj Singh was declared the man of the tournament.[3] This was the first time in World Cup history that two Asian teams had appeared in the final. It was also the first time since the 1992 World Cup that the final match did not feature Australia.
All the matches were One Day Internationals, and all were played over 50 overs. Fourteen national cricket teams took part, including 10 full members and four associate members of the ICC.[4] The opening ceremony was held on 17 February 2011 at Bangabandhu National Stadium, Dhaka,[5] and the tournament was played between 19 February and 2 April. The first match was played between India and Bangladesh at the Sher-e-Bangla National Stadium in Mirpur, Dhaka.[6]
Pakistan was also scheduled to be a co-host, but after the 2009 attack on the Sri Lanka national cricket team in Lahore, the International Cricket Council (ICC) cancelled that,[7] and the headquarters of the organising committee, originally in Lahore, was transferred to Mumbai.[8] Pakistan was to have held 14 matches, including one semi-final.[9] Eight of the games (including the semi-final) were awarded to India, four to Sri Lanka, and two to Bangladesh.[10]
Host selection
The ICC announced on 30 April 2006 which countries would host the 2011 World Cup. Australia and New Zealand had also bid for the tournament; if successful, they would have shared the hosting equally, leaving the location of the final still to be decided. The Trans–Tasman bid, Beyond Boundaries, was the only one delivered to the ICC headquarters in Dubai before the 1 March deadline, but the Asian bidders were granted an extension by the ICC.[11] The New Zealand government had given assurance that Zimbabwe would be allowed to compete in the tournament, following political discussions in the country over whether their cricket team should be allowed to tour Zimbabwe in 2005.
The extra time needed for the Asian bid had weakened its prospects, but when the time came to vote, Asia won the hosting rights by ten votes to three.[11] The Pakistan Cricket Board (PCB) has revealed that the vote of the West Indies Cricket Board was decisive, as the Asian bid had the support of South Africa and Zimbabwe as well as the four bidding countries.[12] The Pakistani newspaper Dawn reported that the Asian countries had promised to hold fund-raising events for West Indian cricket during the 2007 World Cup, which may have influenced the vote.[13] However, I. S. Bindra, chairman of the Monitoring Committee of the Asian bid, said that their promise of extra profits of around US$400 million had been decisive,[14] that there "was no quid pro quo for their support",[15] and that playing the West Indies had "nothing to do with the World Cup bid".[15]
The ICC prefers to rotate World Cup venues its full member nations. They have been hosted by England (in 1975, 1979, and 1983), India and Pakistan (1987), Australia and New Zealand (1992), India, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka (1996), England and the Netherlands (1999), South Africa, Zimbabwe, and Kenya (2003), and the West Indies (2007). Australia/New Zealand were awarded the 2015 World Cup.
Format
Late in 2007, the four host nations agreed on a revised format for the 2011 World Cup, identical to that of the 1996 World Cup, except that there would be 14 teams instead of 12. The first round of the tournament would consist of two groups of seven teams. Each team in a group would play all the others once, and the top four from each group would qualify for the quarter-finals.[16] This ensured that every team would play at least six matches.
Qualification
As per ICC regulations, all 10 full members automatically qualify for the World Cup, including Zimbabwe who have given up their Test playing status until the standard of their team improves.[17]
The ICC also organised a qualifying tournament in South Africa to determine which Associate teams would participate in 2011 event. Ireland, who had been the best performing Associate nation since the last World Cup, won the tournament, beating Canada in the final. The Netherlands and Kenya also qualified by virtue of finishing third and fourth respectively.[18] All 4 associates kept their ODI status as well as Scotland who this time failed to qualify for the World Cup.
