Nelarabine
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intravenous |
| ATC code | L01BB07 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | n/a |
| Protein binding | <25% |
| Metabolism | By adenosine deaminase, to 9-β-D-arabinofuranosylguanine |
| Biological half-life |
30 minutes (nelarabine) 3 hours (ara-G) |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
121032-29-9 |
| PubChem (CID) | 3011155 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 7090 |
| DrugBank |
DB01280 |
| ChemSpider |
2280207 |
| UNII |
60158CV180 |
| KEGG |
D05134 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL1201112 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.170.768 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
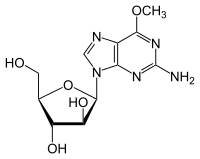
| Formula | C11H15N5O5 |
| Molar mass | 297.268 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
Nelarabine is a chemotherapy drug used in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. It was previously known as 506U78.
Nelarabine is arabinosylguanine nucleotide triphosphate (araGTP), a type of purine nucleoside analog, which causes inhibition of DNA synthesis and cytotoxicity.[1] Pre-clinical studies suggest that T-cells are particularly sensitive to nelarabine. In October 2005, it was approved by the FDA for acute lymphoblastic leukemia and T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma that has not responded to or has relapsed following treatment with at least two chemotherapy regimens.[2] It was later approved in the European Union in October 2005. Complete responses have been achieved with this medication.
It is marketed in the US as Arranon and as Atriance in the EU by Novartis.[3]
References
- ↑ "Nelarabine". Guide to Pharmacology. IUPHAR/BPS. Retrieved 21 August 2015.
- ↑ Cohen, M. H.; Johnson, J. R.; Justice, R; Pazdur, R (2008). "FDA drug approval summary: Nelarabine (Arranon) for the treatment of T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma". The Oncologist. 13 (6): 709–14. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2006-0017. PMID 18586926.
- ↑ http://www.novartisoncology.com/products/atriance.jsp