Abortion in the Czech Republic
Abortion in the Czech Republic is legally allowed up to 12 weeks of pregnancy, with medical indications up to 24 weeks of pregnancy, in case of grave problems with the fetus at any time. Those performed for medical indications are covered by public health insurance, but, otherwise abortion is relatively affordable in the Czech Republic. In Czech, induced abortion is referred to as interrupce or umělé přerušení těhotenství, often colloquially potrat ("miscarriage").
History
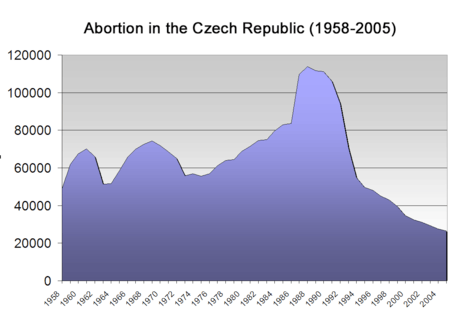
In 1957 abortions were legalized in Czechoslovakia, although with restrictions that depended on the current policy of the government. In 1986 the restrictions were lifted resulting in growth of the number of abortions.
Since 1993, abortions for non-medical reasons have not been paid for by the public health system. The absolute peak of the number of abortions was reached in 1990 at over 100,000 per year, but has declined steadily down since then, reaching less than 1/3 of the peak level in 2004. Reasons for this decrease have included the wider availability of contraception and better sex education.
Statistics
Total number of abortions in 2009 was 40 528 [1][2] of which 14 629 (i.e. 3.1%) were spontaneous abortions, 24 636 (60,79%) induced abortions (historically the lowest number ever) of which 77% were "mini-interruptions" (within 8 weeks of pregnancy). 1,300 ectopic pregnancies were aborted. Total abortions per woman is 0.53, induced abortions is 0.34.
As of 2010, the abortion rate was 10.7 abortions per 1,000 women aged 15–44 years.[3]
Regionally, the highest abortion ratio is in northern and north-western Bohemia due the structure of the population (in 2002 in Tachov District 31.3% of abortions were induced). The lowest ratios are in rural districts of southern Moravia and Bohemian-Moravian Highlands (in 2002 in Žďár nad Sázavou District 15.5% of abortions were induced).[4][5] Abortion ratios in large industrial cities are generally higher compared to small towns and the countryside.
Married women form the largest segment but their ratio is decreasing in favour of unmarried young women. Women with tertiary level of education have about 6% of induced abortions. In 2009 7.5% of the women are foreigners living in the Czech Republic. Official statistics about abortion tourism (mainly from neighbouring Poland where legal induced abortion is strictly limited) do not exist but the numbers are estimated to be low.
Public opinion
The public in the Czech Republic generally supports the legality of abortion. This has been confirmed by a number of opinion polls.
- An April 2003 CDC/ORC Macro report examined opinions on abortion among women aged 15 to 44, asking, "Do you think that a woman always has the right to decide about her pregnancy, including whether to have an abortion?" In 1993, 85% of Czechs surveyed thought a woman always had the right to an abortion and 15% did not. Of those 15%, 91% believed abortion was acceptable in cases of life endangerment, 74% in cases of fetal defects, 72% in cases of risk to health, 71% in cases of rape, 16% if the family could not financially support a child, and 8% if the woman was unmarried.[6]
- A May 2005 Euro RSCG/TNS Sofres poll examined attitudes toward abortion in 10 European countries, asking polltakers whether they agreed with the statement, "If a woman doesn't want children, she should be allowed to have an abortion". 66% of Czechs replied "very much", 15% replied "a little", 8% replied "not really", and replied 10% "not at all". Support for the availability of abortion in the Czech Republic, at 81%, was the highest out of all the nations featured in the poll.[7]
- A May 2007 CVVM poll found that 72% of Czechs believe that abortion should be allowed "at the request of the woman", 19% that it should be allowed for "societal reasons", 5% that it should be allowed only if "a woman’s health is at risk", 1% that it should be "banned".[8]
- In a Pew Research survey from 2013, when asked about morality of abortion, 49% of respondents in the Czech Republic said that abortion is morally acceptable and 19% said it was unacceptable.[9]
See also
References
- ↑ "Potraty v roce 2009" (PDF) (in Czech). Ústav zdravotnických informací a statistiky (Office of Medical Information and Statistics). Retrieved 2010-05-06.
- ↑ "Potraty 2009 v číslech". [Vitalia.cz] (in Czech). [IInfo.cz]. 2010-05-05. Archived from the original on 7 May 2010. Retrieved 2010-05-06.
- ↑ "World Abortion Policies 2013". United Nations. 2013. Retrieved 3 March 2014.
- ↑ "Regional ratios of induced abortions in 2002" (PDF).
- ↑ "Regional ratios of induced abortions in 2006".
- ↑ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and ORC Macro. (2003). Reproductive, Maternal and Child Health in Eastern Europe and Eurasia: A Comparative Report. Retrieved February 12, 2007.
- ↑ TNS Sofres. (May 2005). European Values. Retrieved January 11, 2007.
- ↑ "Most in Czech Republic Support Abortion Rights." (June 10, 2007). Angus Reid Global Monitor. Retrieved June 20, 2007.
- ↑ "Global Views on Morality | Pew Research Center". Pewglobal.org. 2014-04-15. Retrieved 2016-04-09.
External links
(all texts in Czech language)
- Legal details
- Abortion statistics: overview, detailed.
- Text of current abortion law (PDF)