List of qualified teams
The following 14 teams qualified for the final tournament.
| Group A | Group B | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Team | Rank | Team |
| Full Members | |||
| 1 | 2 | ||
| 3 | 4 | ||
| 5 | 6 | ||
| 7 | 8 | ||
| 9 | 10 | ||
| Associate Members | |||
| 11 | 12 | ||
| 13 | 14 | ||
Preparations
.jpg)
Pakistan loses co-host status
In April 2009 the ICC announced that Pakistan had lost its right to co-host the 2011 World Cup because of concerns about the "uncertain security situation" in the country, especially in the aftermath of the 2009 attack on the Sri Lanka national cricket team in Lahore.[19][20] The PCB estimated that this would lose them $10.5 million.[21] This figure took account only of the fees of $750,000 per match guaranteed by the ICC. The overall loss to the PCB and the Pakistani economy were expected to be much greater.
On 9 April 2009 PCB chairman Ijaz Butt revealed that they had issued a legal notice to oppose ICC's decision.[22] The ICC, however, claimed that the PCB was still a co-host, and that they had only relocated the matches out of Pakistan.[23] Pakistan proposed that South Asia host the 2015 World Cup and that Australia and New Zealand host the 2011 event, but this option did not find favour with their co-hosts and was not implemented.[24]
Allocation of matches
On 11 April 2005 PCB chairman Shaharyar Khan announced an agreement on the allocation of games,[25] under which India would host the final, Pakistan and Sri Lanka the semi-finals,[26] and Bangladesh the opening ceremony.[27] After being stripped of its status as a co-host, Pakistan proposed to host its allocated games in the United Arab Emirates as a neutral venue. They had played matches in Abu Dhabi, Dubai, and Sharjah in the preceding months. On 28 April 2009, however, the ICC announced that matches originally intended to be played in Pakistan would be reallocated. As a result, India hosted 29 matches across eight venues, including the final and one semi-final; Sri Lanka hosted 12 matches at three venues, including one semi-final; and Bangladesh hosted 8 matches at two grounds, as well as the opening ceremony on 17 February 2011.[28]
On 1 June 2010 the first tranche of tickets were put on sale after a meeting of the tournament's Central Organising Committee in Mumbai. The cheapest tickets cost 20 US cents in Sri Lanka.[29] In January 2011 the ICC declared the Eden Gardens ground in Kolkata, India, to be unfit and unlikely to be complete by 27 February, when it was scheduled to host a match between India and England. The match was moved to Bangalore.[30]
Media and promotion
 |
De Ghuma Ke
The official song of the 2011 World Cup |
| Problems playing this file? See media help. | |
The World Cup has grown as a media event with each tournament. The ICC sold the broadcasting rights for the 2011 event to ESPN Star Sports and Star Cricket for around US$2 billion. For the first time, the tournament was broadcast in high-definition format, and it was to be covered by at least 27 cameras using recent technology. It was also planned to be shown across platforms such as online and mobile 3G. It was the first time that an ICC event had the Umpire Decision Review System (UDRS).[31]
The final was watched live by 135 million people in India,[32][33] as recorded by the ratings agencies TAM and aMap, including 67.6 million Indian cable and satellite viewers.[34] The final was watched by 13.6% of Indian TV-equipped households on average, with a peak of 21.44% at the end of the game,[35] thus beating the semi-final between India and Pakistan, which had an estimated 11.74% TV rating in India for the whole match.[33]
The official event ambassador was Sachin Tendulkar.[36]

Song
The official song of the 2011 Cricket World Cup has three versions, in Bengali, Hindi, and Sinhala, corresponding to the three host countries.[37] "De Ghuma Ke" (Swing It Hard) is the Hindi version, composed by the trio of Shankar–Ehsaan–Loy.[38] It employs an array of Indian rhythms combined with elements of rock and hip hop. The Sinhala version, "Sinha Udaane", was adapted by Sri Lankan R&B and hip hop artist Ranidu Lankage and composed by lyricist Shehan Galahitiyawa.[37] Both songs were performed at the opening ceremony. "Sinha Udaane" was performed by Lankage.[39]
Mascot
Stumpy, a young elephant, was the official mascot for the 2011 Cricket World Cup.[40] He was unveiled at a function in Colombo, Sri Lanka, on 2 April 2010,[41] and his name was revealed on 2 August 2010 after an online competition conducted by the ICC in the last week of July.[42]
Opening ceremony
The opening ceremony was held in the Bangabandhu National Stadium in Dhaka, Bangladesh, on 17 February 2011, two days before the first match.
Prize money
The 2011 Cricket World Cup winning team would be taking home a prize money of US$3 million and US$1.5 million for runner-up, with the International Cricket Council deciding to double the total allocation for the tournament to US$8.01 million. The winning team will also take home a replica of the ICC Cricket World Cup Trophy, that has been awarded since 1999. The decision was taken at the ICC Board meeting which was held in Dubai on April 20, 2010.[43]
- US$250,000 – To each team exiting after the quarter-finals (4 teams)
- US$500,000 – Fourth placed team
- US$500,000 – Third placed team
- US$1,500,000 – Runner up
- US$3,250,000 – Winner
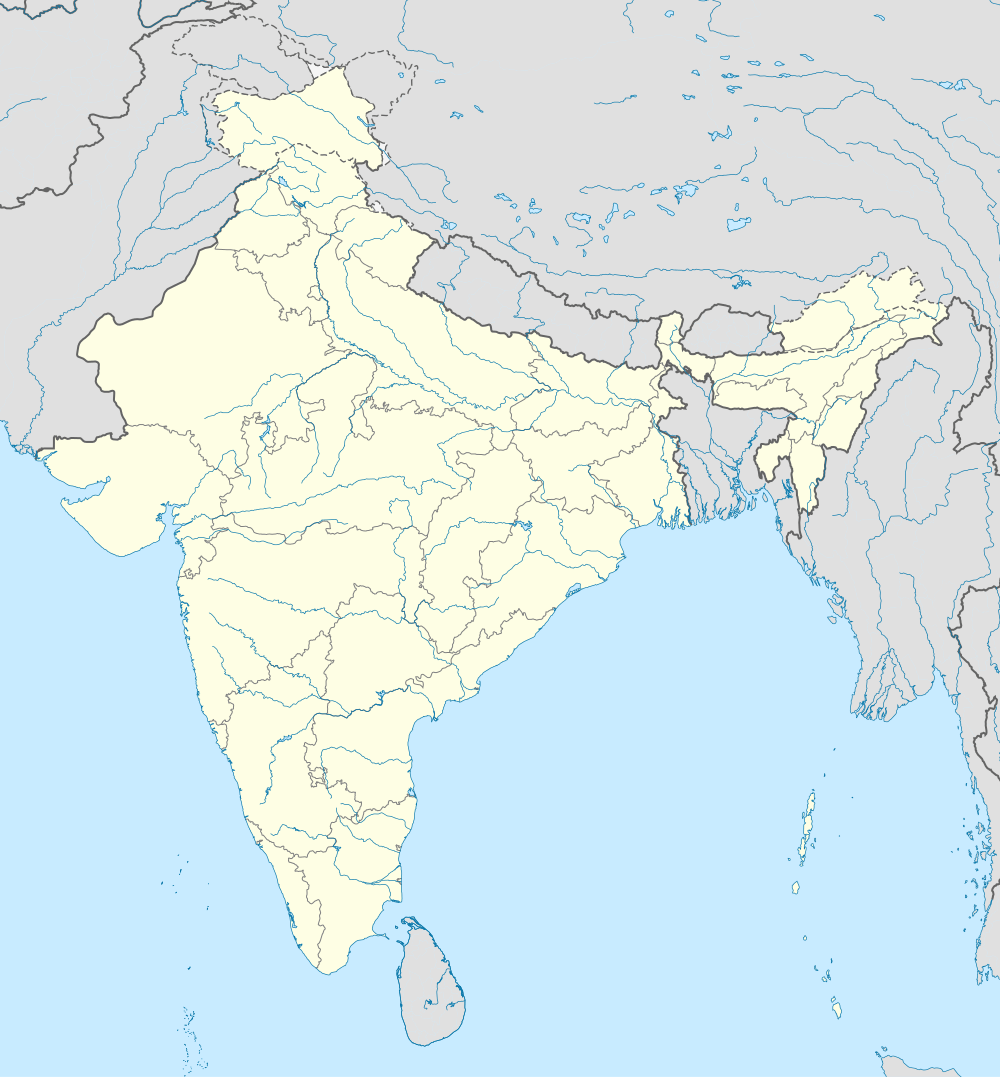
Venues
All the Indian stadiums for the tournament had been finalised by mid-October 2009,[44] and those of Bangladesh and Sri Lanka in late October 2009. The ICC announced all the venues in Mumbai on 2 November 2009. Two new stadiums were constructed in Kandy and Hambantota, Sri Lanka, for the event.[45]
| Kolkata | Chennai | New Delhi | Nagpur | Ahmedabad |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eden Gardens | M. A. Chidambaram Stadium | Feroz Shah Kotla Ground | Vidarbha Cricket Association Stadium |
Sardar Patel Stadium |
| Capacity: 66,349 | Capacity: 37,220 | Capacity: 40,715 | Capacity: 45,000 | Capacity: 54,000 |
 |
 |
|||
| Mumbai | Mohali | Bangalore | ||
| Wankhede Stadium | Punjab Cricket Association Stadium |
M. Chinnaswamy Stadium | ||
| Capacity: 32,000 | Capacity: 42,000 | Capacity: 36,430 | ||
 |
 |
 |
||
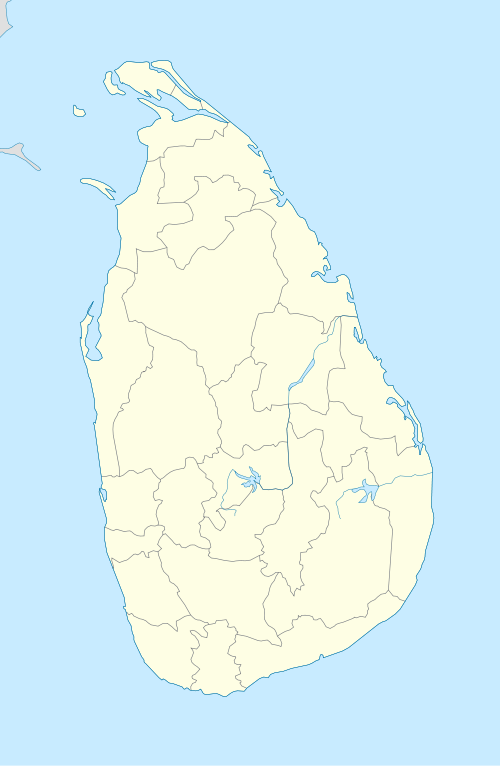
| Colombo | Pallekele | Hambantota | Chittagong | Dhaka |
| R. Premadasa Stadium | Pallekele International Cricket Stadium |
Mahinda Rajapaksa International Stadium |
Zohur Ahmed Chowdhury Stadium |
Sher-e-Bangla National Cricket Stadium |
| Capacity: 35,000 | Capacity: 35,000 | Capacity: 35,000 | Capacity: 20,000 | Capacity: 26,000 |
 |
 | |||
|
Venues in Sri Lanka |
Venues in Bangladesh |
Umpires
The Umpire selection panel selected 18 umpires excluding a reserve umpire, Enamul Haque (Bangladesh) to officiate at the World Cup: 5 from Australia, 6 from Asia, 3 from England, 2 from New Zealand and 1 each from South Africa and West Indies.
|
|
|
Squads
Each country chose a 30-member preliminary squad, which would then be reduced to 15. All the 14 teams announced their final squads before 19 January 2011.
Matches
Warm-up matches
The following 14 warm-up matches were played before the World Cup started.[46][47] For statistical purposes, these matches are not considered to be One Day Internationals.
Group stage
Group A
The top four teams from each group qualified for the quarter-finals (indicated in green).
| v |
| v |
| v |
| v |
| v |
| v |
| v |
| v |
| v |
| v |
| v |
| v |
| v |
| v |
| v |
| v |
| v |
Group B
| Team | Pld | W | L | T | NR | NRR | Pts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | +2.026 | 10 | |
| 6 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | +0.900 | 9 | |
| 6 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | +0.072 | 7 | |
| 6 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | +1.066 | 6 | |
| 6 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | –1.361 | 6 | |
| 6 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 0 | –0.696 | 4 | |
| 6 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | –2.045 | 0 |
The top four teams from each group qualified for the Quarter finals (indicated in green).
| v |
| v |
| West Indies 222 (47.3 overs) |
v |
| v |
| v |
| West Indies 330/8 (50 overs) |
v |
| v |
| v |
59/1 (12.2 overs) |
| v |
| v |
| v |
| v |
South Africa won by 3 wickets Vidarbha Cricket Association Stadium, Jamtha, Nagpur Attendance : 46,500 |
| v |
| v |
| v |
225 (44.4 overs) |
| v |
188 (43 overs) |
Knockout stage
| Quarter-finals | Semi-finals | Final | ||||||||
| 23 March – Dhaka, Bangladesh | ||||||||||
| |
112 | |||||||||
| 30 March – Mohali, India | ||||||||||
| |
113/0 | |||||||||
| |
231 | |||||||||
| 24 March – Ahmedabad, India | ||||||||||
| |
260/9 | |||||||||
| |
260/6 | |||||||||
| 2 April – Mumbai, India | ||||||||||
| |
261/5 | |||||||||
| |
277/4 | |||||||||
| 25 March – Dhaka, Bangladesh | ||||||||||
| |
274/6 | |||||||||
| |
221/8 | |||||||||
| 29 March – Colombo, Sri Lanka | ||||||||||
| |
172 | |||||||||
| |
217 | |||||||||
| 26 March – Colombo, Sri Lanka | ||||||||||
| |
220/5 | |||||||||
| |
229/6 | |||||||||
| |
231/0 | |||||||||
Quarter-finals
| West Indies 112 (43.3 overs) |
v |
| v |
| v |
| v |
Semi-finals
| v |
Final
| v |
Statistics
|
|
Controversies
- Bangladeshi fans threw rocks at the West Indies team bus as it returned players to their hotel after their win over Bangladesh in Dhaka on 4 March. It was later claimed that the rock-throwers had confused the bus with the Bangladesh team bus.[48] The elite Rapid Action Battalion of Bangladesh arrested 38 people after the attack, and the West Indies later received an apology.[49]
- The political party Shiv Sena threatened to disrupt the final in Mumbai if the Pakistani team qualified.[50]
- During the group stage match between India and England, Ian Bell was given not out for leg before wicket despite the ball hitting him in line with the wickets and being on a path to hit the stumps. India captain MS Dhoni referred the decision to the TV umpire, who confirmed the original decision as the ball had struck Bell at a point more than 2.5 m (8 ft 2 in) from the stumps, a point at which the reliability of the Hawk-Eye system diminishes below acceptable levels. Dhoni later complained that the rule had deprived his side of what seemed like an obvious wicket.[51] The rules were subsequently revised and the umpires were given new guidelines.[52] The Sri Lankan captain, Kumar Sangakkara, later criticised the decision to alter the 2.5-metre rule while a tournament was in progress.[53]
- In the final between India and Sri Lanka, loud crowd noise prevented match referee Jeff Crowe from hearing Sri Lankan captain Sangakkara's call as the coin was tossed by Indian captain Dhoni. The toss had to be redone – an extremely unusual event, especially at as prominent an event as the World Cup final.[54]
See also
References and notes
- ↑ Sri Lanka won the 1996 World Cup as co-hosts, but the final was played in Pakistan.
- ↑ India beat Sri Lanka to win ICC World Cup 2011 Times of India. Retrieved 20 November 2011
- ↑ Yuvraj Singh named man of the tournament Times of India. Retrieved 21 November 2011
- ↑ "2011 World Cup Schedule". from CricketWorld4u. Archived from the original on 4 October 2009. Retrieved 7 October 2009.
- ↑ "Opening ceremony of 2011 World Cup on Feb 17 in Bangladesh: ICC". Daily News and Analysis. PTI. 2 September 2009. Retrieved 31 December 2010.
- ↑ "Final World Cup positions secured". BBC. 17 April 2009. Archived from the original on 18 April 2009. Retrieved 17 April 2009.
- ↑ "No World Cup matches in Pakistan". BBC. 18 April 2009. Archived from the original on 18 April 2009. Retrieved 17 April 2009.
- ↑ "World Cup shifts base from Lahore to Mumbai". Cricinfo. Archived from the original on 30 April 2009. Retrieved 17 April 2009.
- ↑ "Pakistan counts cost of Cup shift". BBC. 18 April 2009. Archived from the original on 18 April 2009. Retrieved 18 April 2009.
- ↑ "Pakistan nears solution to World Cup dispute". AFP. 31 July 2009. Archived from the original on 9 May 2010. Retrieved 31 July 2009.
- 1 2 "Asia to host 2011 World Cup". Cricinfo. Archived from the original on 16 May 2006. Retrieved 30 April 2006.
- ↑ "West Indies deal secured 2011 World Cup". Cricinfo. Archived from the original on 20 May 2006. Retrieved 2 May 2006.
- ↑ "Asia promises spectacular World Cup". Dawn. 2 May 2006. Retrieved 2 July 2012.
- ↑ "Promise of profit won Asia the bid – Bindra". Cricinfo. 7 May 2006. Retrieved 2 July 2012.
- 1 2 "Bindra: No deal with West Indies board". Cricinfo. 5 May 2006. Retrieved 2 July 2012.
- ↑ New format for World Cup Sky Sports. Retrieved 10 December 2009.
- ↑ "No Test Cricket For Zimbabwe – ICC". Radiovop.
- ↑ "CC Cricket World Cup Qualifier 2009 News". ICC World Cup Qualifier. Archived from the original on 16 March 2010. Retrieved 10 March 2010.
- ↑ "World Cup matches moved out of Pakistan". Cricinfo. Archived from the original on 22 April 2009. Retrieved 17 April 2009.
- ↑ Pakistan loses 2011 World Cup Sky Sports. Retrieved 2 December 2009
- ↑ "Cricket-Pakistan counts financial losses of World Cup shift". Reuters. 18 April 2009. Retrieved 2 July 2012.
- ↑ "PCB issues legal notice to ICC". Content.cricinfo.com. Pakistan Cricket News. 9 May 2009. Retrieved 2 July 2012.
- ↑ "ICC clears air over PCB's claims". Cricinfo. Archived from the original on 16 May 2009. Retrieved 15 May 2009.
- ↑ "Pakistan discusses two World Cup options". Cricinfo. Archived from the original on 19 May 2009. Retrieved 17 May 2009.
- ↑ "Asian bloc faces stiff competition over 2011 bid". Cricinfo. Archived from the original on 2 May 2006. Retrieved 22 April 2006.
- ↑ "India to host 2011 World Cup final". Cricinfo. Archived from the original on 13 July 2006. Retrieved 8 July 2006.
- ↑ "India lands 2011 World Cup final". BBC. 8 July 2006. Archived from the original on 10 July 2006. Retrieved 9 July 2006.
- ↑ "India to host 2011 World Cup final". Cricinfo. Archived from the original on 1 May 2009. Retrieved 28 April 2009.
- ↑ "2011 World Cup tickets go on sale". ESPN. 1 June 2010. Retrieved 2 July 2012.
- ↑ Gollapudi, Nagraj (29 January 2011). "Bangalore to host India-England game extension". Cricinfo. Retrieved 29 January 2011.
- ↑ "Over 180 countries to view WC". Daily News. 18 February 2011. Archived from the original on 21 February 2011. Retrieved 23 June 2011.
- ↑ "135 mn saw World Cup final: TAM", Hindustan Times, 10 April 2011, retrieved 19 April 2011
- 1 2 "World Cup final had highest rating: TAM". Economic Times. Retrieved 13 February 2015.
- ↑ "World Cup win shatters all records as 67.6mn tune in". Hindustan Times. 3 April 2011.
- ↑ Arora, Rajat (April 4, 2011). "India-Sri Lanka ICC World Cup Final match breaks all TRP records". Best Media Info. Retrieved 27 March 2015.
- ↑ "Sachin Tendulkar to be event ambassador for ICC world cup 2011". ICC. Archived from the original on 25 January 2011. Retrieved 19 January 2011.
- 1 2 Weerasuriya, Sanath. "Ranidu Sings 'Sinha Udaane'". The Sunday Times. UK. Archived from the original on 12 July 2011. Retrieved 23 June 2011.
- ↑ "Shankar-Ehsaan-Loy score a hit with World Cup song". Hindustan Times. Indo-Asian News Service. 3 January 2011. Archived from the original on 6 January 2011. Retrieved 9 January 2011.
- ↑ Khurana, Suanshu (31 December 2010). "De ghuma ke... Countdown to World Cup begins today". Indian Express. Retrieved 9 January 2011.
- ↑ "2011 World Cup mascot to be called 'Stumpy'". NDTVSports.com. NDTV Cricket. 2 August 2010. Retrieved 2 July 2012.
- ↑ First Look: Mascot for 2011 Cricket World Cup by Rediff Sport. Retrieved 2 April 2010.
- ↑ "ICC to name ICC Cricket World Cup 2011 mascot on 2 August". International Cricket Council. 20 July 2010. Archived from the original on 6 April 2012. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ↑ Prize Money for ICC Cricket World Cup 2011 confirmed by the ICC. Retrieved on 10 November 2014.
- ↑ "India unveil eight World Cup venues". Agence France-Presse. 14 October 2009. Archived from the original on 12 April 2010. Retrieved on 17 October 2009.
- ↑ "CWC 2011 Venue". International Cricket Council. Archived from the original on 13 April 2010. Retrieved 10 March 2010.
- ↑ Warm up matches schedule. Cricinfo. Retrieved 1 February 2011.
- ↑ World Cup Warm up matches schedule. Yahoo! Cricket. Retrieved 1 February 2011.
- ↑ West Indies team bus stoned in Dhaka. Espncricinfo.com. Retrieved 3 August 2011.
- ↑ "Bangladeshi Fans stone bus of WI Team". Cricket Blog. 6 March 2011. Archived from the original on 20 September 2012. Retrieved 25 March 2011.
- ↑ "Shiv Sena threat over ICC CWC final". ESPN STAR. Archived from the original on 19 July 2012.. Espnstar.Com (2011-02-17). Retrieved 3 August 2011.
- ↑ "Dhoni angered by UDRS ruling". ESPNcricinfo. ESPN Sports Media. 27 February 2011. Retrieved 3 August 2011.
- ↑ Ugra, Sharda (6 March 2011). "ICC tweaks 2.5 metre DRS rule for 'consistency'". ESPNcricinfo. ESPN Sports Media. Retrieved 15 February 2015.
- ↑ "Sangakkara slams ICC for changing 2.5 meter UDRS rule during World Cup". The Times of India. 8 March 2011.
- ↑ "India v Sri Lanka: Toss taken twice after confusion over call". ESPNcricinfo. ESPN Sports Media. 2 April 2011. Archived from the original on 4 April 2015. Retrieved 3 August 2011.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to 2011 Cricket World Cup. |